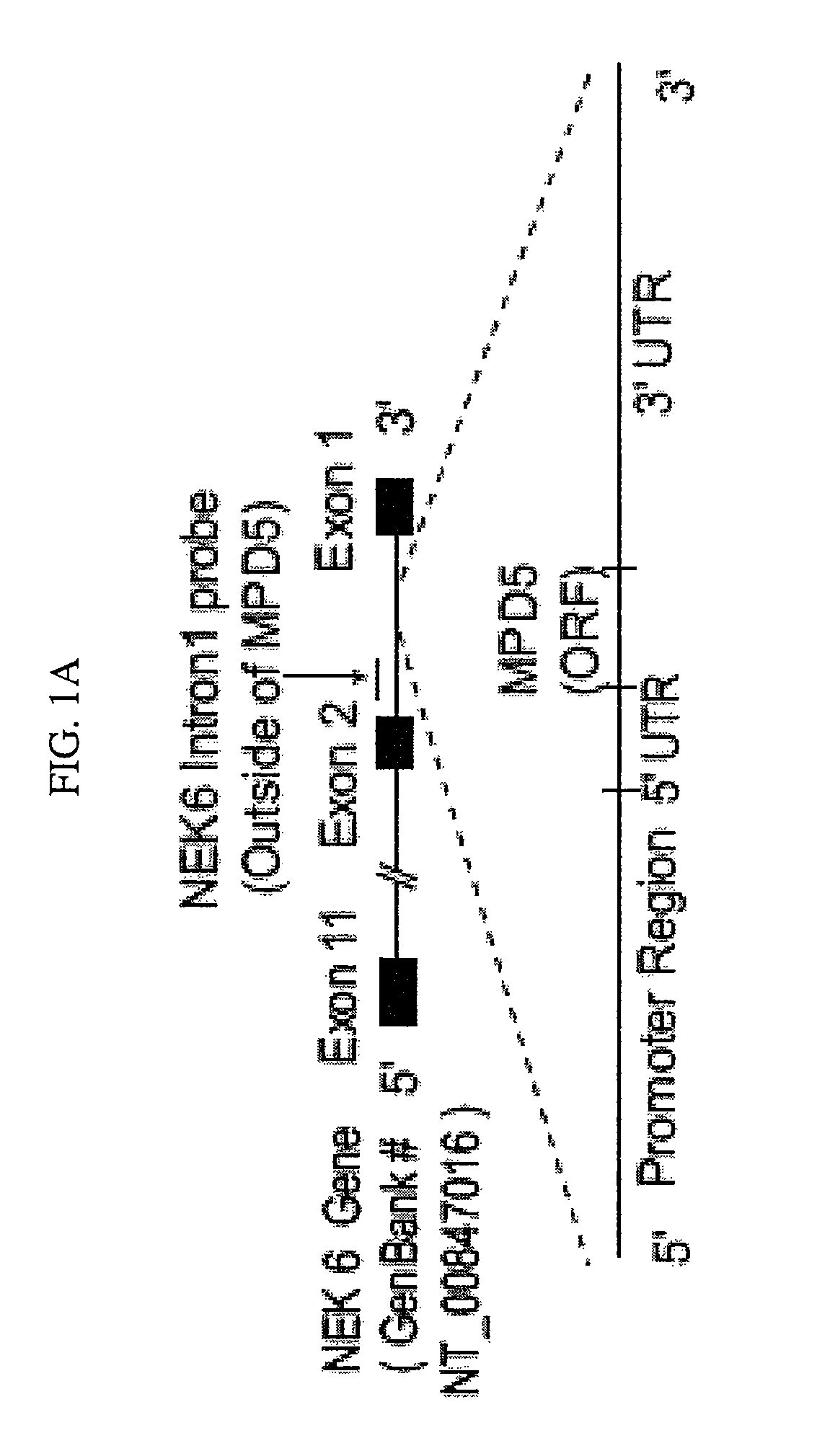
Tumor antigens elicit anti-tumor humoral immune reactions in a subset of patients with polycythemia vera
a technology of humoral immune reaction and tumor antigen, which is applied in the field of self-tumor antigens, can solve the problems of limited use practicability of internal ribosome entry sites, and achieve the effect of higher expression and higher expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0130]In accordance with a protocol approved by the Institutional Review Board at Temple University and established guidelines, serum samples were obtained from patients with PV and CML receiving IFN-α therapy enrolled into Baylor College of Medicine (eight patients with PV receiving IFN-α treatment, 8 PV patients receiving other treatments), A. D. Anderson Cancer Center (! 0 patients with C!\L receiving TFN-(X treatment), New York Presbyterian Hospital-Weill Cornell Medical Center (13 PV patients receiving IFN-α treatment, 26 PV patients receiving other treatments, six PV patients having not yet received any treatments) Institutional Review Board-approved trials. The therapeutic regimens other than IFN-α for the 34 patients with PV included imatinib mesylate (Gleevec, 16 patients), hydroxyurea ci 2 patients), hydroxyurea plus agrelin (three patients), agrelin plus phlebotomy (one patient), phlebotomy (one patient), and thalidomide (one patient). The patients in the oth...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| fluorescent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com