Providing phase diversity combining of digital radio broadcast signals
a digital radio and phase diversity technology, applied in the field of providing phase diversity combining of digital radio broadcast signals, can solve the problems of increased bit error rate, long multipath delay (or frequency selective fading), deep fade of wideband, etc., and achieve the effect of greater weigh
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
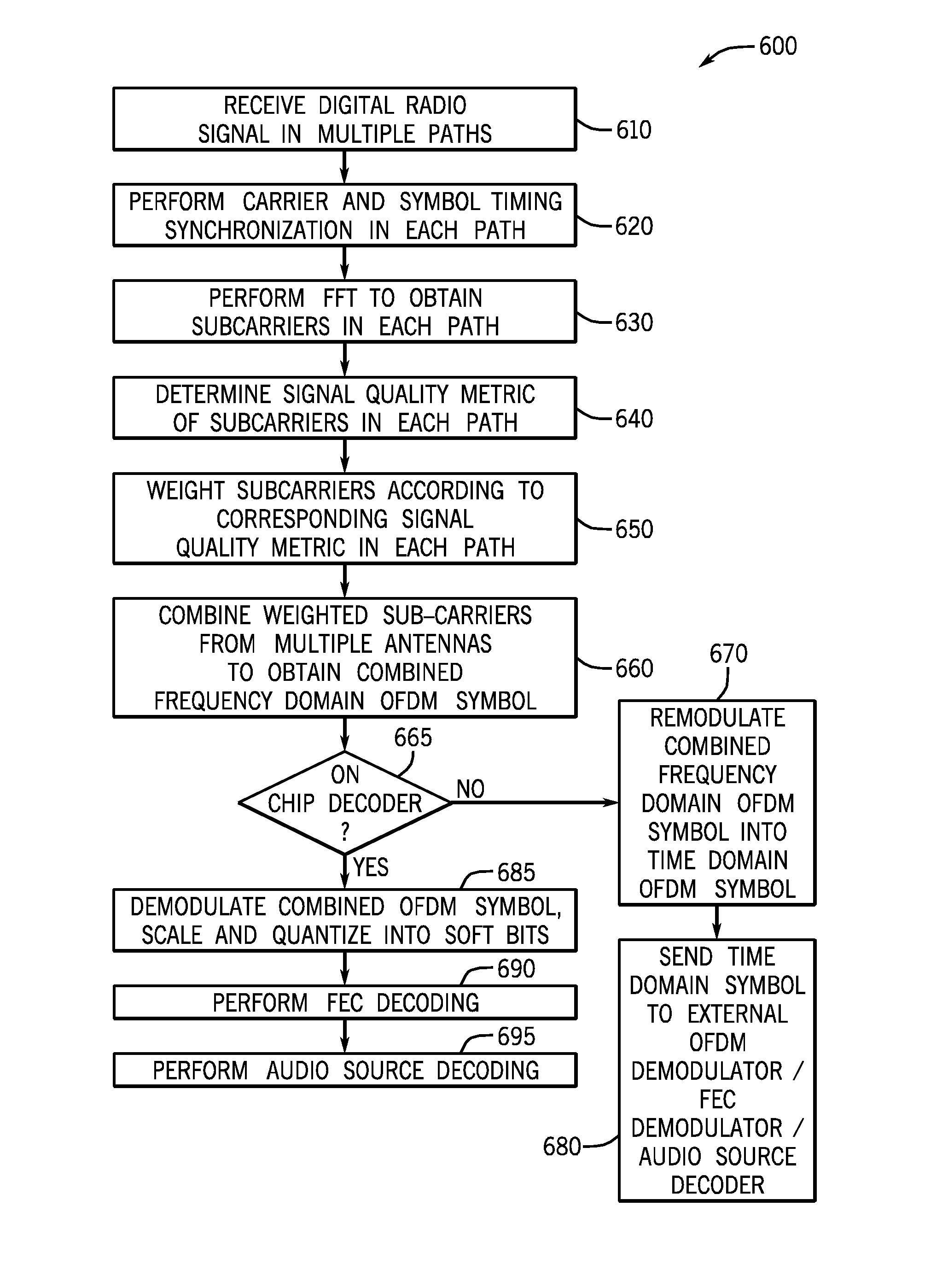
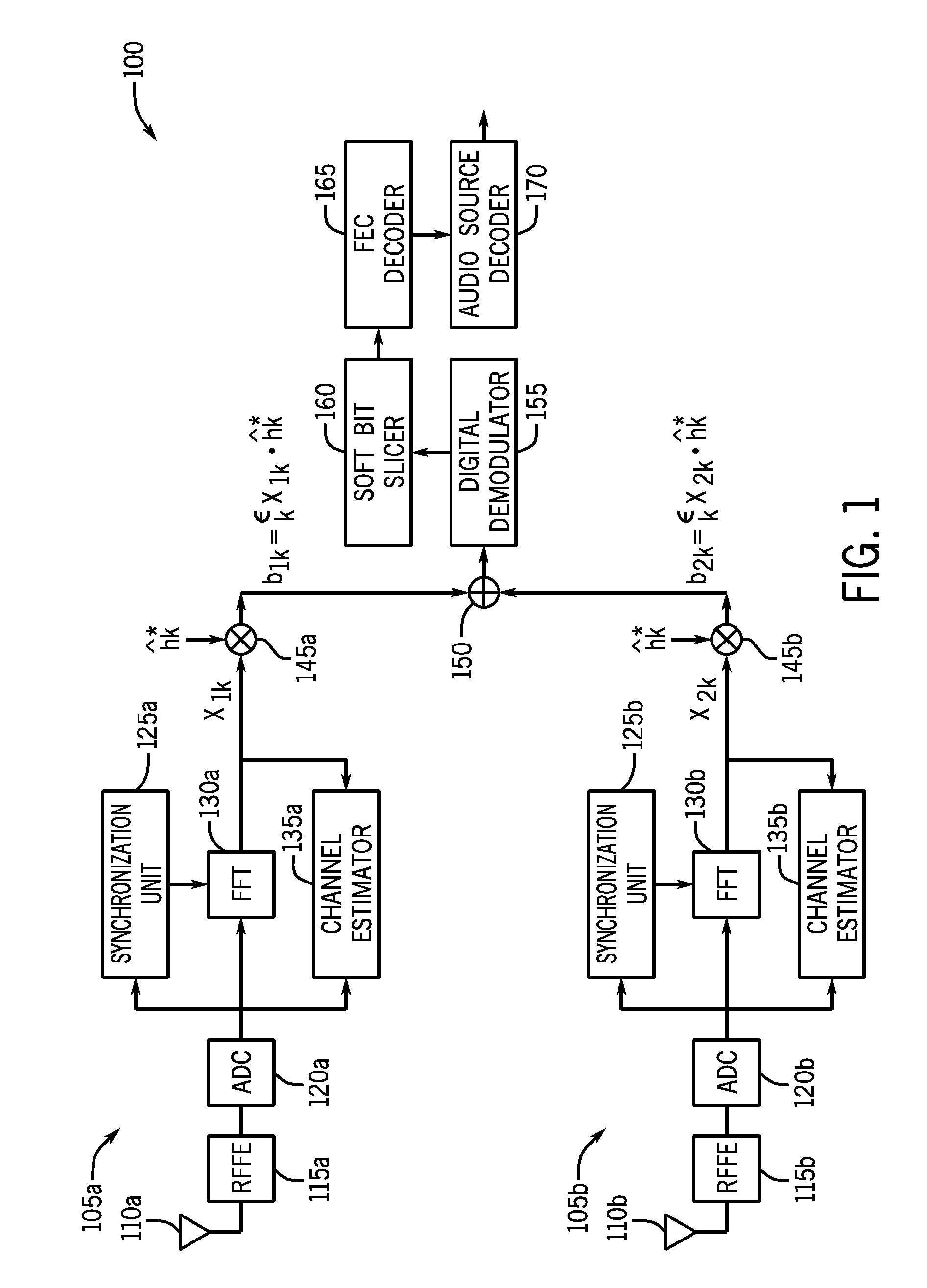
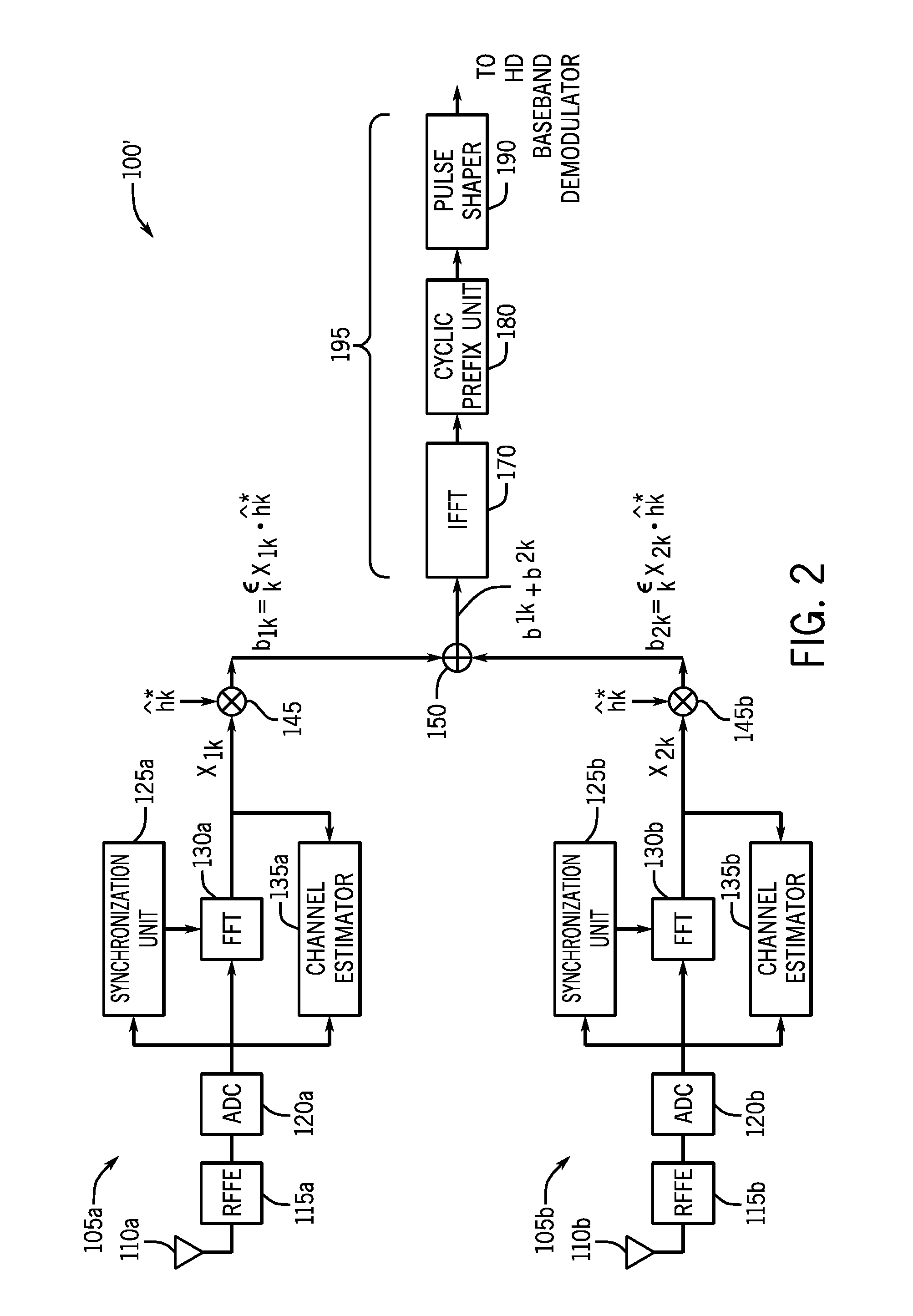
[0017]Embodiments may provide for a multi-tuner phase diversity scheme for reception of digital broadcast radio signals, such as transmitted according to an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) scheme. After receipt in the given tuner from an associated antenna, the radio frequency (RF) signal may be downconverted. In turn, a digitized signal from each tuner is coherently combined in the frequency domain to obtain a combined digital signal that may then be provided to a digital demodulator and forward error correction (FEC) decoder. The signals from the multiple antennas may be combined in a predetermined manner based on relative quality metrics associated with each signal to produce a combined signal that is more robust to multipath fading.
[0018]Implementations may vary. However, certain implementations may be used for automotive radios. In such an automotive system, multiple antennas may be provided, with the output of each antenna provided to a separate and independe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com