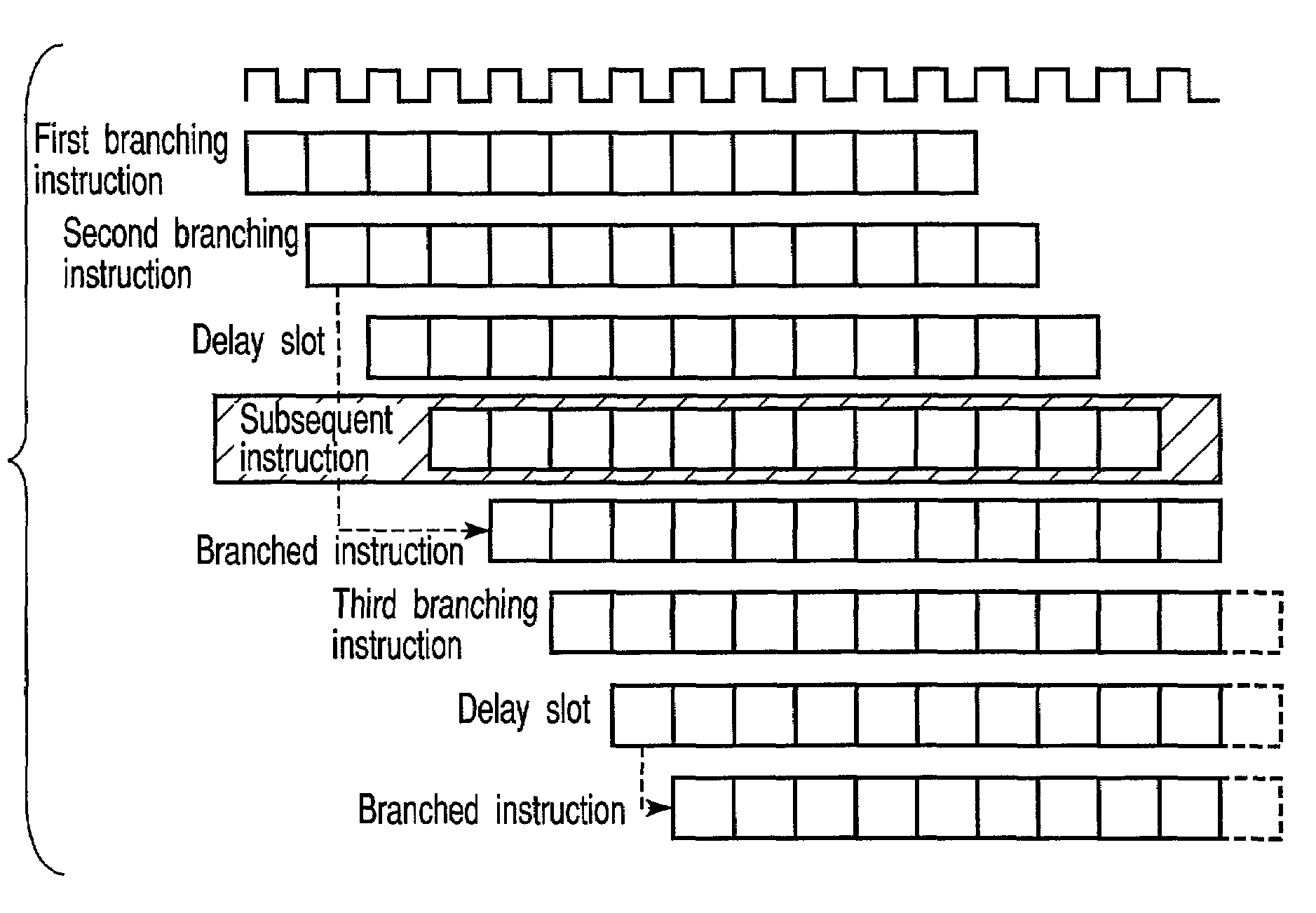
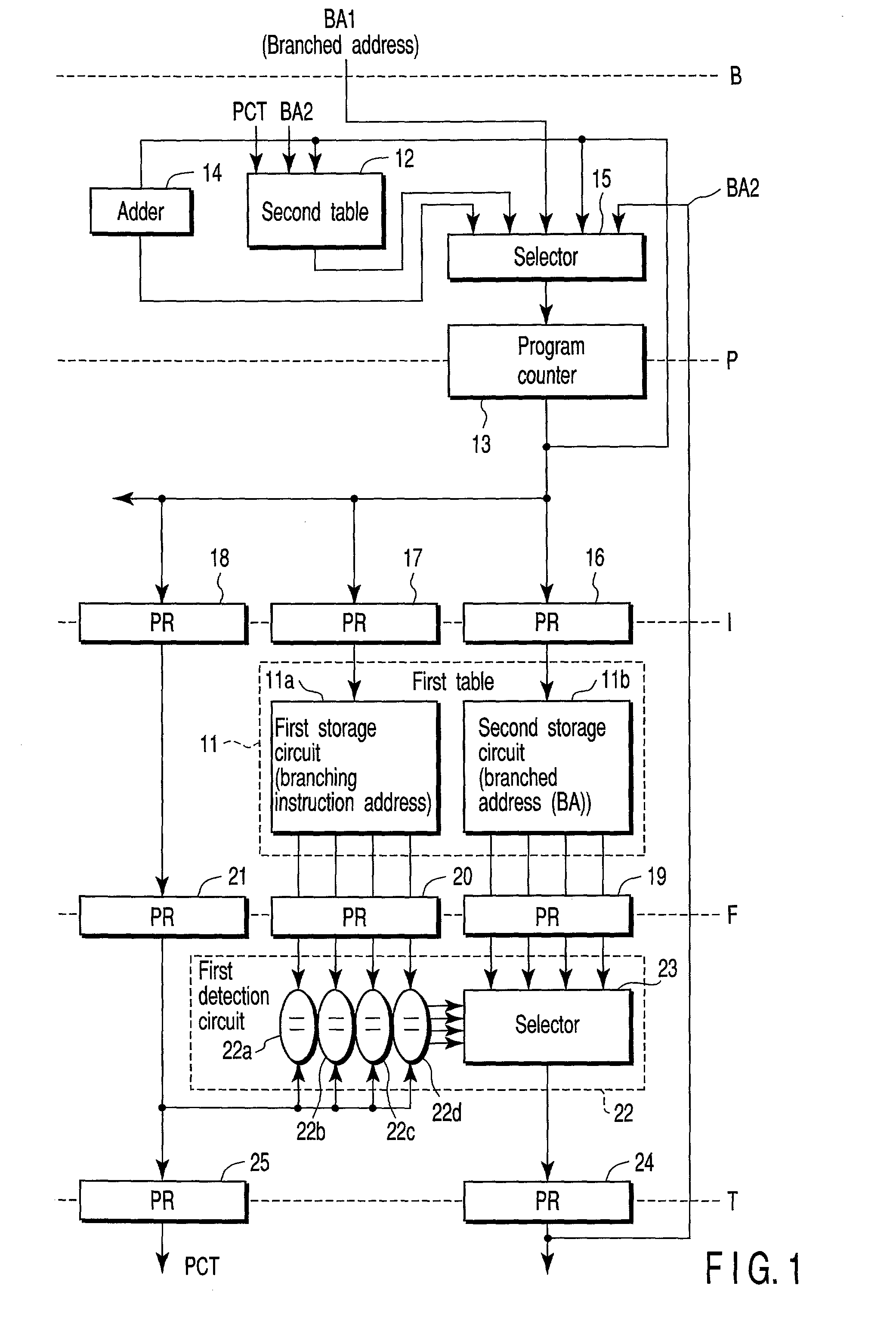
Multi-table branch prediction circuit for predicting a branch's target address based on the branch's delay slot instruction address
a branch prediction circuit and delay slot technology, applied in the direction of computation using denominational number representation, instruments, program control, etc., can solve the problems of remarkably degrading processing efficiency, invalidating a plurality of subsequent instructions, and reducing processing capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022]An embodiment of the present invention will be described hereinafter with reference to the drawings.
[0023]FIG. 1 shows a branch prediction circuit according to the embodiment of the present invention. The branch prediction circuit has a first table 11 as a first storage unit, and a second table 12 as a second storage un it. The first table 11 is a large-capacity memory which is constituted, for example, of a static RAM (SRAM) and which has, for example, 1024 entries. The second storage unit is a small-capacity and high-speed memory which is constituted, for example, of a flip-flop circuit and which has, for example, about four entries. In FIG. 1, a concrete constitution regarding the writing of information with respect to the first and second tables 11, 12 is omitted.
[0024]The branch prediction circuit is constituted of a pipeline which has, for example, five stages B to T. The first stage B is a stage for starting, for example, branch prediction, the second stage P is a progr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com