Method and system for implementing evolutionary algorithms
a technology of evolutionary algorithms and methods, applied in the field of methods and systems for implementing evolutionary algorithms, can solve the problems of heterogeneous capabilities, most ubiquitous parallel systems available currently, intranets or the internet, and limited computation requirements for each node, and achieve the effect of efficient and effectiv
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
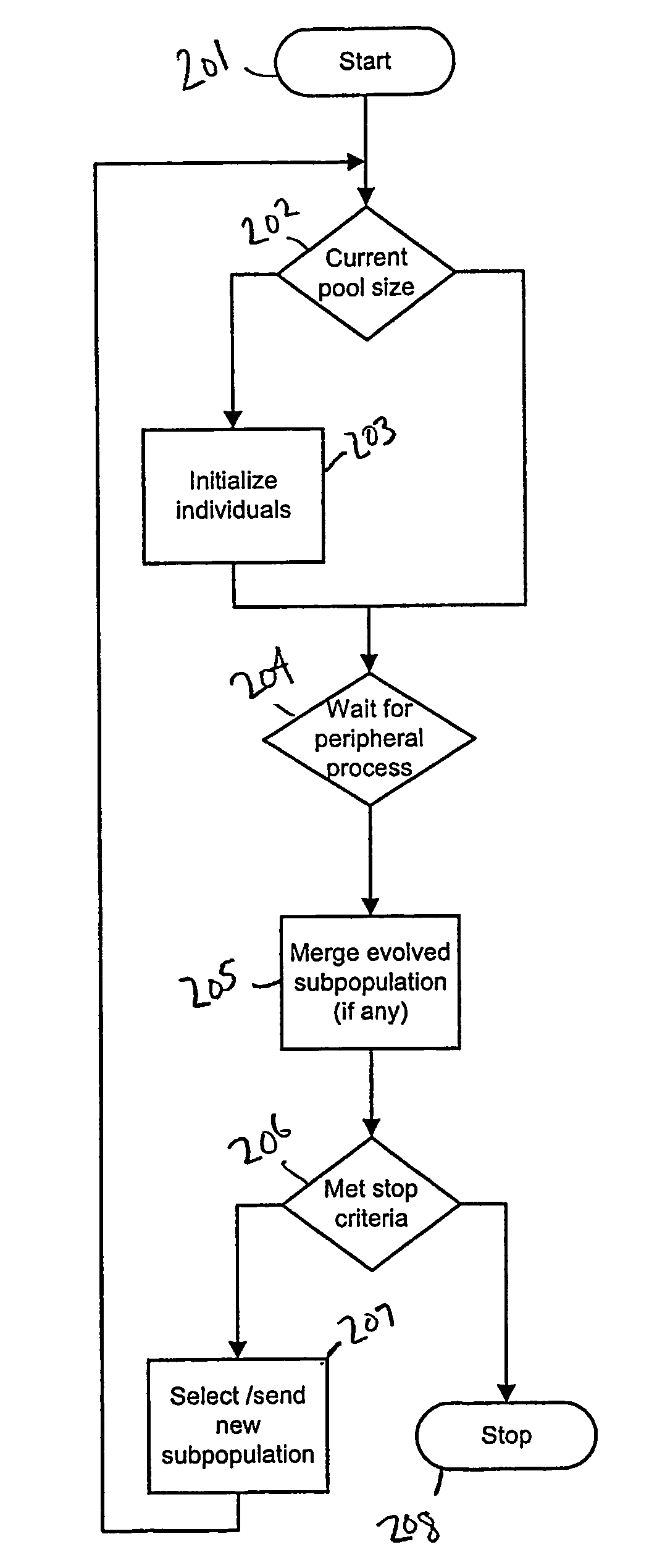
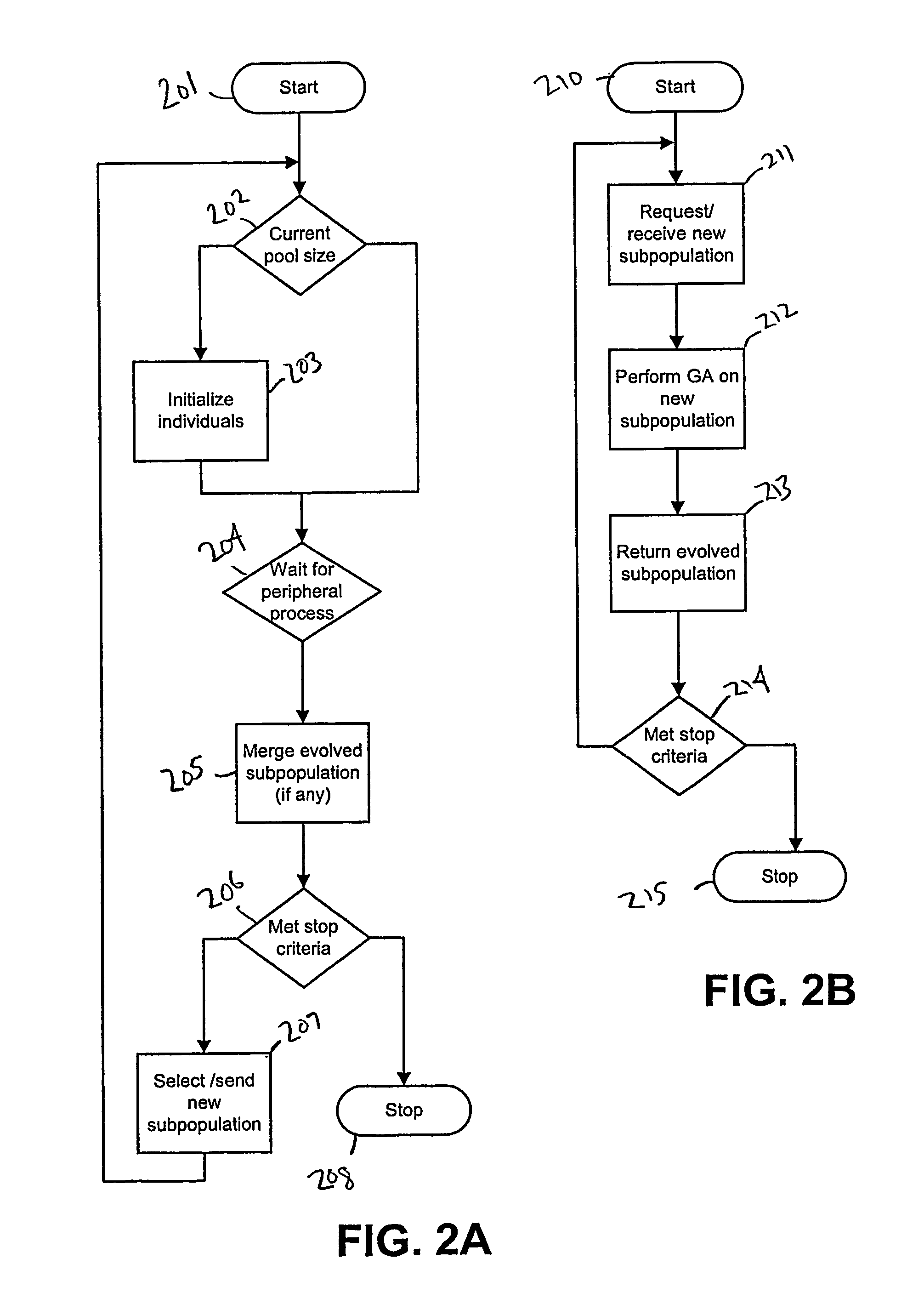
[0040]As a preliminary matter, although the invention is described herein as, inter alia, a method for implementing EAs, it is equally applicable to implementing other similar algorithms, such as genetic algorithms. One of skill in the art will recognize from the following description that the invention may be used to implement algorithms that maintain a population of intermittently interacting, independent individuals that have associated fitness values or ranks.
[0041]Further, although the invention is also described as including communicating processes which carry out work requests, these processes are functional descriptions without any limitation intended concerning implementation in any particular operating system (OS). For example, in one implementation, the functional processes described are implemented as actual OS processes, while in another implementation no such OS processes may be discernible. In the latter case, the process functions maybe performed by native OS compone...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com