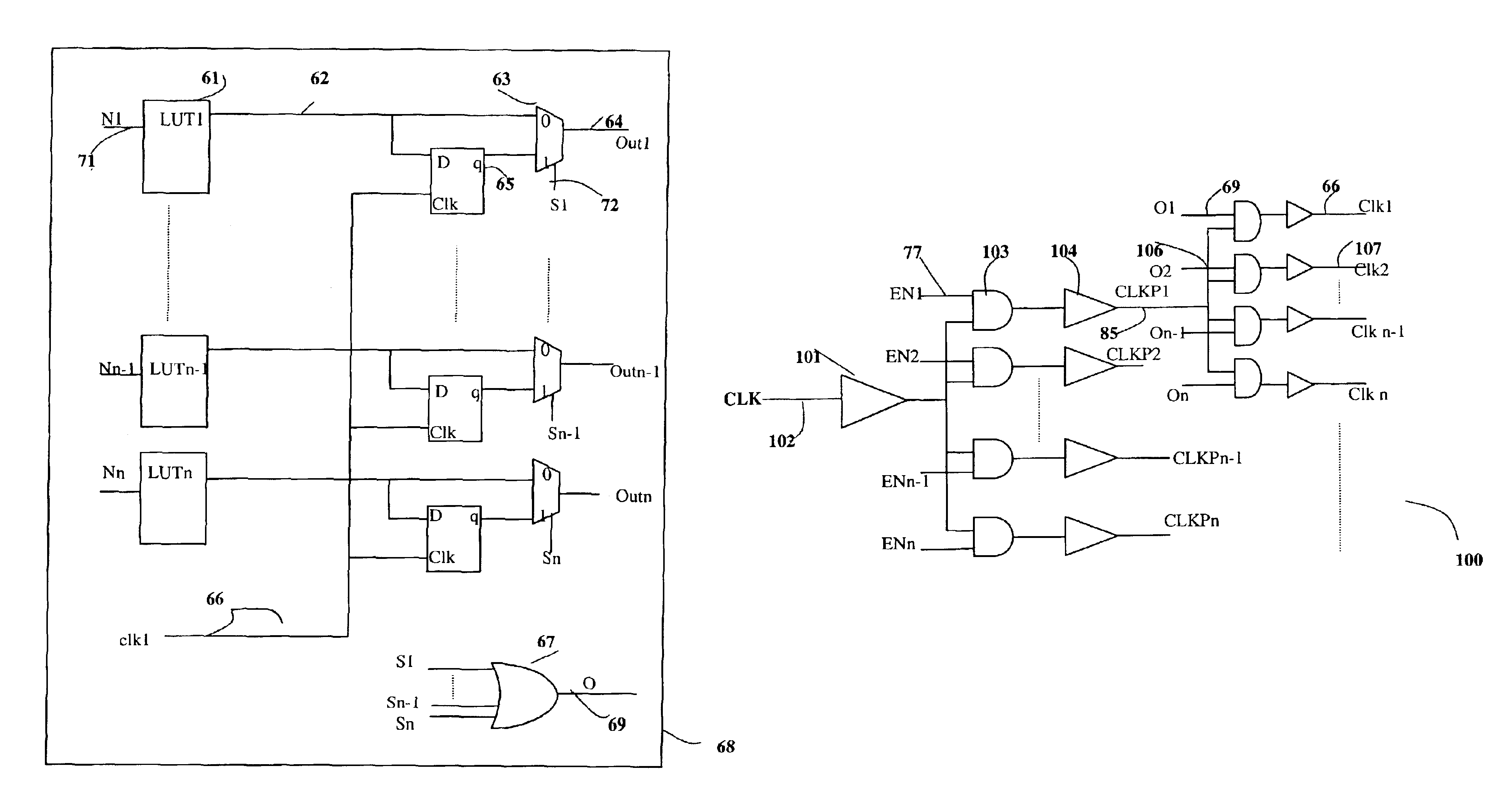
Low power clock distribution scheme
a clock distribution and low power technology, applied in the field of low power clock distribution in electronic circuits, can solve the problems of reducing reliability, reducing dynamic power consumption, and extremely low static power consumption, and achieve the effect of reducing power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
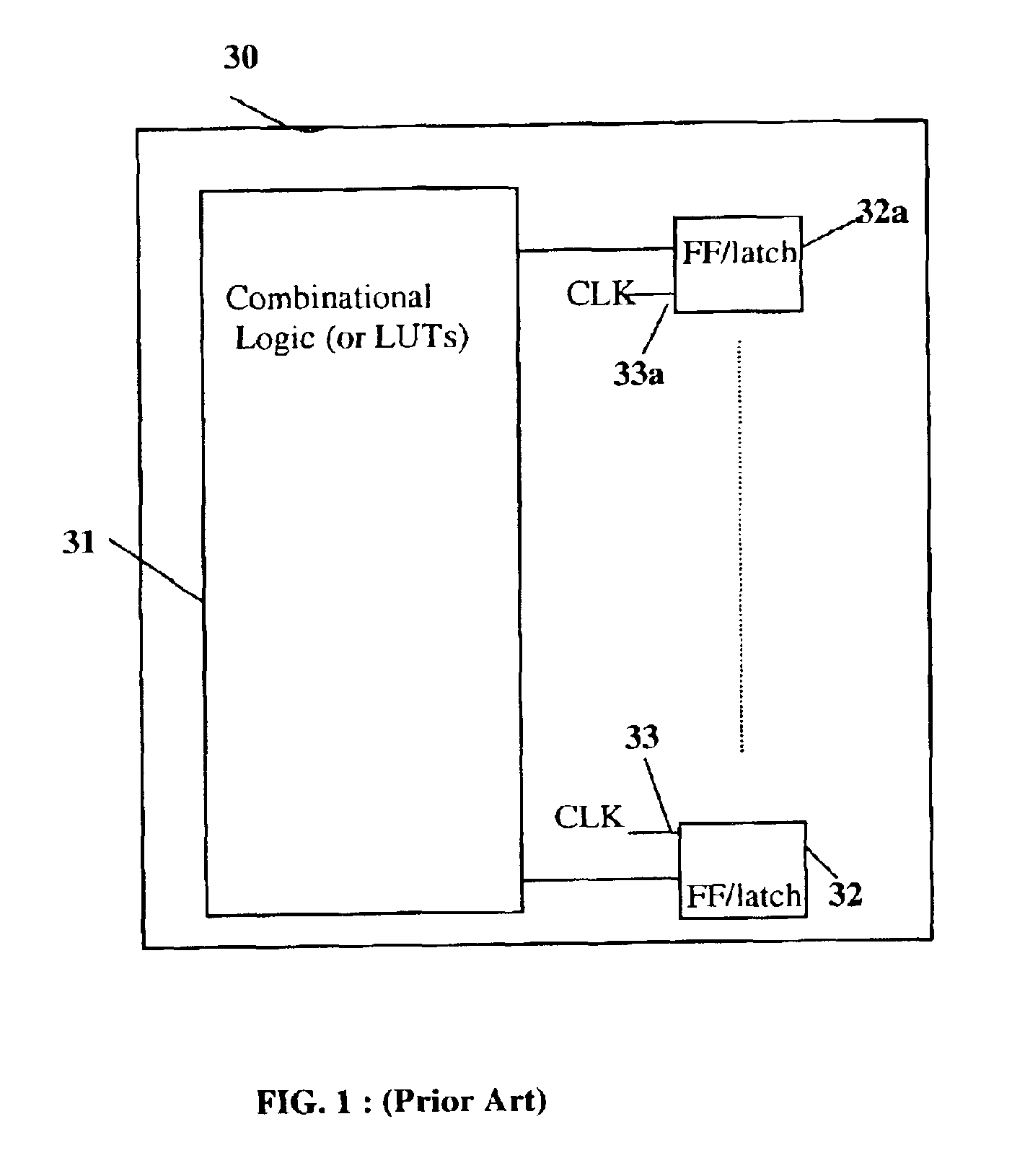
FIG. 1 shows the block diagram of a Programmable Logic Block (PLB) 30, of the type used in an FPGA, according to the prior art. The PLB contains one or more Look Up Tables (LUTs) 31 that define programmable, combinational-logic functions. The output of each LUT 31 is connected to a Flip Flop / Latch 32-32a. All the latches 32-32a in a PLB 30 share a common clock signal Clk 33-33a. Various combinational or sequential logic functions can be obtained by programming the LUT 31 suitably and selecting either the latched output or the combinational signal at the input of the latch 32-32a.
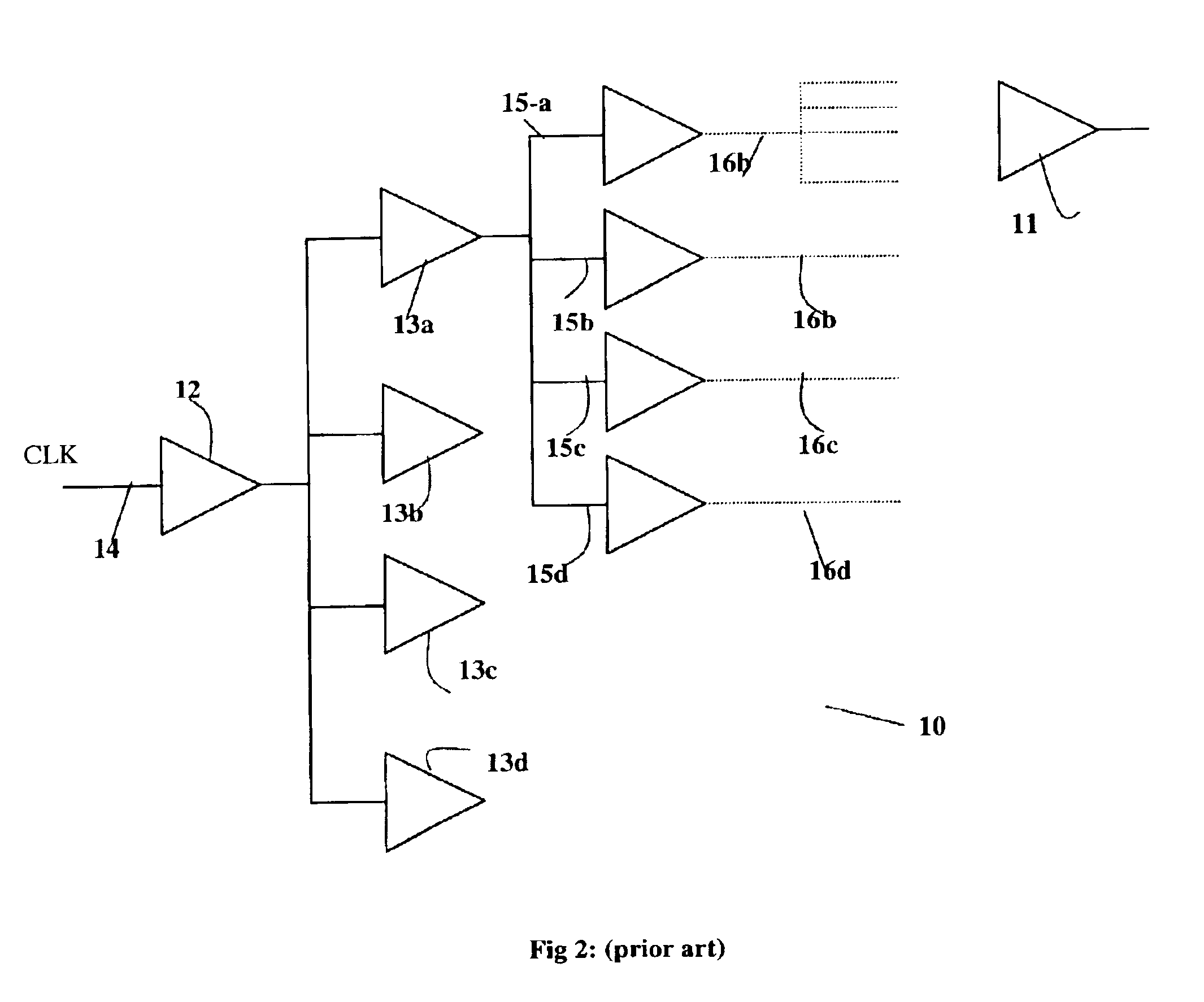
FIG. 2 shows a typical clock tree structure 10, according to prior art, used for supplying the clock signal to the PLBs. An external clock Clk 14 supplied to the entire device is buffered by buffer 12 and then distributed by first level distribution buffers 13a-13d. Each first level distribution buffer 13a-13d in turn supplies the clock signal to second level distribution buffers 15a-15d that supply the clo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com