Methods and compositions for treating a serpinc1-associated disorder
a serpinc1-associated disorder and composition technology, applied in the field of methods and compositions for treating a serpinc1-associated disorder, can solve the problems of refractory to replacement coagulation factor, difficult treatment of bleeds in such subjects, and inability to properly control bleeds, etc., to inhibit or reduce the expression of the serpinc1 gene
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
ation of a Single Dose of AD-57213 to Healthy Human Subjects
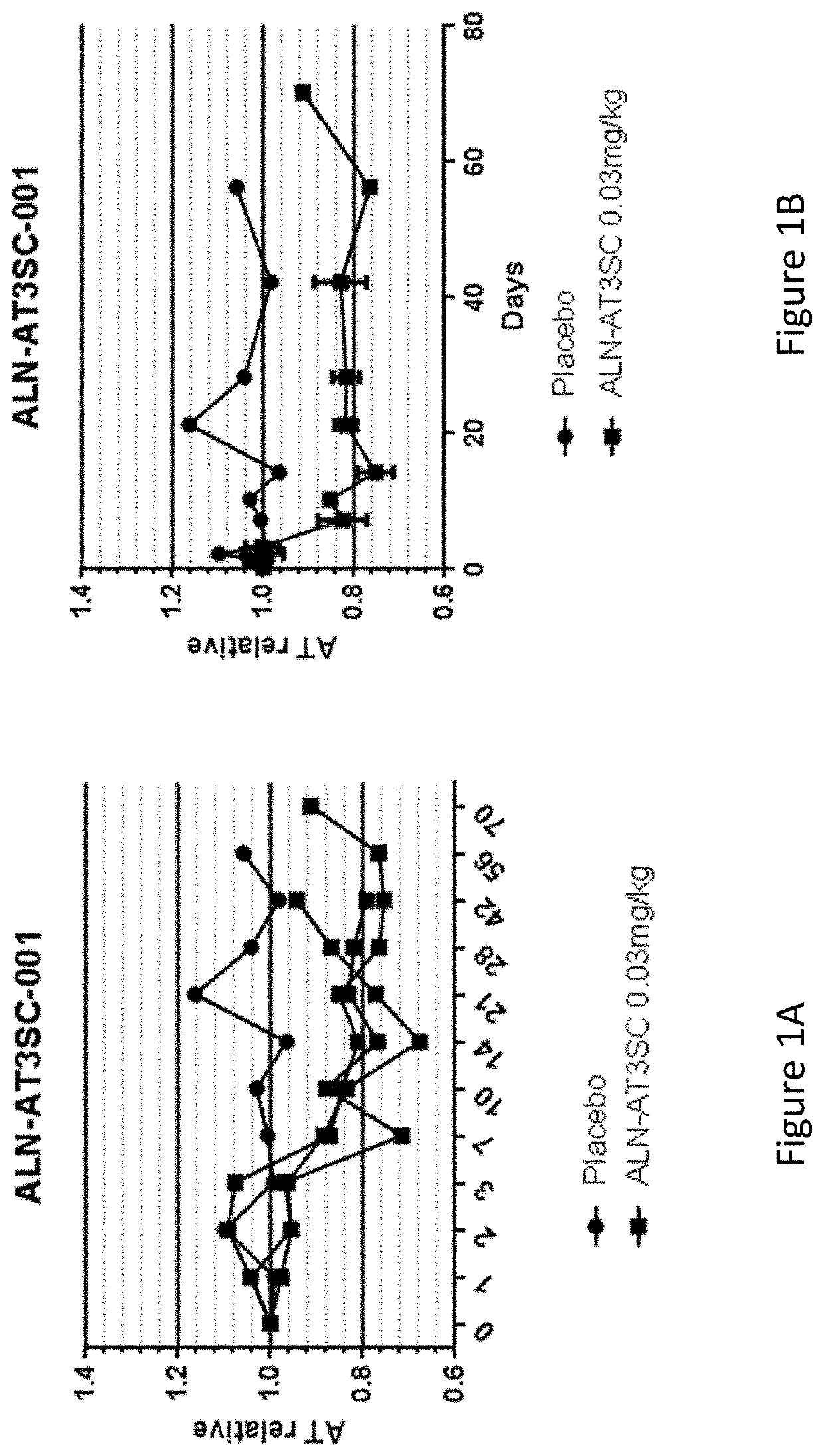
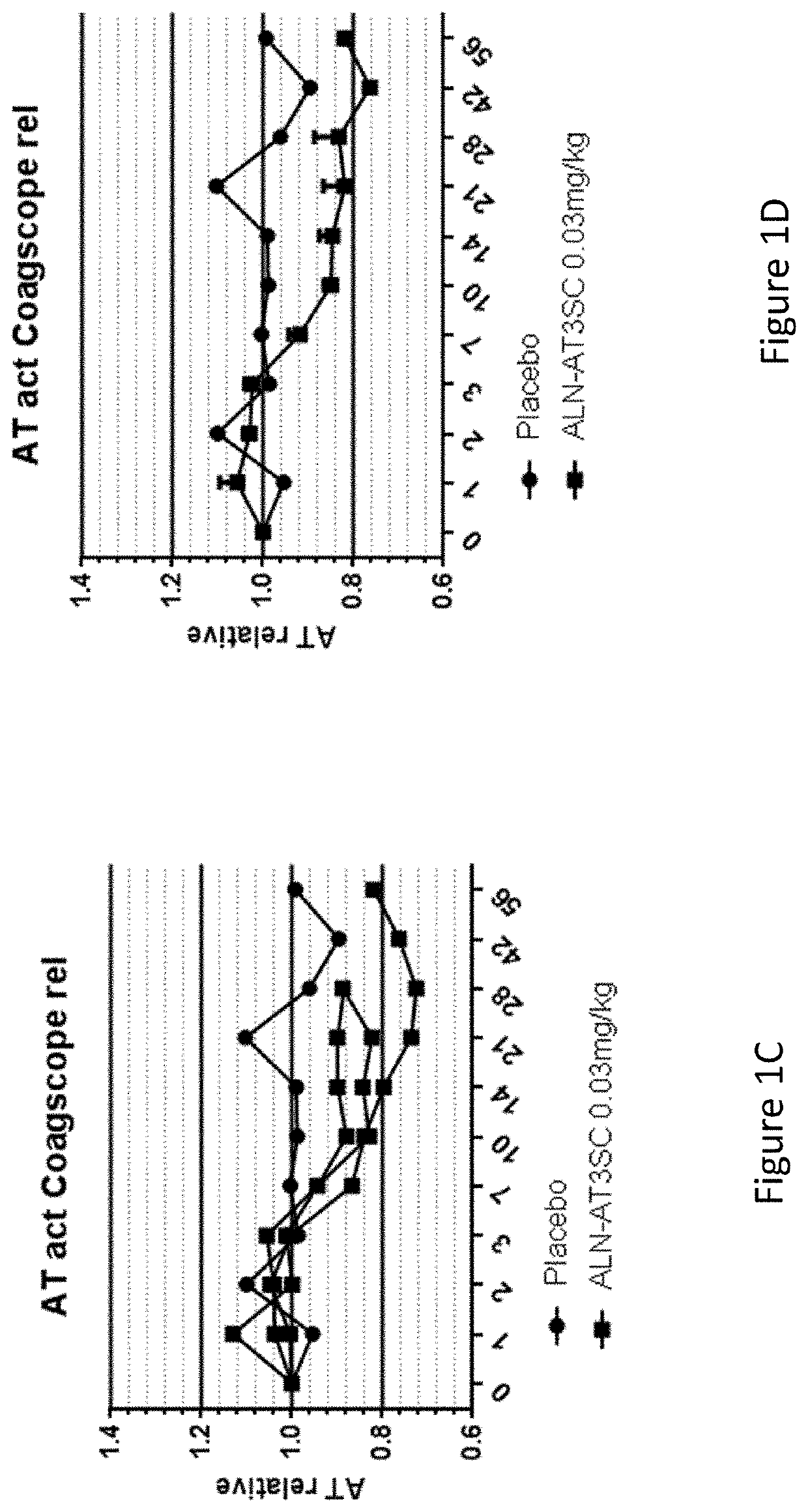
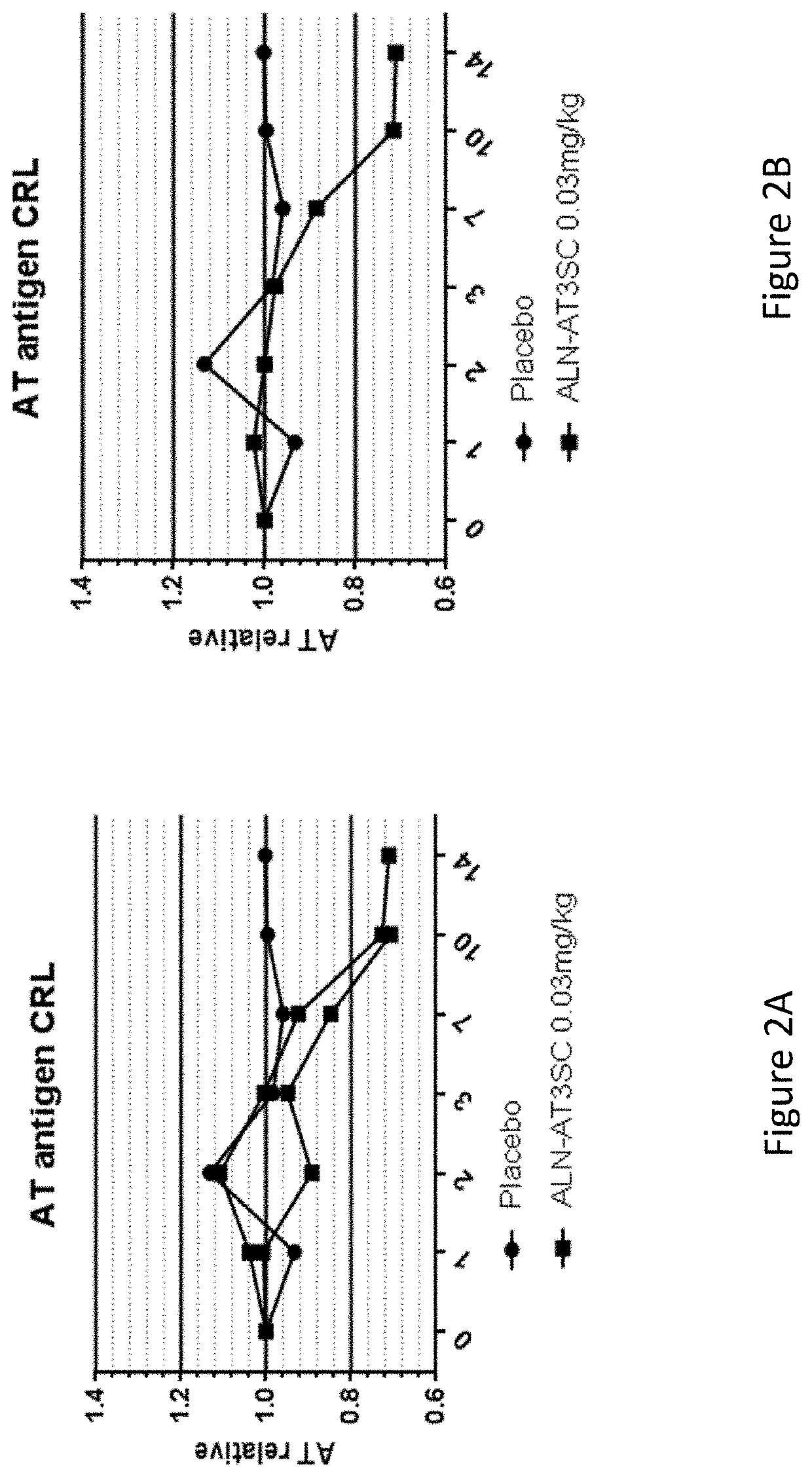
[0774]Twenty-four healthy human volunteers, in cohorts of 3:1 (active: placebo), were administered a single dose of 0.03 mg / kg, 0.1 mg / kg, 0.3 mg / kg, 0.6 mg / kg, or 1.0 mg / kg of AD-57213 (Sense (5′ to 3′): GfsgsUfuAfaCfaCfCfAfuUfuAfcUfuCfaAfL96 (SEQ ID NO: 13); Antisense (5′ to 3′): usUfsgAfaGfuAfaAfuggUfgUfuAfaCfcsasg (SEQ TD NO: 14)). Plasma samples were collected at days 0, 1, 2, 3, 7, 10, 14, 21, 28, 42, 56, and 70 after administration to monitor AT protein levels, AT activity, and duration duration of AT protein silencing. AT protein levels were monitored using ELISA and AT activity levels were monitored by generation of thrombin generation curves using a Calibrated Automated Thrombinoscope (tissue factor=1 pM). Fold change in peak thrombin was calculated relative to the average peak thrombin value for two pre-dose values for each subject.
[0775]There were no serious adverse events, 3 mild adverse events that were not li...
example 2
ation of Multiple Doses of AD-57213 to Human Patients Having Hemophilia A or B
Phase I—Parts B, C, and D Clinical Trial
[0778]In Part B of a Phase I clinical trial of AD-57213 (Sense (5′ to 3′): GfsgsUfuAfaCfaCfCfAfuUfuAfcUfuCfaAfL96 (SEQ ID NO:13); Antisense (5′ to 3′): usUfsgAfaGfuAfaAfuggUfgUfuAfaCfcsasg (SEQ ID NO:14)), three patients having Hemophilia A (n=2) or B (n=1) were subcutaneously administered 0.015 mg / kg weekly for three weeks (15 micrograms / kg qw×3; 15 mcg / kg) of AD-57213; six patients having Hemophilia A were subcutaneously administered 0.045 mg / kg weekly for three weeks (45 micrograms / kg qw×3; 45 mcg / kg) of AD-57213; and three patients having Hemophilia A (n=2) or B (n=1) were subcutaneously administered 0.075 mg / kg weekly for three weeks (75 micrograms / kg qw×3; 75 mcg / kg) of AD-57213.
[0779]In Part C of a Phase I clinical trial of AD-57213 (Sense (5′ to 3′): GfsgsUfuAfaCfaCfCfAfuUfuAfcUfuCfaAfL96 (SEQ ID NO:13); Antisense (5′ to 3′): usUfsgAfaGfuAfaAfuggUfgUfuAfaCfcs...
example 3
ation of Multiple Doses of AD-57213 to Human Patients Having Hemophilia A or B
Phase II Open Label Extension (OLE) Clinical Trial
[0798]In a Phase II OLE study of AD-57213 (Sense (5′ to 3′): GfsgsUfuAfaCfaCfCfAfuUfuAfcUfuCfaAfL96 (SEQ ID NO:13); Antisense (5′ to 3′): usUfsgAfaGfuAfaAfuggUfgUfuAfaCfcsasg (SEQ ID NO:14)), patients without inhibitors previously administered AD-57213 in the Phase I Part B and C clinical trials described above, were eligible to be enrolled into a Phase II open-label extension (OLE) study. Twelve patients from the Phase I Part B study having Hemophilia A or B that had been subcutaneously administered 0.015 mg / kg weekly for three weeks (15 micrograms / kg qw×3; 15 mcg / kg) of AD-57213; or had been subcutaneously administered 0.045 mg / kg weekly for three weeks (45 micrograms / kg qw×3; 45 mcg / kg) of AD-57213; or had been subcutaneously administered 0.075 mg / kg weekly for three weeks (75 micrograms / kg qw×3; 75 mcg / kg) of AD-57213; and 18 patients from the Phase I P...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com