Amplicon generation
a technology of amplicons and amplicons, which is applied in the direction of microbiological testing/measurement, biochemistry apparatus and processes, etc., can solve the problems of large overall savings, high cost and time consumption, and the inability to directly diagnose celiac disease, etc., to achieve accurate and specific sequencing and detection, and high efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Initial Preliminary Method
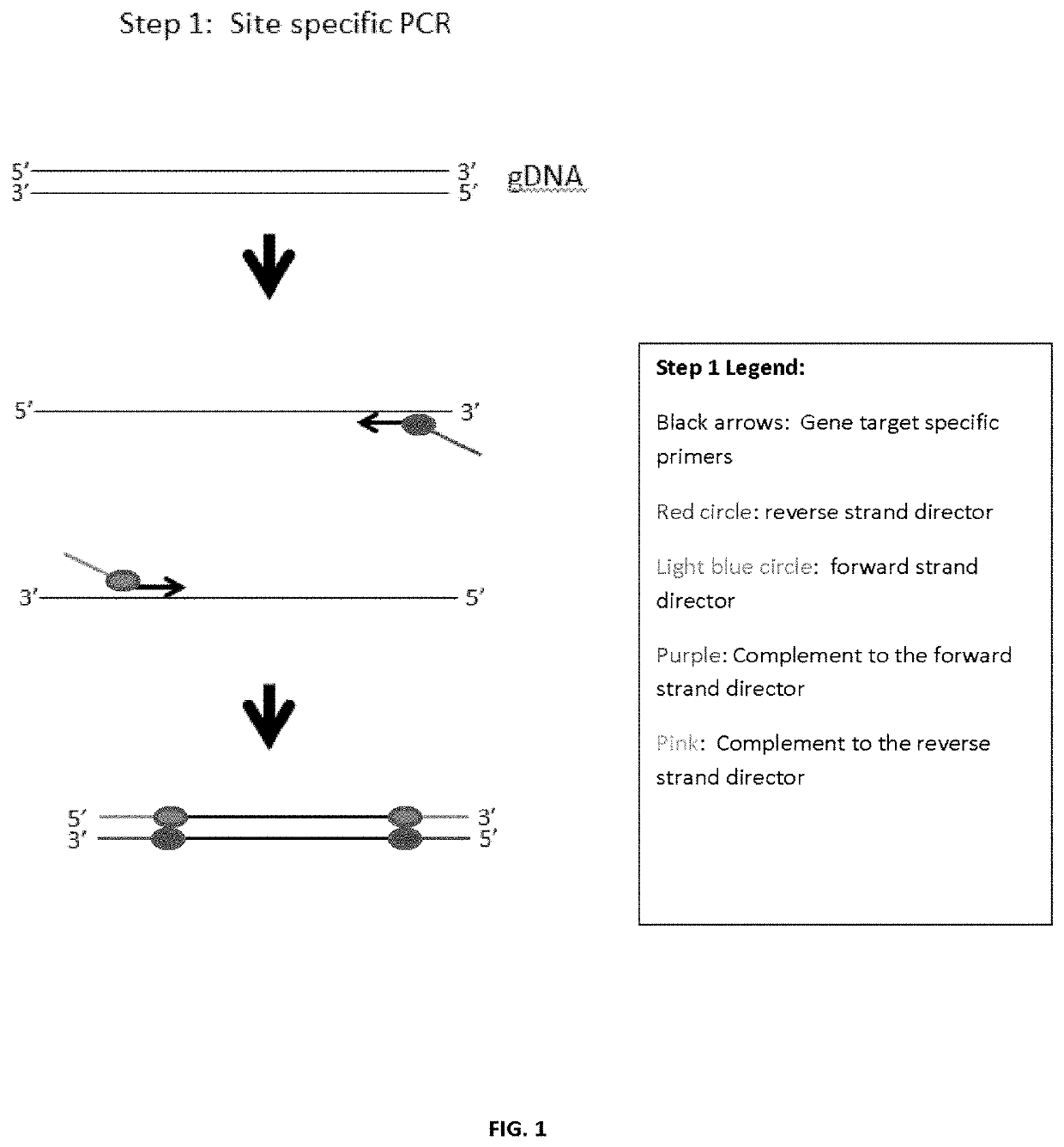
[0103]One initial strategy in developing the invention's methods (Example 1) attempted to sequence a few targeted regions of <300 bp of the hypervariable regions that define specific alleles in the celiac disease HLA DQA and HLA DQB genes, by using universal tags to randomly add the index adapter or universal adapter to either the forward or reverse strand. A schematic of the initial strategy is shown in FIG. 4.
[0104]As can be seen, because of the random nature of universal adapter and index adapter extensions, there were several undesired products generated by this method. Additionally, while much simpler than other library preparation methods, there are still four separate steps. Furthermore, presumably due to the number of product species a qPCR using the KAPA kit showed that the amount of sequenceable product was very limited. Also, as PCR optimization was performed we were unable to find sites within DQB1 that were both specific to DQB1 as well as not ...
example 2
Sequence Amplification Using an Exemplary 3 Bp Driver Sequence
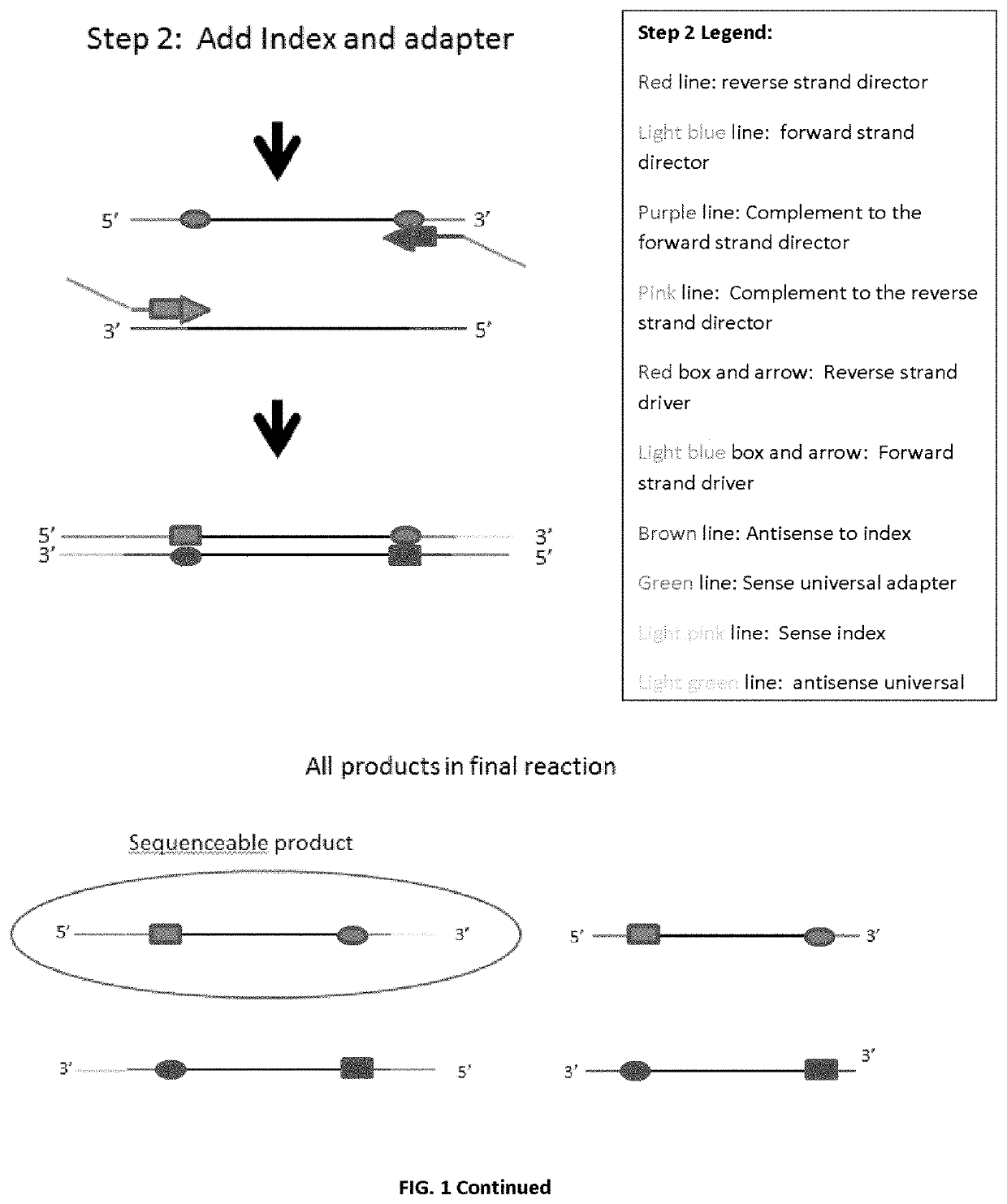
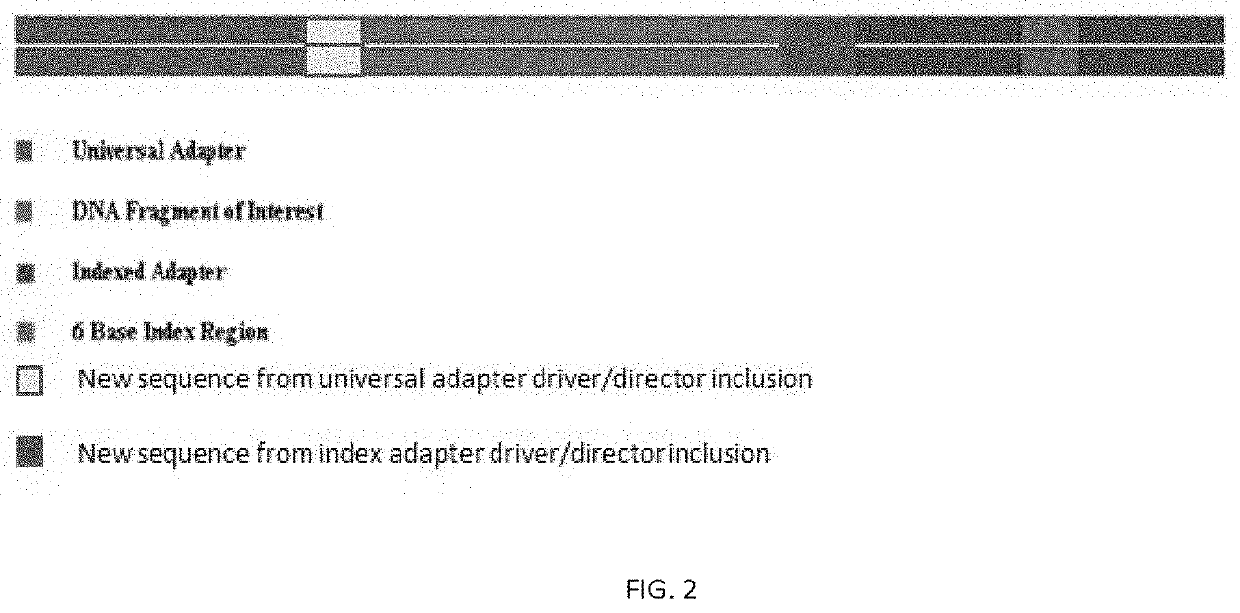
[0105]In view of the lack of optimization of the initial strategy to sequence targeted regions of the hypervariable regions that define specific alleles in the celiac disease HLA DQA and HLA DQB genes, alternative methods were carried out, in which the specificity requirement was lifted. This allowed for multiple genes such as HLA-DQB2 to be amplified as long as it reduced allelic dropout compared to the initial strategy of Example 1. In view of the removal of the specificity requirement, this new method therefore uses bioinformatics to eliminate the off-target reads. To resolve all of the non-sequenceable products, to reduce the number of steps, and to increase the efficiency of the reaction we modified the universal tags by adding a 3 bp change to the PCR primers and the 3′ end of the universal adapter and index primers. This now forces directional specificity to the universal adapter and index adapter incorporation. Th...
example 3
Effect of Driver Length on Percentage of Reads Using Exemplary 0, 1, 2, 3, 6, and 15 Bp Drivers
[0132]In Example 2, an exemplary three base pair (bp) driver sequence was successfully used to direct the index sequence and adapter sequence to their respective locations. This Example addresses whether other lengths of driver sequence may be used in the invention's methods.
[0133]To do this, six different driver sequence lengths were designed for each of the various PCRs, universal adapters, and index sequences including 0, 1, 2, 3, 6, and 15 bp. Sequences were selected to not interfere with either Illumina or gene specific regions, to avoid long stretches of the same base in a row, to have limited G / C ratios in order to not radically affect melting temperature, and were designed to not cause secondary structures such as hairpin folding. The sequences used are shown in FIG. 9
[0134]The PCR primers, index sequences, and universal adapter sequences were used as described above in Example 2. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com