Methods for altering the reactivity of plant cell walls
a technology of plant cell walls and reactivity, which is applied in the direction of dyeing process, transportation and packaging, transferases, etc., can solve the problems of not possessing the chemical versatility of synthetic fibers, not having the chemical versatility of natural cellulose containing fibers, and not able to withstand well washing, so as to increase the amount of positively charged oligosaccharides and improve reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
ion of Chimeric Plant-Expressible Genes Encoding a N-Acetylglucosamine Transferase Protein Fused to a Golgi Signal Anchor Sequence
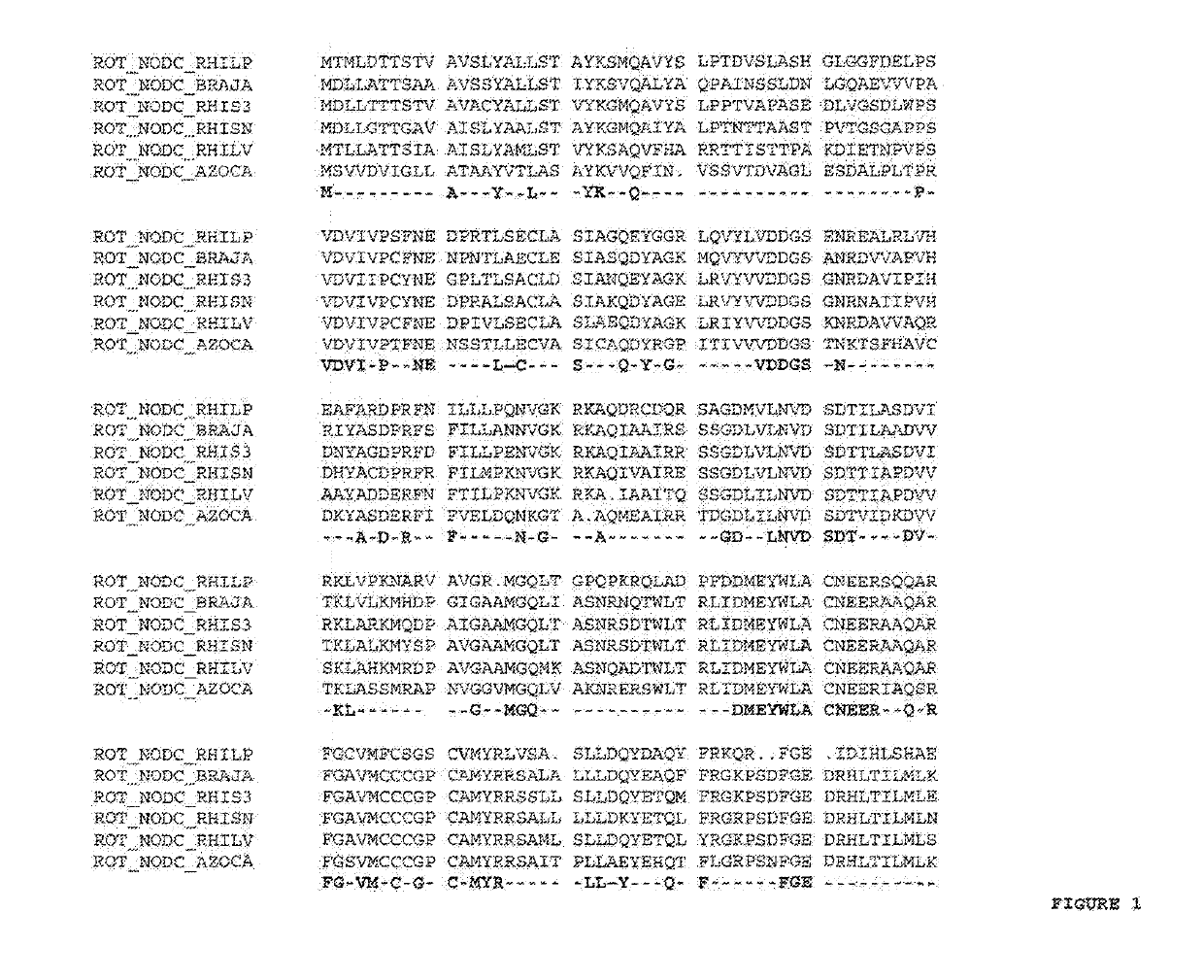
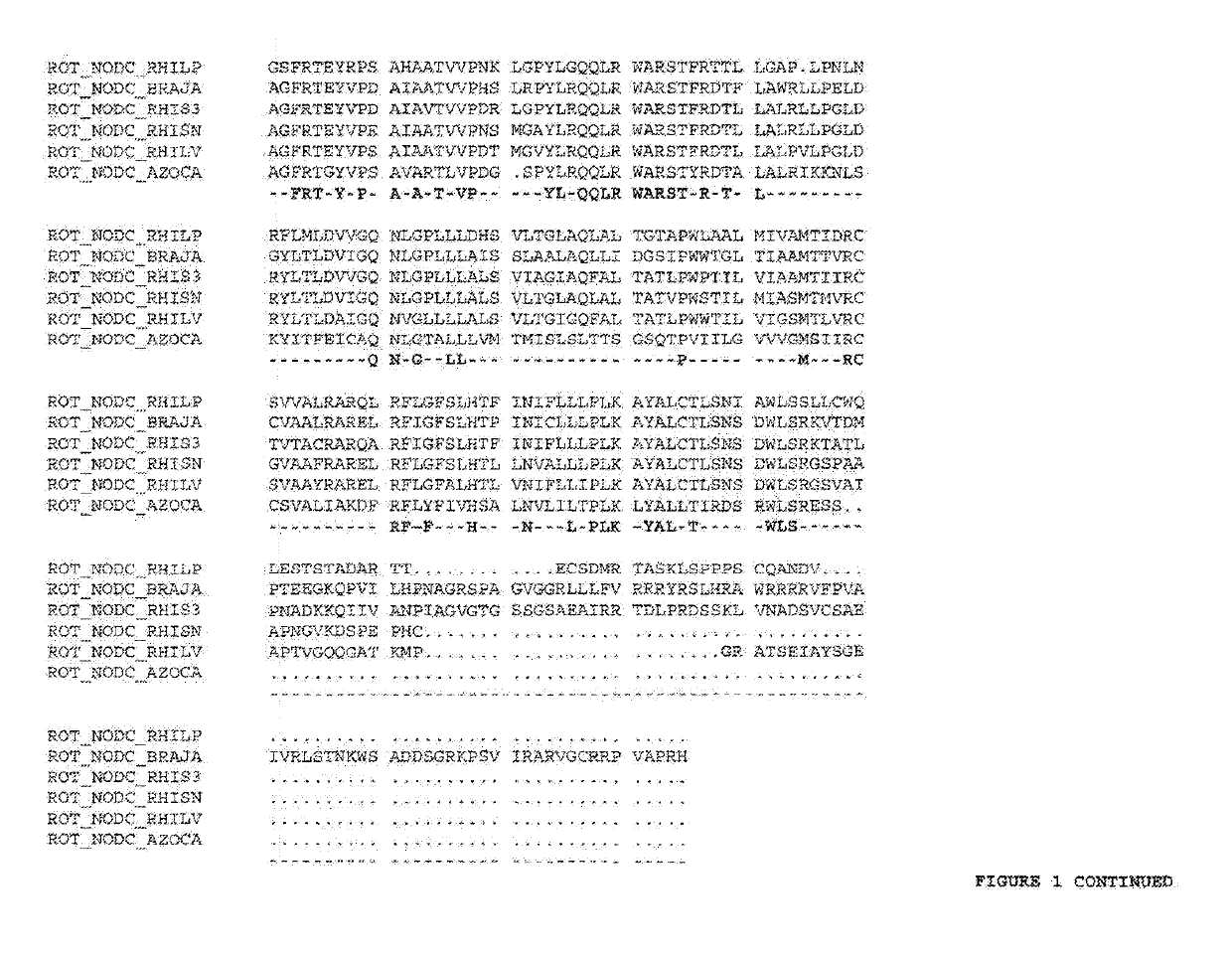
[0101]Using standard recombinant DNA techniques, a plant expressible NODC chimeric gene was constructed containing the following operably linked DNA fragments:[0102]a 35S promoter region from CaMV[0103]a DNA fragment coding for an untranslated leader sequence (5′Cab22L)[0104]a DNA fragment coding for the 35 N-terminal amino acids of β-1,2-xylosyltransferase from Arabidopsis thaliana [0105]a DNA fragment coding for NODC of Azorhizobium caulinodans cloned in frame with the previous DNA fragment[0106]a transcription termination and polyadenylation signal from the 35S transcript of CaMV (3′ 35S)
[0107]The chimeric gene was introduced between T-DNA borders of a T-DNA vector together with a chimeric bar gene providing resistance to phosphinotricin. The resulting T-DNA vector was named pTJN 6. The sequence of the T-DNA of this vector is provided in SEQ ID No 10.
[...
example 5
cific Expression of NODC Fused to a Golgi Signal Anchor Sequence in Cotton
[0115]Transgenic cotton plants comprising a chimeric NODC gene fused to a Golgi signal anchor sequence as outlined in example 1, under control of the F286 fiber-selective promoter (which is disclosed in US2003 / 106097) (=pTDBI146), the GluclA (=pTDBI158) and Gluc1D (=pTDBI159) promoter (WO 2008 / 083969), the E6 promoter (U.S. Pat. No. 6,096,950) (=pTGK96) or with the expansin promoter (U.S. Pat. No. 6,566,586) (=pTDBI165) were generated using the transformation method as described in U.S. Pat. No. 6,483,013. Fibers from these transgenic cotton plants were isolated and analyzed for N-acetylglucosamine polymers by HPLC. These transgenic fibers contained up to 0.5% of glucosamine which could only be detected upon TFA hydrolysis, showing that it is part of a polymer. Fibers of untransformed lines contained less than 0.01% of GlcN. The presence of chitobiose was demonstrated in the fiber from one of the lines transfo...
example 6
bers with Increased Reactivity
[0116]Transgenic cotton plants comprising a chimeric NODC gene fused to a Golgi signal anchor sequence operably linked to a fiber-specific promoter were generated as described in Example 5. Mature cotton fibers are harvested from these plants and can be stained with Congo Red or can be reacted with WGA-Alexa fluor 555. In addition, the resulting mature cotton fibers can be stained with commercial dyes including cotton reactive dyes (e.g. Reactive Red 120, Levafix Blue CA), acid dyes (Acid Orange 7, Acid Blue 281) and wool reactive dyes (e.g. Reactive Red 116, Realan Amber EHF).
WGA-Alexa 555 Staining
[0117]Cotton fibers do not need to be dehydrated or permeabilized. Instead, lipids and waxes are removed by treating the fibers for 3 times 10 minutes in a chloroform: methanol mixture (1:1), follow by twice a treatment of 10 minutes in acetone and twice 5 minutes in ether. The fibers are allowed to air dry.
[0118]Fibers can be stained with either WGA-Alexa555...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com