Methods, apparatus, and systems for monitoring and/or controlling dynamic environments
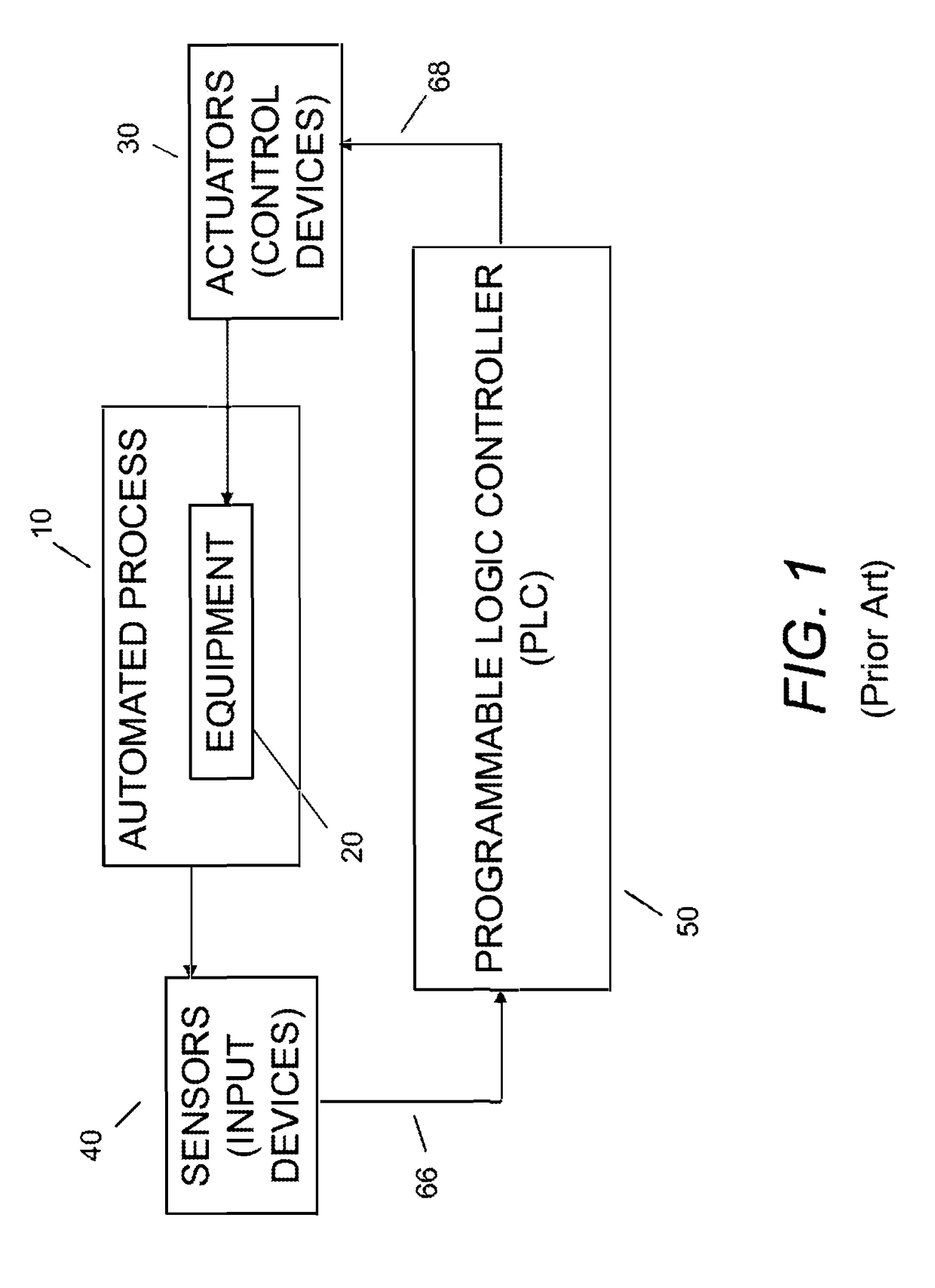
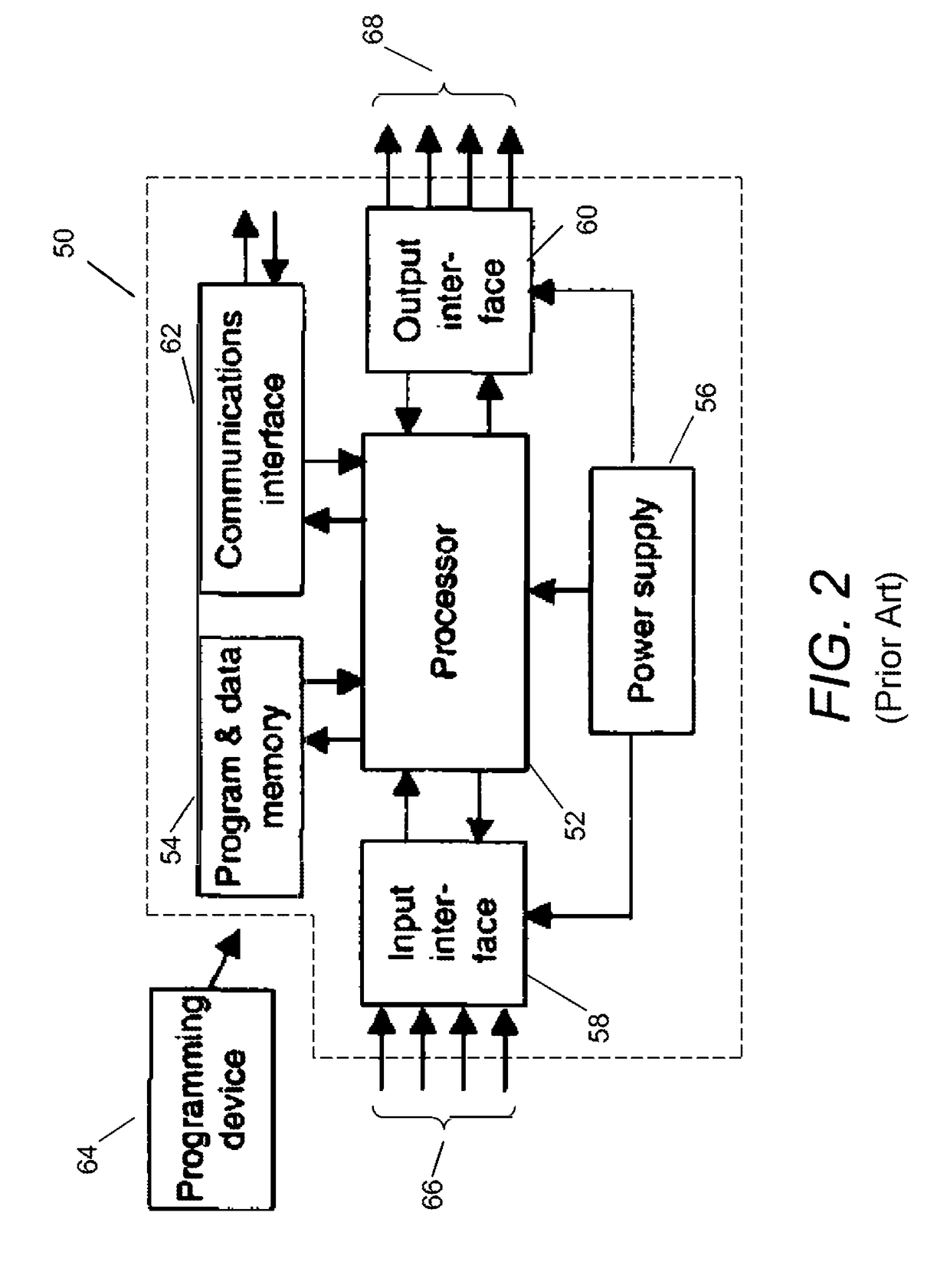
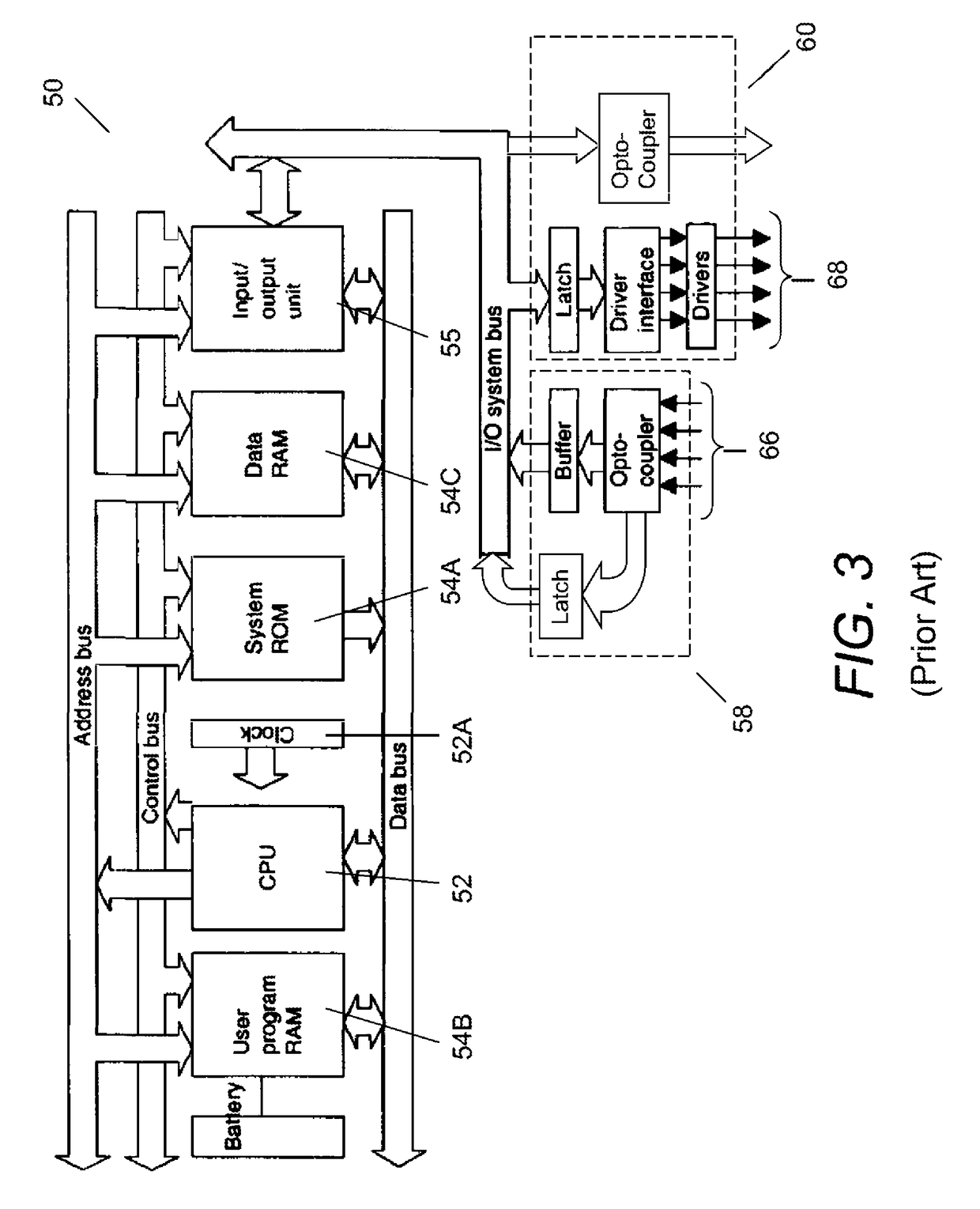
a dynamic environment and apparatus technology, applied in the direction of electrical programme control, program control, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of excessive latencies of conventional programmable logic controllers (plcs) for monitoring and/or controlling some types of dynamic environments, processor-based control devices employing a general-purpose computer architecture, and conventional plcs as well as other more general-purpose computers are often not appropriately suited for applications involving monitoring and/or controlling dynamic environments. , to achieve the effect o
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Continuous One-State Process
[0135]
continuous process send_on_edge with instances i := 0..7beginwait for rising edge of input i# state (condition no. 1)send sender i# action (executed by co-processor)end
[0136]Example 1 is a continuous process, called “send_on_edge,” in which a co-processor is tasked with waiting for a rising edge (the condition) of input i and sending a packet (the action) to another device upon satisfaction of the condition. The co-processor also notifies the master processor that its condition has been met upon detecting the rising edge. In this example, once the co-processor has sent the packet, the master processor reloads the same condition and action opcode pair in the co-processor's memory. The co-processor continues to monitor the rising edge of input i until the co-processor is halted or interrupted, e.g., by the master processor 190. This process is implemented eight times (i=0 . . . 7), with each instance running on a separate slot in the action engine or ...
example 2
Continuous Two-State Process
[0137]
continuous process send_on_pulse with instances i := 0..7beginwait for rising edge of input i # state no. 1 (condition no. 1)send sender i# action no. 1a (executed by co-processor)set output i+8# action no. 1b (also executed by co-processor)wait for 100ms# state no. 2 (condition no. 2)clear output i+8# action no. 2 (executed by co-processor)end
[0138]Example 2 is a continuous process, called “send_on_pulse,” in which a co-processor alternates between two states depending on the evolution of the dynamic environment. In the first state, the co-processor waits for a rising edge to appear on input i as in Example 1 (this is the first condition of this process). Once the co-processor detects the input, it sends a packet to another device and notifies the master processor that the first condition has been met as above. It also performs another action—it sets output i+8—before proceeding to its second state (“wait for 100 ms”). In this second state, the co-...
example 3
Continuous Process with Master Processor Action
[0140]
continuous process send_sequence with instances i := 0..7beginstatic unsigned integer sequence := 0# declarationpayload p; # declarationp.dword[0] := sequence; # master processor actionwait for rising edge of input i# condition no. 1send sender i with payload p # action no. 1a (co-processor)sequence++; # action no. 1b (master processor)wait for sender to finish # condition no. 2; action 2 is a no-opend
[0141]Example 3 is another continuous process, entitled “send sequence,” in which a co-processor monitors conditions and the co-processor and the master processor each execute actions in response to detection of the conditions. In this case, the process begins with the declaration of a static variable named “sequence” (“static unsigned integer sequence”) and a 16-byte payload p that goes out with every event packet. Once these have been initialized, the master processor sets a word (“p.dword”) in the payload to the value of the “sequ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com