Dual targeting of tafi and pai-1
a technology of tafi and pai, which is applied in the field of treatment and prevention of thrombotic disorders, can solve the problems of reducing the activity of tafi, affecting the thrombolytic function of patients, and reducing so as to reduce the risk of intracranial haemorrhage and short activity, the effect of reducing the size of the lesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Improving Expression and Efficacy of an Unstable Bispecific Inhibitor (Db-RT36A3F5×33H1F7) Against TAFI and PAI-1 Through Antibody Engineering
A. CDR-Grafting to Engineer Stable Variable Domains
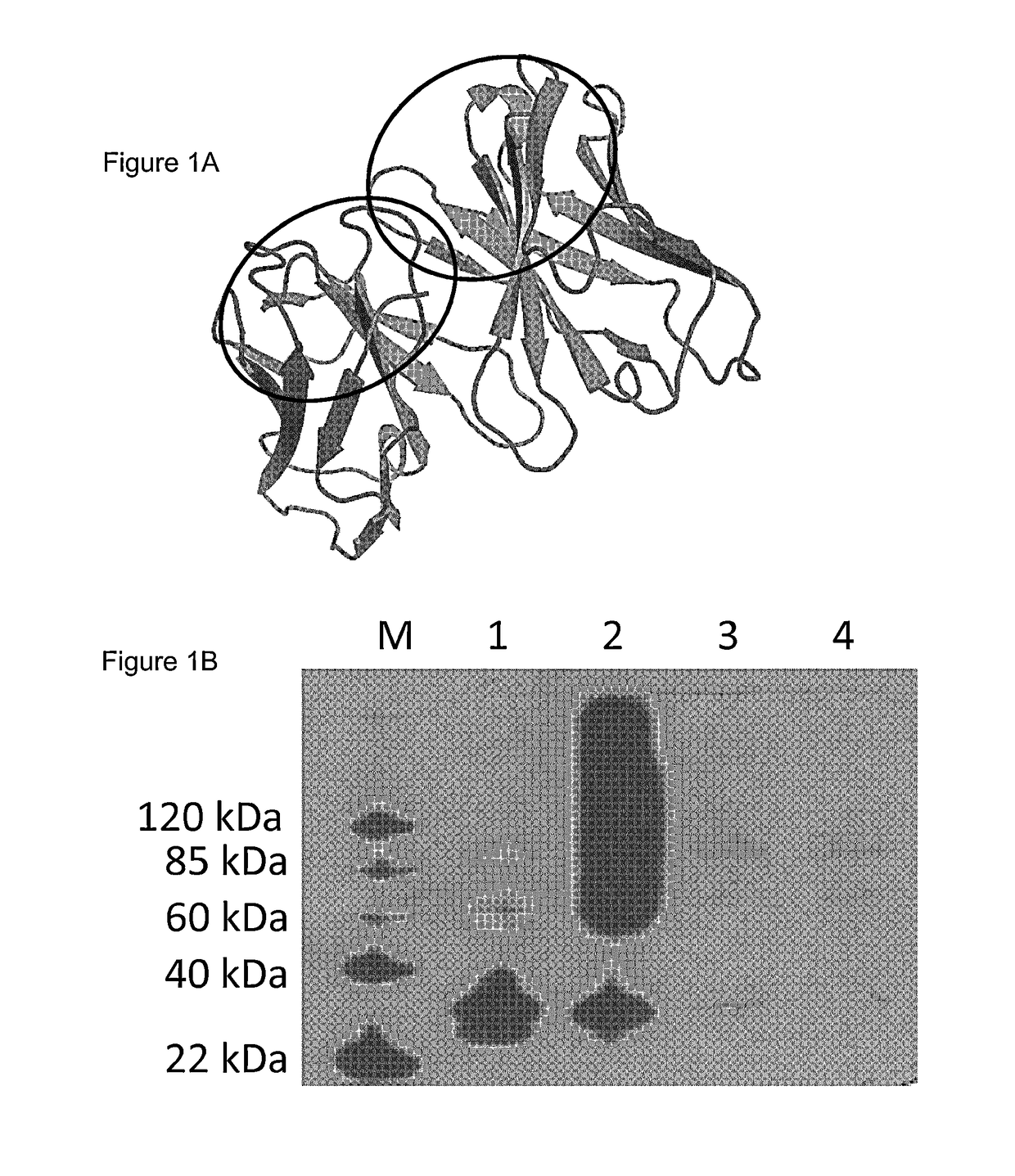
[0095]In a previous study, scFv-RT36A3F5 was generated, but could not be produced by bacteria and corresponding Db-RT36A3F5×33H1F7 was found to be unstable resulting in a diminished effect on clot lysis. Thus, the variable domains of MA-RT36A3F5 were optimized by complementarity determining region (CDR)-grafting onto the stable scaffolds of scFv-4D5 (FIG. 1A) [Jung S. & Plückthun A. (1997) Protein Eng. 10, 959-966. This article discloses the 4D5 humanised antibody used in the CDR grafting]. Two approaches were performed: (i) structure alignment-based strategy of scFv-RT36A3F5 and of scFv-4D5, generating scFv-RT36A3F5-4D5DM (in collaboration with prof Marc Demaeyer) and (ii) evidence-based strategy, generating scFv-RT36A3F5-4D5 [Ewert S. et al. (2004) Methods. 34, 184-199]. The latter approach ...
example 2
In Vitro Evaluation of the Profibrinolytic Properties of a Novel Bispecific Inhibitor Against TAFI and PAI-1
A. Generation of Db-TCK26D6×33H1F7
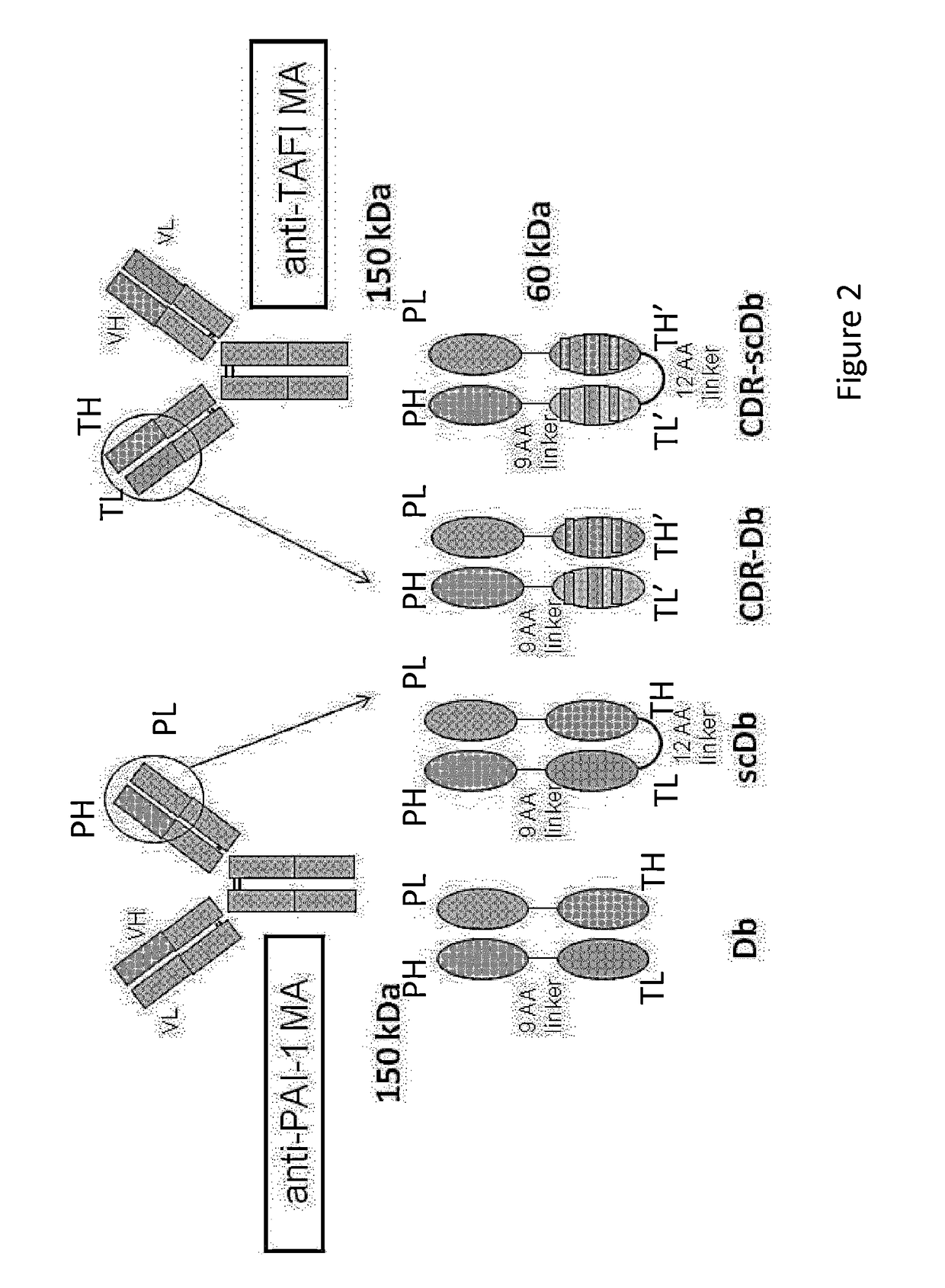
[0100]Based on the successful generation of stable scFvs with preserved inhibitory capacity of the respective parental antibodies (MA-TCK26D6 and MA-33H1F7), Db-TCK26D6×33H1F7 was generated. This diabody contains two polypeptide chains as depicted in FIG. 2 left bottom. The first one is a fusion protein of the VH chain of the anti TAFI antibody and the VL chain of the anti PAI-1 antibody. The second one is a fusion protein of the VL chain of the anti TAFI antibody and the VH chain of the anti PAI-1 antibody.
[0101]The production level of Db-TCK26D6×33H1F7 was approximately 2 mg / L culture.
B. Characterization of the Inhibitory Effect Towards TAFI and PAI-1
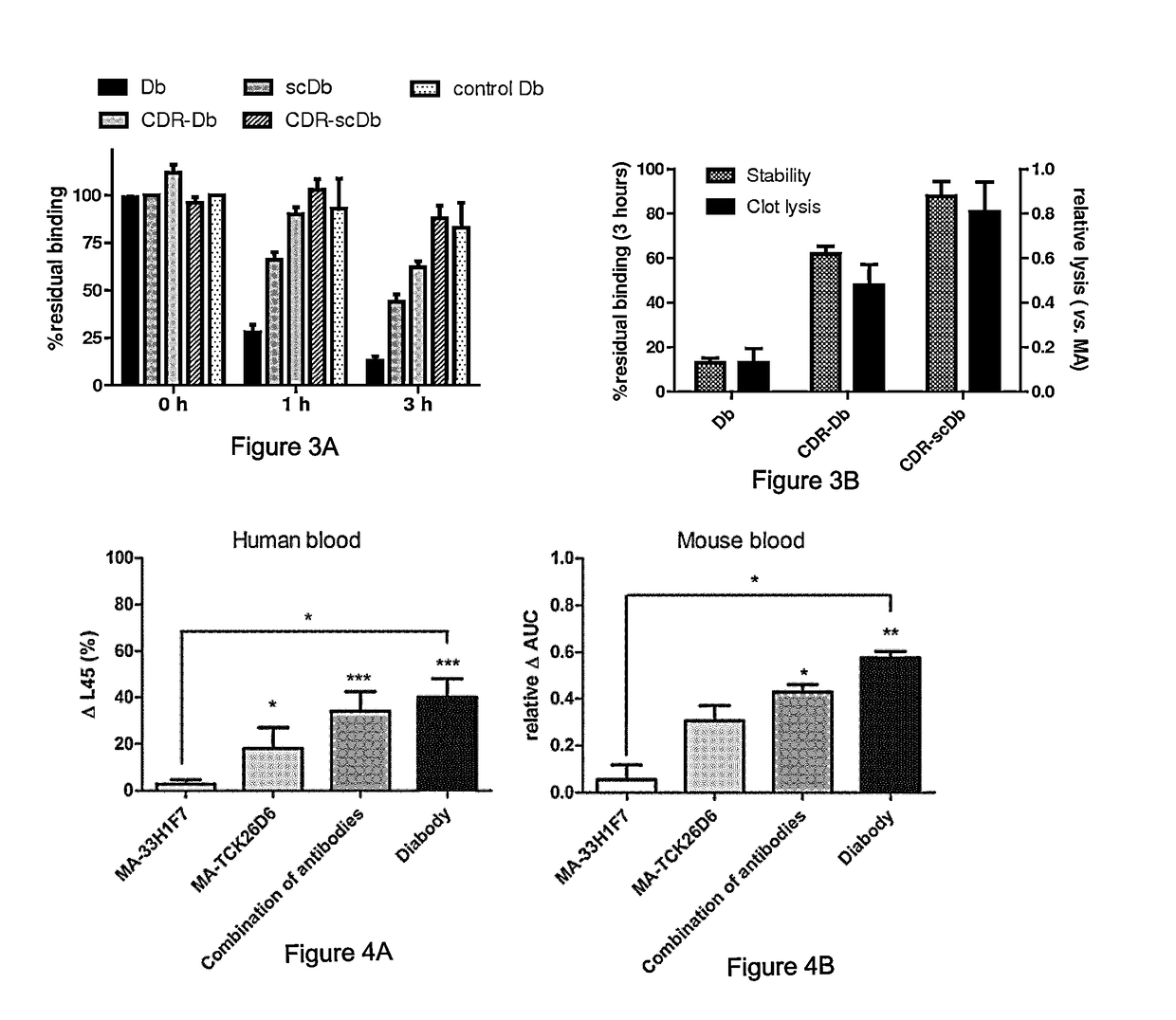
[0102]Inhibitory properties of the parental antibodies against human and mouse TAFI and PAI-1 were preserved in Db-TCK26D6×33H1F7 as confirmed by functional assays. Moreover, Db-TCK26D6×33H1F7 r...
example 3
In Vivo Evaluation of the Profibrinolytic Properties of a Bispecific Inhibitor Against TAFI and PAI-1
1. Complementary Effect of Dual TAFI / PAI-1 Inhibition After Systemic Thrombotic Challenge
[0106]Mice, pre-treated with a dose of MA-TCK26D6 or MA-33H1F7 targeting all circulating antigen, were subjected to thromboembolism by systemic administration of thromboplastin. Fibrin deposition in lungs was only decreased to baseline levels upon administration of a TAFI inhibitor (FIG. 5). Since PAI-1 levels are extremely low in mice, no effect of PAI-1 inhibition was detected.
[0107]To evaluate simultaneous inhibition of TAFI and PAI-1 in this model, endotoxemia was induced to upregulate PAI-1 levels in plasma. Fibrin deposition in the lungs was reduced through TAFI inhibition with MA-TCK26D6 (5 mg / kg) or through PAI-1 inhibition with MA-33H1F7 (10 mg / kg). However, this reduction did not reach a maximal degree. After administering a mixture of MA-TCK26D6 (5 mg / kg) and MA-33H1F7 (10 mg / kg), fibr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| body weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com