Methods for Molecular Classification of BRCA-Like Breast and/or Ovarian Cancer
a technology of ovarian cancer and molecular classification, applied in the field of oncology, can solve problems such as genetic instability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
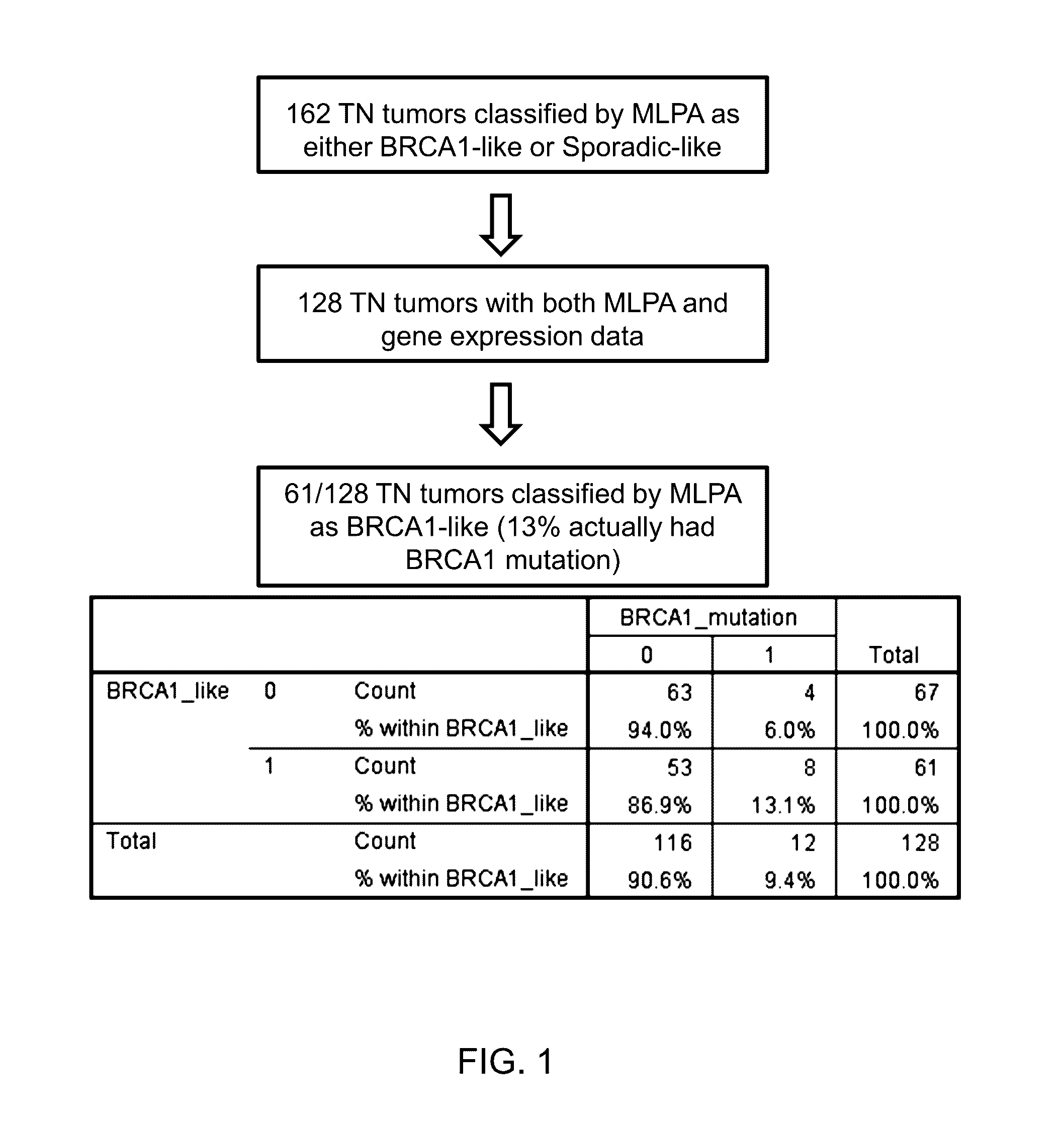
[0077]Patient Samples 128 triple negative breast cancer samples (fresh frozen) with long-term follow-up were collected from two European cancer centers. BRCA1 mutation and promoter methylation was determined by next generation sequencing and methylation-specific multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MS-MLPA) and BRCA1-like classification by MLPA [Lips et al., 2011. Breast Cancer Research 13: R107]. In addition we collected full genome expression data for all patients and mutation data for 21 known DNA repair genes. Differential gene expression was examined between tumors that classify as BRCA1-like with no mutation or methylation for mutations or dysregulation in another gene or genes involved in DNA repair, which may be responsible for the BRCA1-like phenotype. and sporadic-like.
Gene Expression Preprocessing Methods:
i) Exploratory Biological Analysis
[0078]The RNA quality was assessed by a Bioanalyzer and samples with RIN above 5 were selected for fu...
example 2
[0096]A validation set comprising 53 samples was used to test the signature. This validation set had been hybridized on the Illumina microarray platform. The data for each sample was scaled to the same median as the test set.
[0097]Tables 3-6 are presented for both the training and the 53 validation samples. The top 3 significant results (2, 72 and 77 genes) are presented in Tables 3, 4 and 5, respectively Table 6 provides the results of other gene sets on the training and the 53 validation samples. For each set of genes, both results for the training dataset and the validation dataset are indicated.
[0098]Following this, a smaller number of genes were analyzed to see if there could be a ‘minimum set’ of genes that could still give the same significance in validation. The sensitivity for a lower number of genes remained the same (or even slightly higher), however the specificity dropped.
[0099]As this signature is also developed in FF a higher number of genes may be more appropriate to...
example 3
Methods
[0102]115 HER2 negative patients (HER2−) were considered in this analysis. The BRCAness classification was computed using the 77 gene panel BRCAness gene signature. Patients were treated with oral PARP inhibitor veliparib (ABT-888) in combination with carboplatin and chemotherapy (V / C) (71 patients), or with chemotherapy alone (44 patients).
[0103]The association between BRCAness classification and response in the V / C and control arms alone (Fisher Exact test), and relative performance between arms (biomarker×treatment interaction, likelihood ratio test) was determined using a logistic model. The BRCAness signature was assessed in the context of a subset of patients that were negative for progesterone receptor, estrogen receptor and HER2 (triple negative; TN). Statistical calculations are descriptive (e.g. p-values are measures of distance with no inferential content).
Results
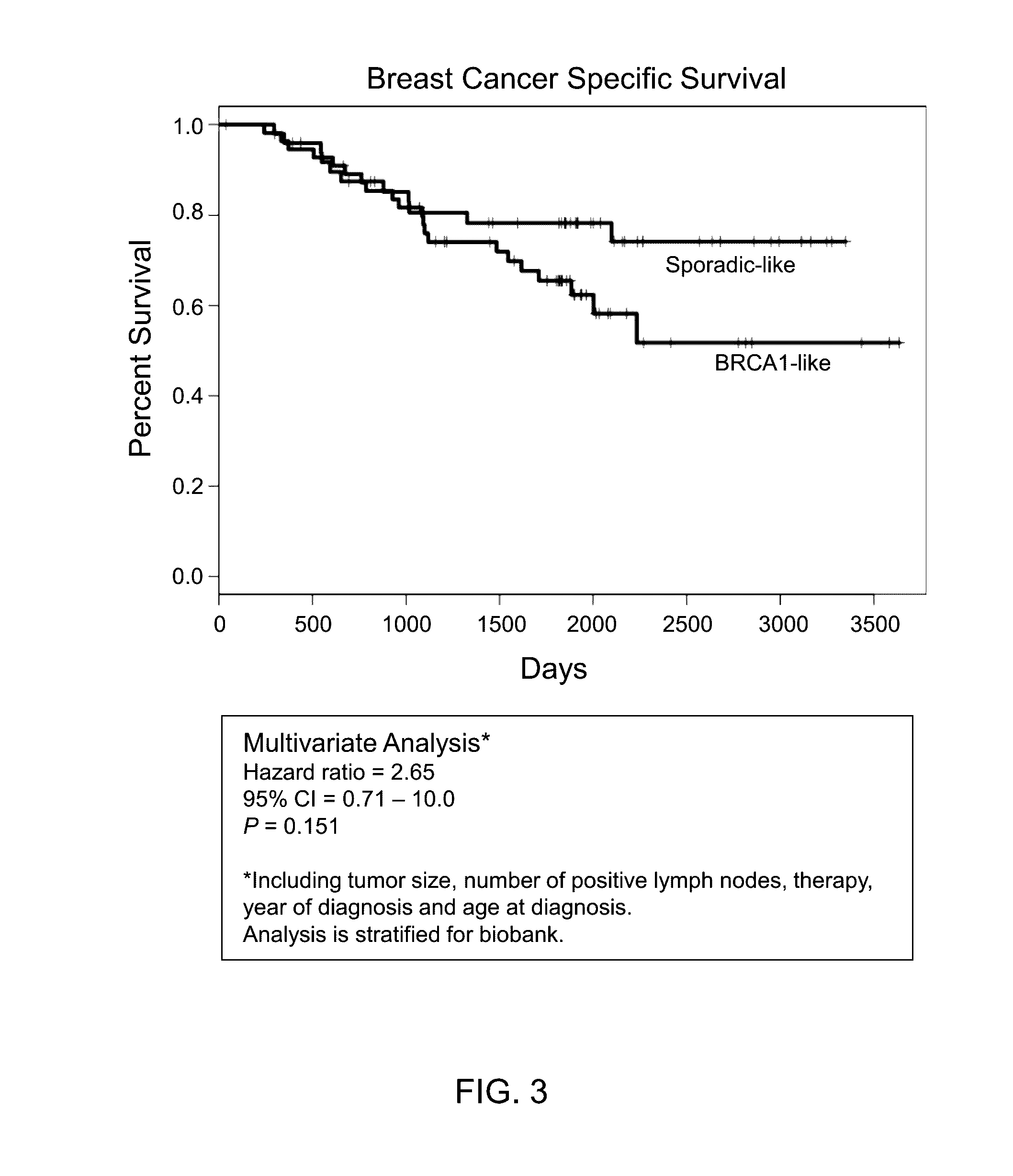
[0104]Of the 115 patients assessed, 56 were classified as BRCA-like using the 77 gene panel BRCAness ge...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Level | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com