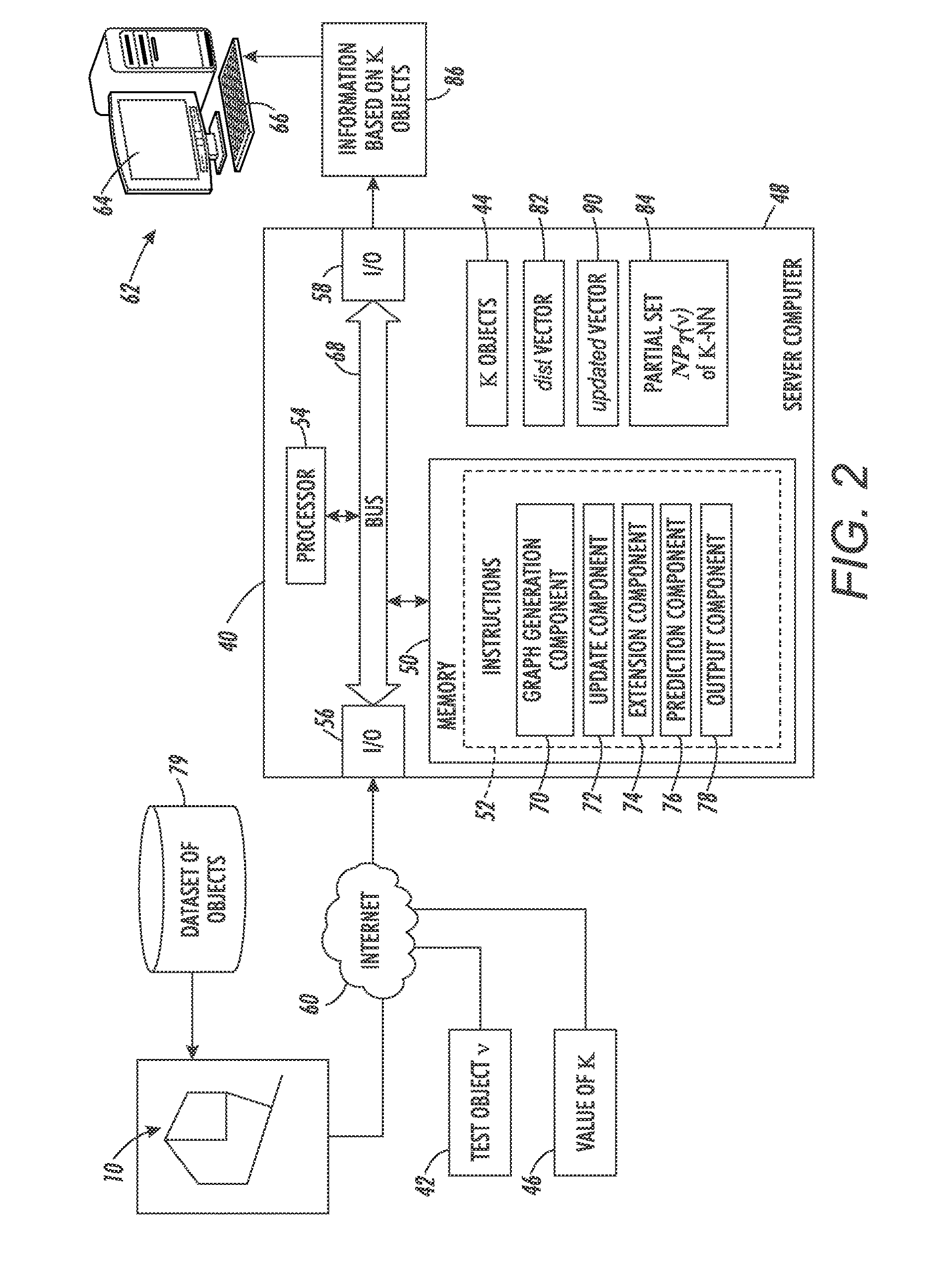
System and method for performing k-nearest neighbor search based on minimax distance measure and efficient outlier detection
a technology of knearest neighbor and minimax distance measure, applied in the field of graph representation of data, can solve the problems of inability to perform knearest neighbor search based on minimax distance measure and efficient outlier detection, complex data structure, and inability to perform priori unknowns
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
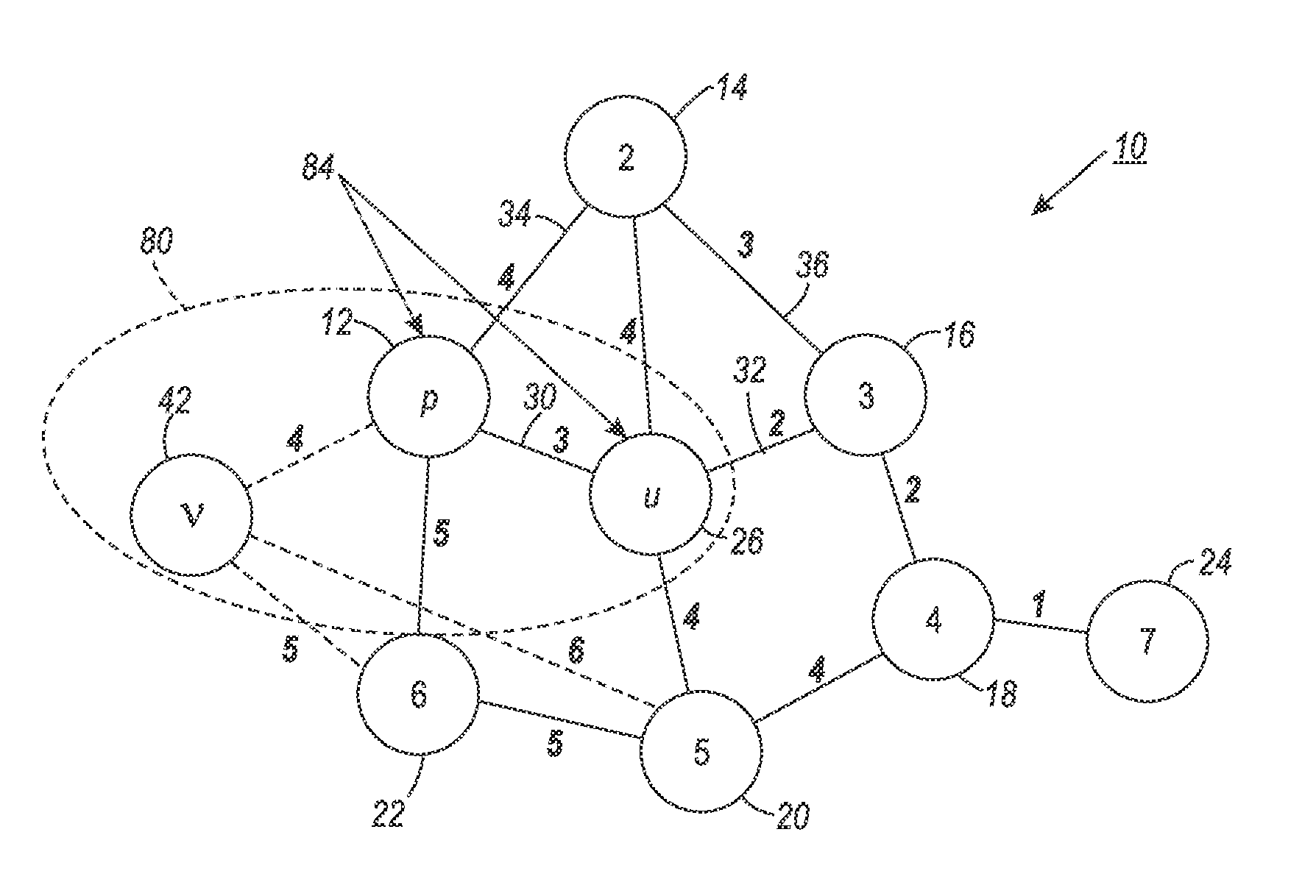
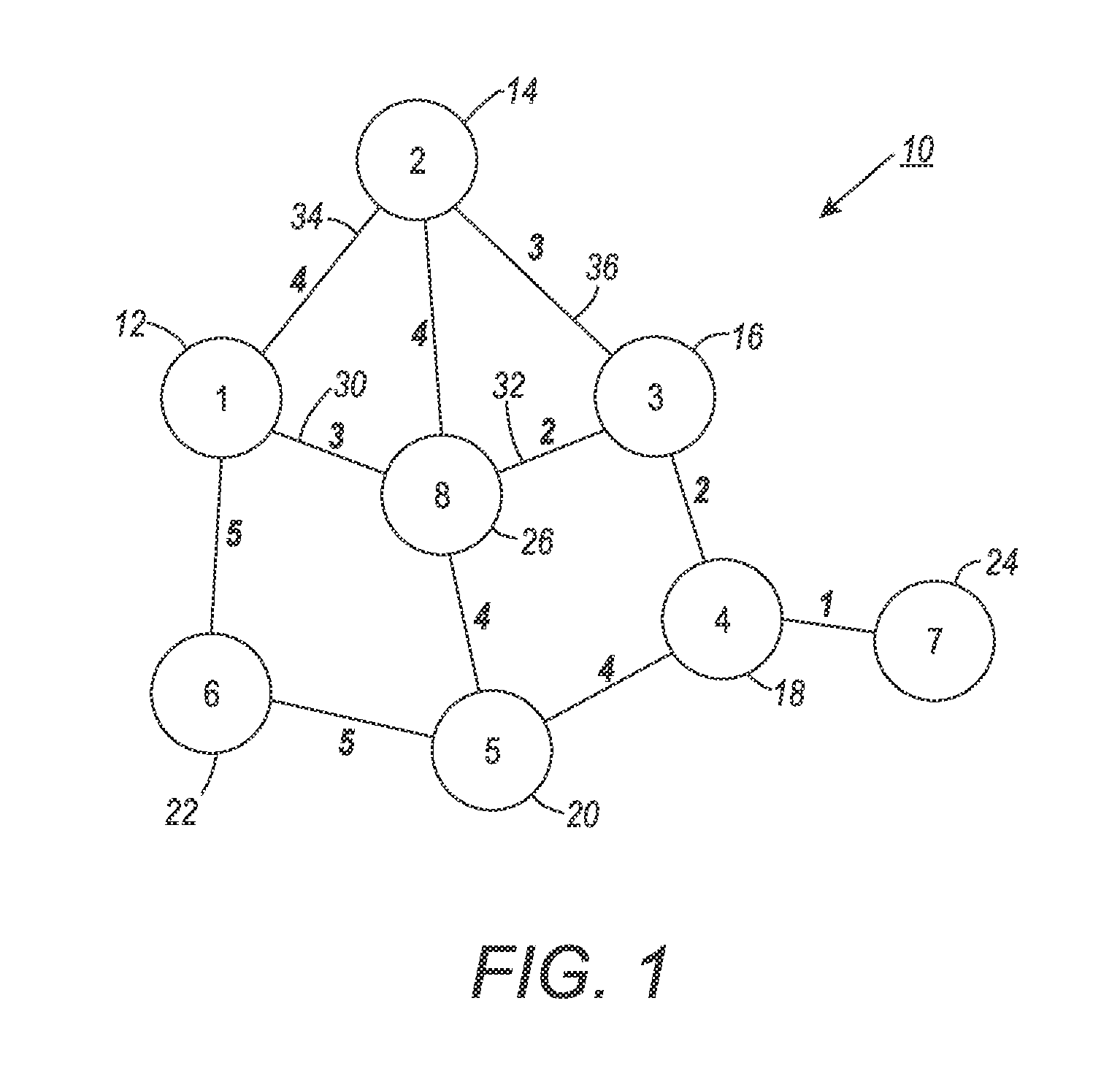
[0155]The effectiveness and performance of the exemplary method on a variety of real-world datasets is evaluated and the results compared against alternative methods.
[0156]Experiments are performed on seven datasets, four of which are text documents selected from the 20 Newsgroup collection (Thomas M. Mitchell, “Machine Learning,” McGraw-Hill, Inc., New York, N.Y., USA, 1st edition, 1997) and the others come from image and plant specification. They are:[0157]1. COMP: a subset of the 20 Newsgroup collection containing 2936 documents focusing on computers: ‘comp.graphics,’‘comp.os.ms-windows.misc,’‘comp.sys.ibm.pc.hardware,’‘comp.sys.mac.hardware,’ and ‘comp.windows.x’.[0158]2. REC: a subset of the 20 Newsgroup collection containing 2389 documents on sports: ‘rec.autos,’‘rec.motorcycles,’‘rec.sport.baseball,’ and ‘rec.sport.hockey’.[0159]3. SCI: a subset of the 20 Newsgroup collection containing 2373 documents about science: ‘sci.crypt,’‘sci.electronics,’‘sci.med,’ and ‘sci.space’.[01...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com