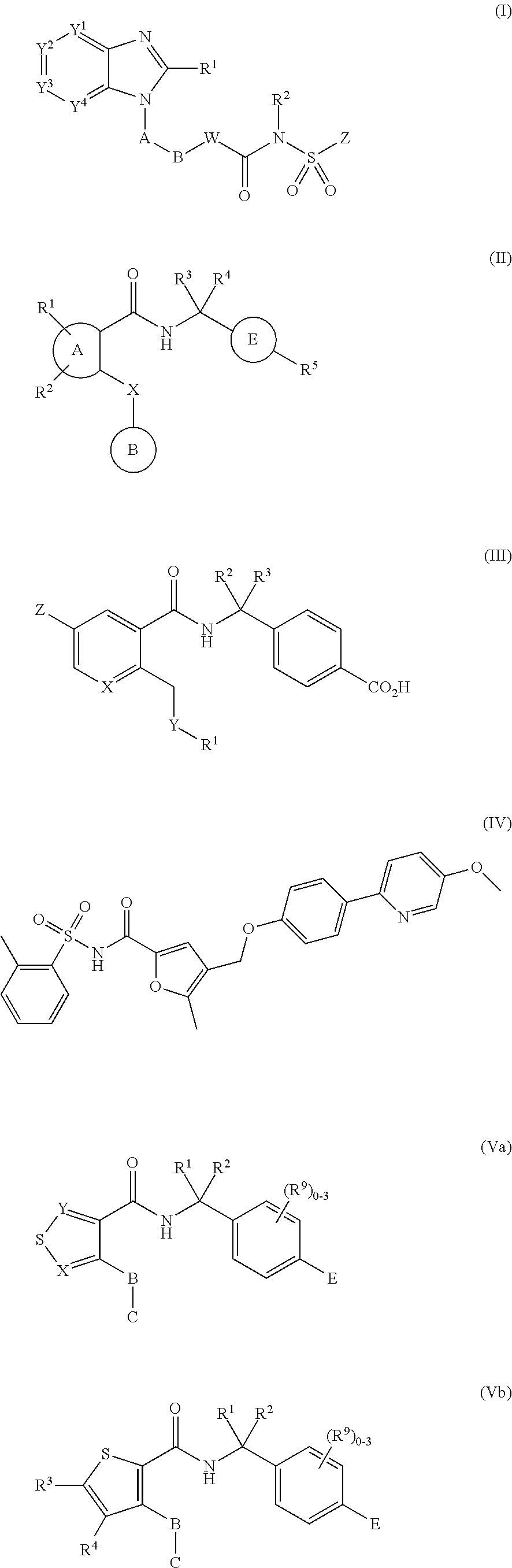
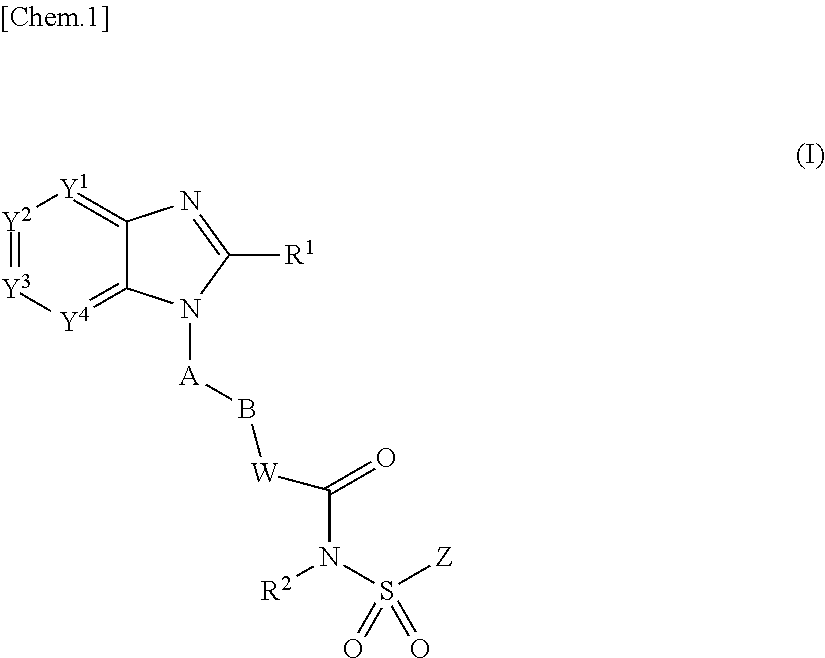
Use of ep4 receptor antagonists in the treatment of cartilage disease
a technology of ep4 receptor and cartilage disease, which is applied in the field of compounds, can solve the problems of no effect, no no anti-ep4 receptor, and all therapeutic methods are only nosotropi
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Ex Vivo Bovine Cartilage Explant Model
[0781]The method of this assay is descrived in the following literature (Rheumatol Int. 2013 February; 33(2):401-11).
[0782]Full-depth cartilage explants were harvested from the knee of either back legs of a cow less than 24 month old. All the FDC explants are divided into different treatment group according to the explants weight and metabolic activity (viability) measured by Alamar Blue. Compounds were freshly added to the explants at each media change. The explants were cultured in serum-free conditions. Supernatants retrieved from the culture were analyzed by biomarkers (P2NP, C2M, AGNx1, AGNx2) at day 7, 14 and 21.
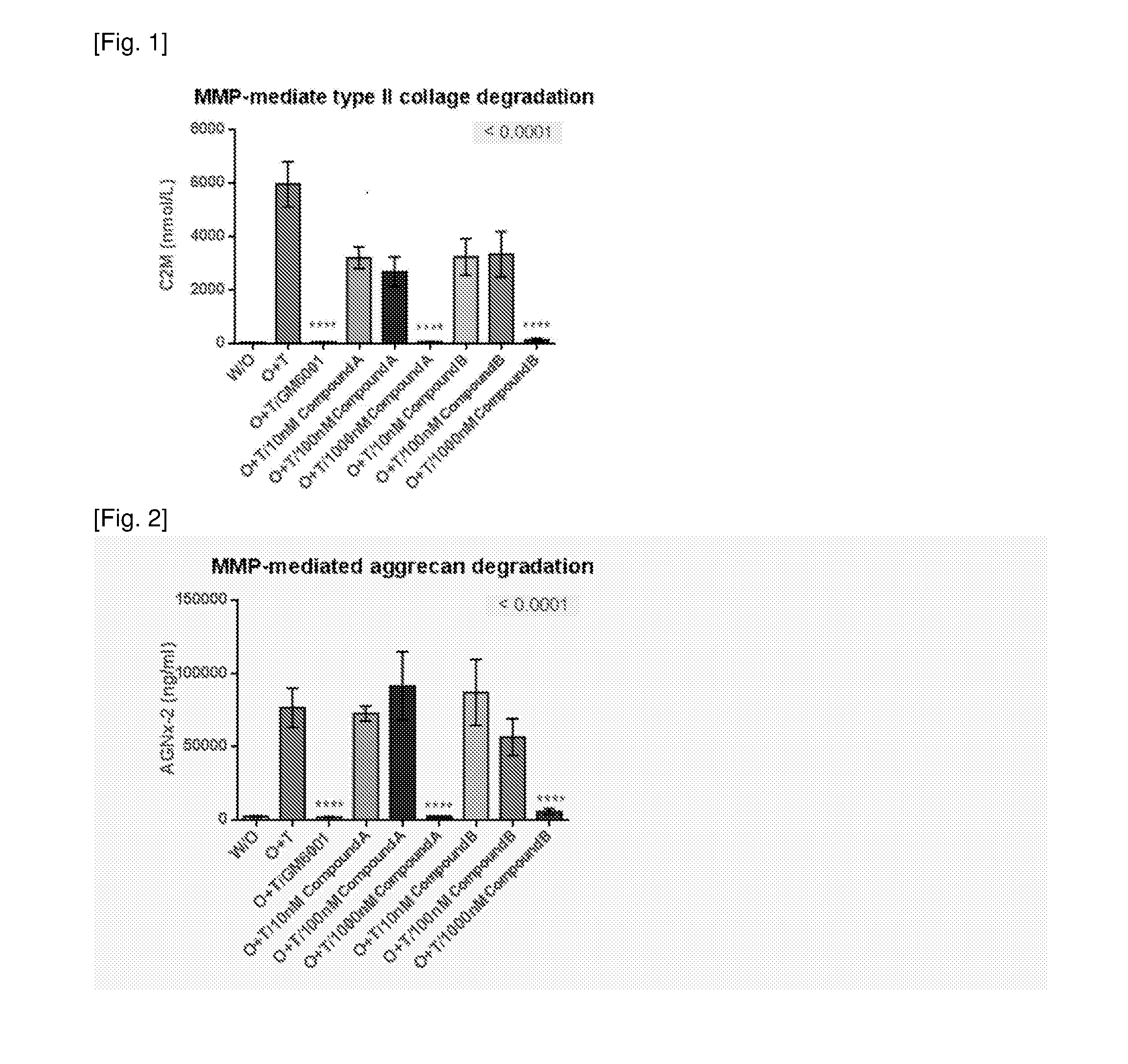
[0783]These results are shown in FIG. 1 and FIG. 2.
[0784]From results of FIG. 1, Compound A and Compound B shows dose-dependent inhibition of cartilage destruction in ex vivo bovine cartilage explant model
[0785]The similar inhibition of cartilage destruction in ex vivo bovine cartilage explant modelis shown in Compound C[0786](4-{(...
example 2
Rat Mono-Iodoacetate and / or Meniscal Transection Model
[0791]The compounds described in the compounds list are conducted in the rat mono-iodoacetate and / or meniscal transection induced osteoarthritis model. These compounds exhibit potent inhibitory activities on cartilage destruction and serum bio-chemical markers associated with cartilage degradation and tissue inflammation in the rat mono-iodoacetate and / or meniscal transection model.
[0792]The study was performed in female Sprague-Dawley rats, age 6 months at MNX surgery.
[0793]7 days after MNX surgery monoiodoacetate 2 mg / 0.2 ml was injected intra-articularly in the right knee joint. The test compounds or vehicle is injected to the animals after the MNX. In the MNX or sham group, the test compounds or vehicle was administered until termination.
[0794]Weekly fasting blood sampling are taken for the analysis of biomarker (P2NP, C2M, AGNx1, AGNx2). Knee joints is isolated at termination. Cartilage damage is scored by experienced histo-...
example 3
Rat Meniscal Transection and / or Ovariectomised Model
[0796]The compounds describe in the compounds list are conducted in the rat meniscal (MNX) transection and / or ovariectomised (OVA) induced osteoarthritis model. These compounds exhibit excellent inhibitory activities on cartilage destruction and serum biochemical markers associated with cartilage degradation and tissue inflammation in the rat meniscal transection and / or ovariectomised model.
[0797]The study is performed in female Sprague-Dawley rats with MNX and OVX surgery.
[0798]The test compounds or vehicle is injected to the animals after the surgery. In the MNX / OVX or sham group, the test compounds or vehicle was administered until termination.
[0799]Weekly fasting blood sampling are taken for the analysis of biomarker (P2NP, C2M, AGNx1, AGNx2). Knee joints is isolated at termination. Cartilage damage is scored by experienced histo-pathologist according to Colombo score.
[0800]The compounds describe in the compounds list are simil...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical conductance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Antagonistic activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com