Inherently concrete-compatible carbon sorbents for mercury removal from flue gas
a carbon sorbent, inherently concrete technology, applied in the direction of sustainable waste treatment, other chemical processes, separation processes, etc., can solve the problems of complex interaction between the sorbent and the aea during concrete manufacture, unfavorable adsorption of aea foaming agents, etc., to reduce the quality of fly ash, the effect of abundant and limited adsorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0031]In this example, the relationship between Iodine Number and the foaming tendencies (AEA exclusion) of the various carbon sorbents is shown in FIG. 1. Iodine Number is normally closely related to total BET adsorption surface area and adsorption pore volume. When compared to BET surface area, Iodine Numbers are usually within roughly 10% of the BET value (H. Sontheimer, J. C. Crittenden, and R. S. Summers, “Activated Carbon for Water Treatment” Second Edition (DVGW-Forschungsstelle, 1988), p. 102, which is incorporated by reference herein). As such, Iodine Number is generally a reasonable indicator of carbon sorbent performance in a given application. However, as shown in FIG. 1, it is clear that this parameter alone is insufficient to specify the composition of a concrete-compatible carbon sorbent independent of the material and process conditions used for its manufacture. For adequate mercury removal from flue gas some minimum Iodine Number or total surface area is generally n...
example 2
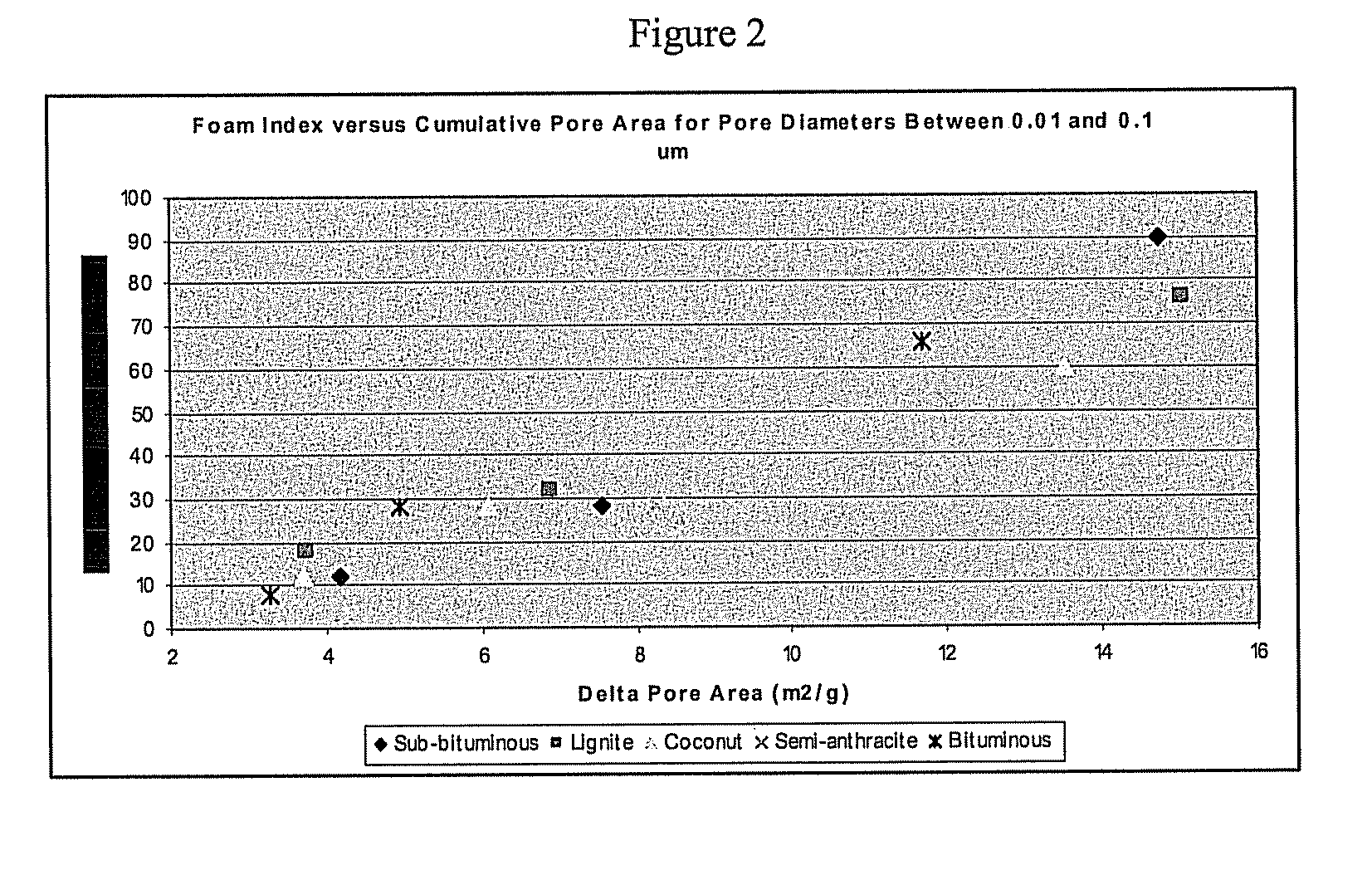
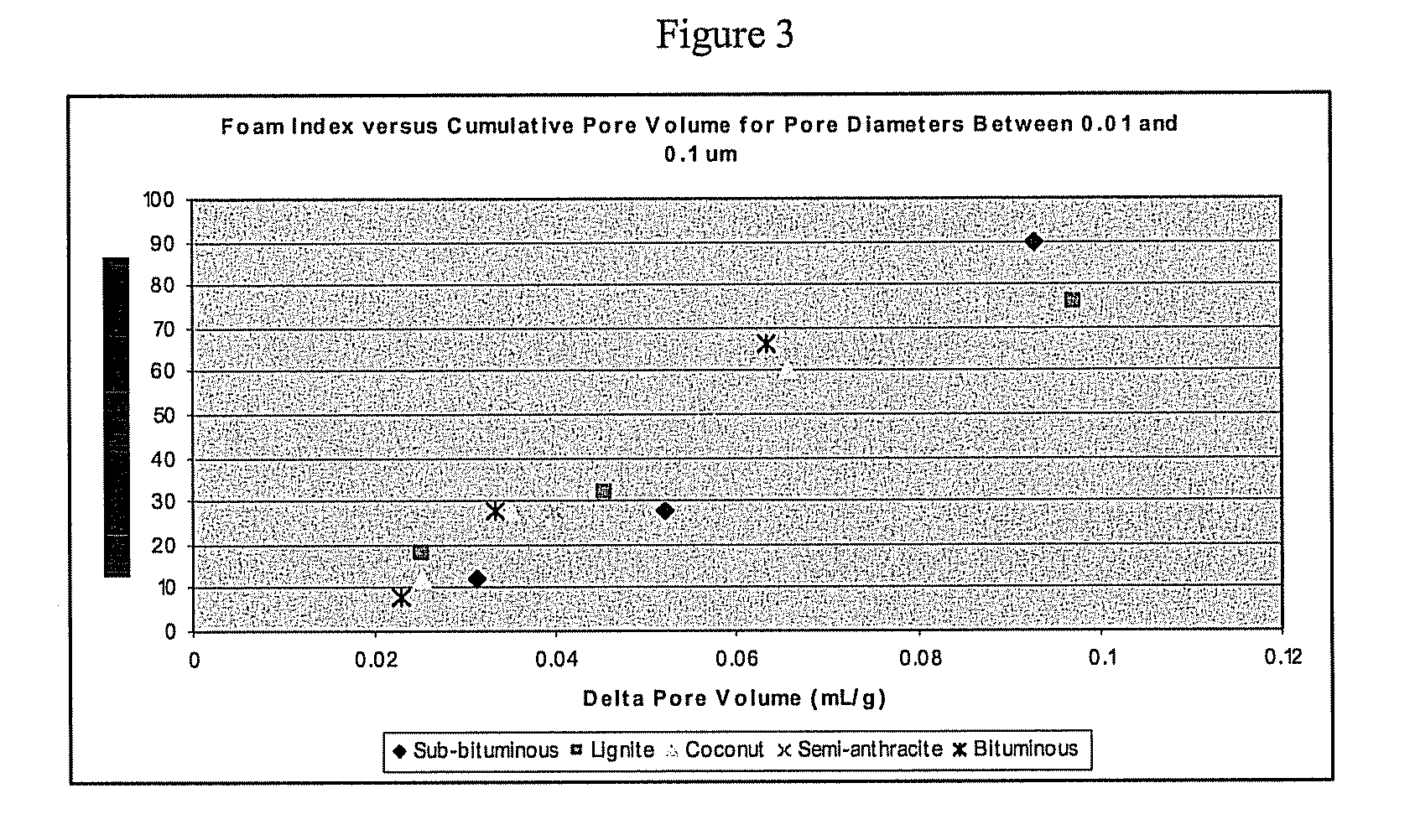
[0032]In this example, a relationship is established between the foaming tendencies of the various carbons (AEA exclusion) and a particular region of the carbon pore structure above about 0.01 microns (10 nm) as determined, for example, by mercury porosimetry or comparable techniques. In mercury porosimetry, elemental mercury is forced into the pore structure of the carbon under pressure. Under low pressure, the largest pores are filled first since they offer the least resistance to the flow of mercury. As the pressure is increased, pores with progressively smaller diameters are filled. From the data obtained during a run, the pore diameters and the cumulative and differential pore volumes and surface areas may be calculated for pore diameters roughly 0.003 microns (3 nm) and larger. In this example, it is seen that the pore region most closely related to the foam index of the carbon sorbent lies more in the region dominated by transport meso- and macro-pores having diameters above ...
example 3
[0034]In this example, the relationship between Molasses Number and foaming tendencies among the various carbon sorbents is shown in FIG. 8. Molasses Number is normally indicative of the pore volume of a carbon sorbent spanning the transition between larger diameter adsorption pores and the transport pores that lead to them. Historically, the test has had wide acceptance in the activated carbon arts, but chemical effects, such as pH, and other test variables may sometimes limit the applicability of the results from sorbent to sorbent. Surprisingly, for concrete-compatible applications, a relationship is seen between Molasses Number and the foaming tendencies of the sorbent that is largely independent of feedstock or manufacturing conditions, as shown in FIG. 8. Since the fly ash alone may produce a Foam Index of 4 to 8 drops of MB-VR™, a concrete-compatible carbon sorbent is defined as one with a foam index less than about 30 drops of MB-VR™. This would require a sorbent with a Mola...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com