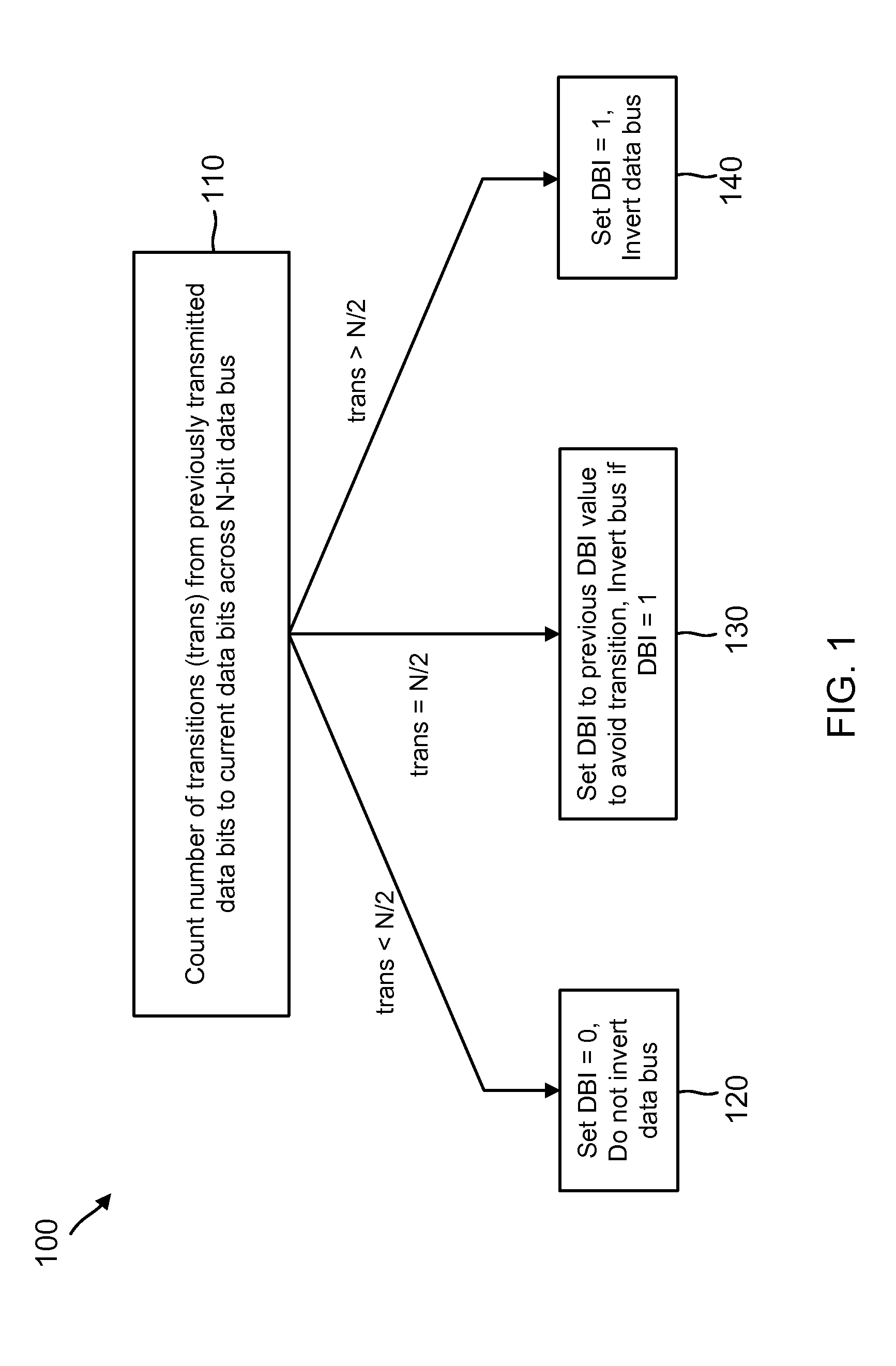
Systems and methods for transition-minimized data bus inversion
a data bus and transition-minimized technology, applied in the field of data bus inversion, to achieve the effect of improving power integrity and maximising power reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example circuit embodiments
[0047]FIG. 5 shows example inversion logic circuits 510 and 520 according to one embodiment. Inversion logic circuits 510 and 520 are shown with eight bits, through it is understood that the scope of embodiments may include inversion logic circuits adapted to employ any appropriate number of bits. For instance, in the embodiment of FIG. 6 (described below), inversion logic circuits 510 and 520 would employ thirty-two data bits as well as the DBI bit. Inversion circuit 510 may be included in a transmit path, whereas inversion circuit 520 may be included in a receive path.
[0048]Inversion logic circuit 510 includes on the left-hand side eight data bit inputs 0-7 and on the right-hand side eight data bit outputs 0-7 and a DBI bit output. Comparing logic 511 is employed to perform actions 110 and 410 (of FIGS. 1 and 4, respectively) to compare currently-received bits to previously-transmitted bits and identify a number of transitions. For instance, the bits may be received (as at action ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com