Biomarkers for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity, and Intensity and Flare
a biomarker and lupus erythematosus technology, applied in immunology, rheumatology and molecular biology, can solve the problems of insufficient onset inability to recognize and treat tissue and organ damage early, and inability to adequately detect the earliest or sufficient biologic signals of worsening diseas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
[0211]Study Population.
[0212]Experiments were performed in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration and approved by the Institutional Review Boards of the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation and the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center. Study participants were enrolled in the SLE Influenza Vaccination Cohort (Crowe et al., 2011) after written informed consent. Female EA SLE patients (meeting ≧4 ACR classification criteria; Hochberg, 1997) with disease flare 6-12 weeks post-vaccination (age 47.0±13.5 years, n=28) were matched by age (±5 years), race, gender, and time of disease assessment to patients with stable disease (age 46.8±11.9 years, n=28), as well as unrelated healthy controls (age 46.8±13.5 years, n=28). Samples from 13 SLE patients pre-flare were compared to samples drawn from the same individuals in a different year with no flare.
[0213]Clinical Data and Sample Collection.
[0214]Demographic and clinical information were collected as previously...
example 2
Results
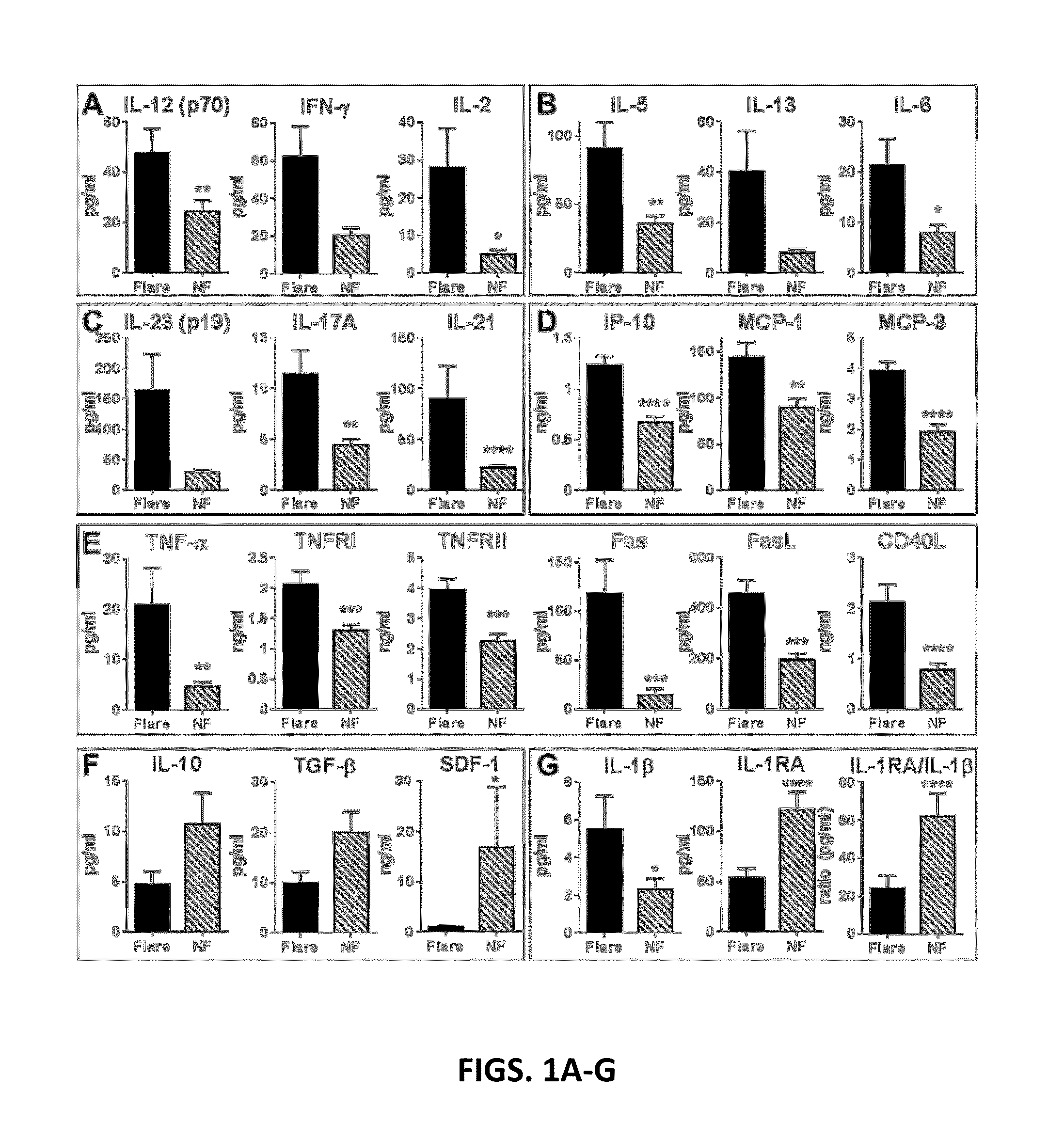
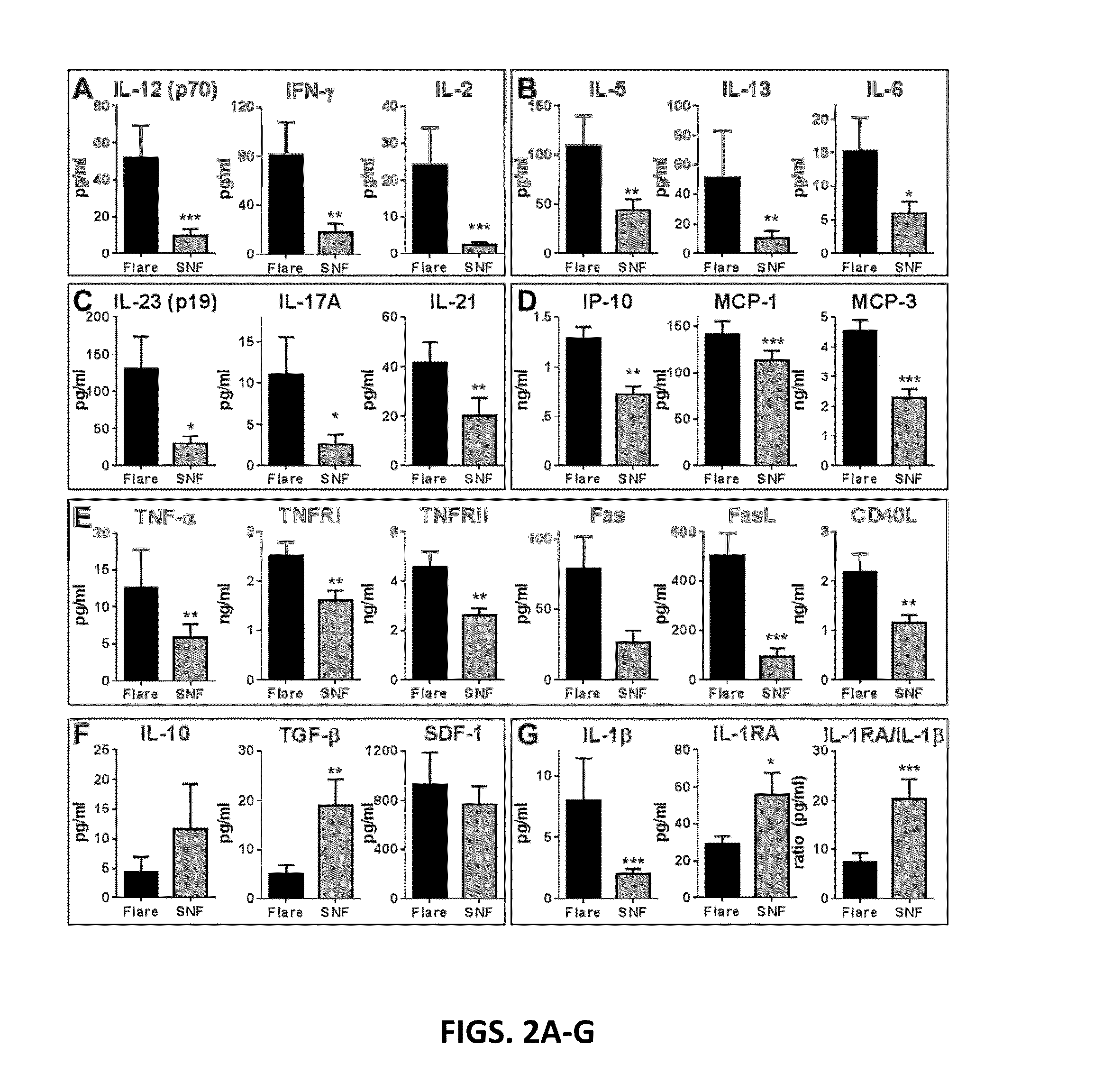
[0221]Inflammatory Mediators and Regulatory Cytokines are Altered Prior to SLE Disease Flare.
[0222]SLE patients within this cohort were followed longitudinally and evaluated for evidence for SELENA-SLEDAI disease flare. The inventors hypothesized that clinical changes in disease activity are the result of a perturbation in the already dysregulated immune system of SLE patients. To test whether markers of immune dysregulation might precede clinical disease flares, 52 soluble analytes were compared in 28 EA SLE patients in whom flare was detected after influenza vaccination, matched SLE patients who did not experience flare for at least 12 weeks post-vaccination, and matched healthy individuals. All SLE patients, with or without subsequent flare, had similar SELENA-SLEDAI scores at baseline (3.8±3.7 flare vs. 2.6±3.2 non-flare [NF], p=0.2451 by Wilcoxon matched-pairs test).
[0223]At baseline and follow-up, non-flare SLE patients had levels of T cell mediators that were similar t...
example 3
Discussion
[0237]Delays in treating SLE flares may potentiate chronic inflammation, leading to recurrent illness and end-organ damage. Immune dysregulation in SLE likely precedes clinical disease, and in some cases, low grade, smoldering inflammation could persist over time, contributing to progressive organ damage in the absence of overt clinical flare. The data point to the “yin-yang” nature of the immune response that either leads to impending disease flare (inflammation) or allows for periods of non-flare (regulation). In this study elevated levels of shed TNF receptors and / or pro-inflammatory Th adaptive pathway cytokines were found in nearly all SLE patients prior to impending flare (FIG. 5). While a predominant inflammatory pathway is evident for a subset of patients, most had elevated inflammatory mediators from multiple pathways, which may help explain variability among previous reports of inflammatory mediators in SLE patients with active disease (Gomez et al., 2004; Tokano...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com