Memory device and method of operation of such a memory device
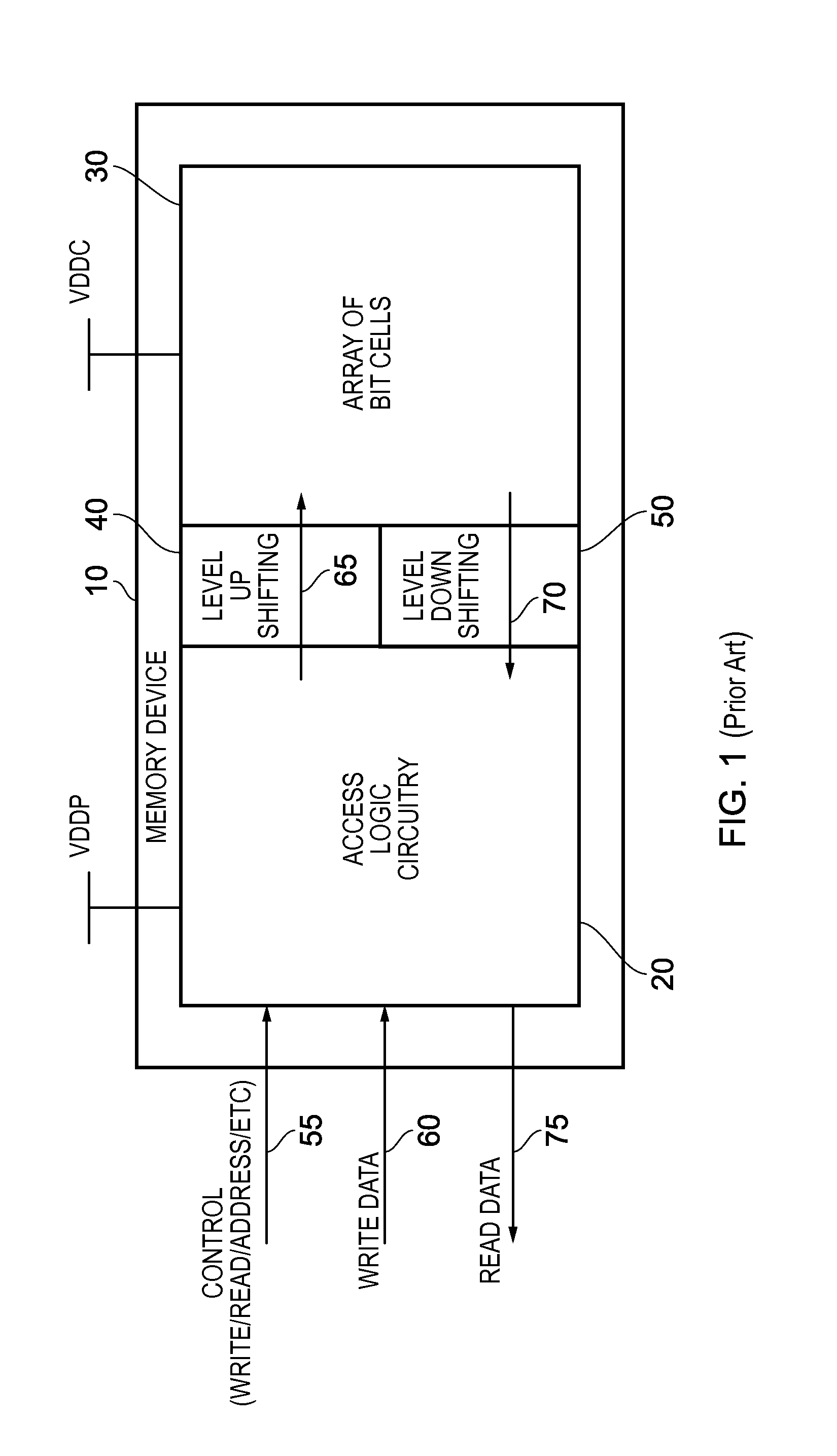
a memory device and memory technology, applied in the field of memory devices, can solve the problems of insufficient write margin, significant power consumption, short circuit current path, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing power consumption in those components
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
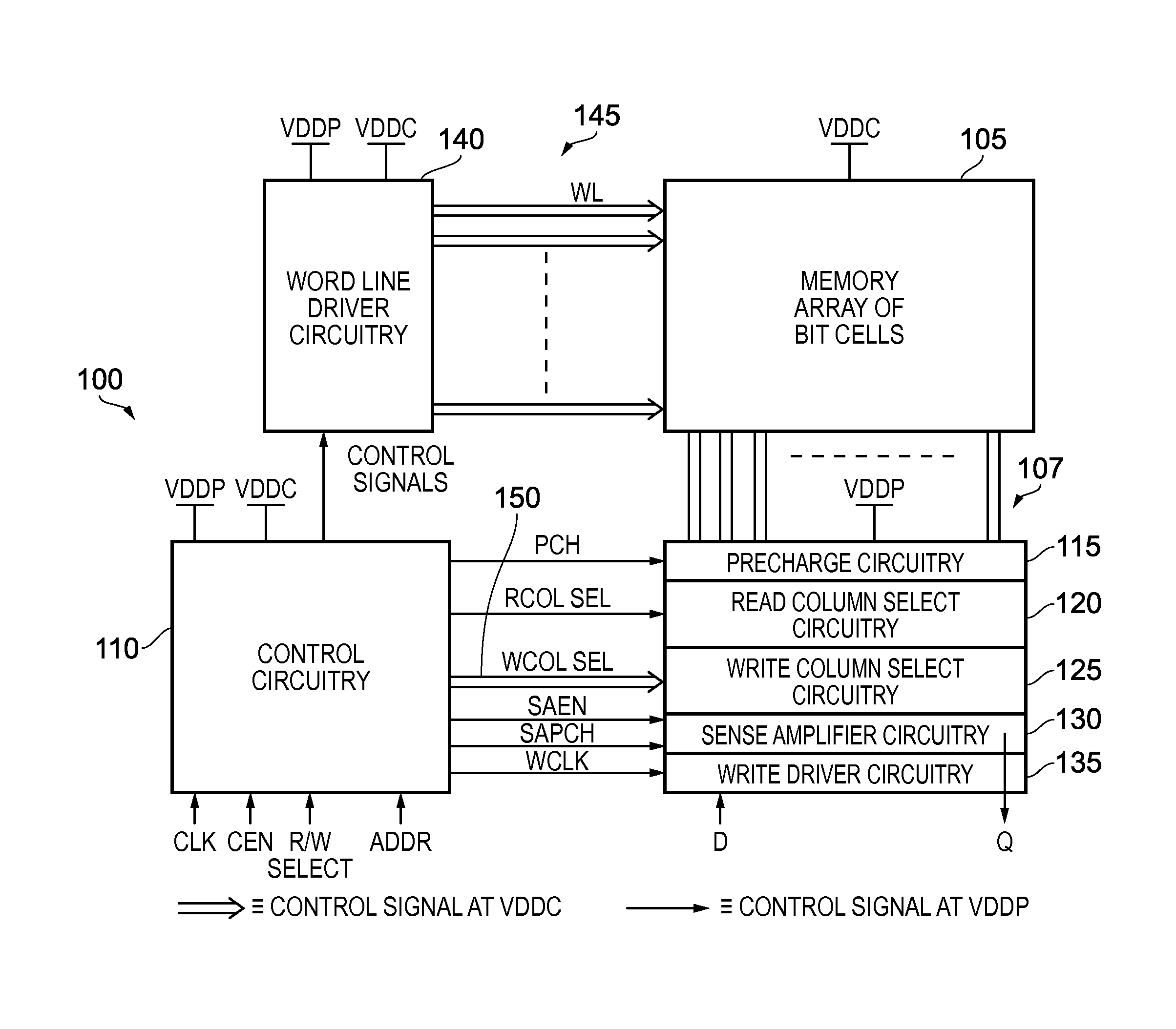
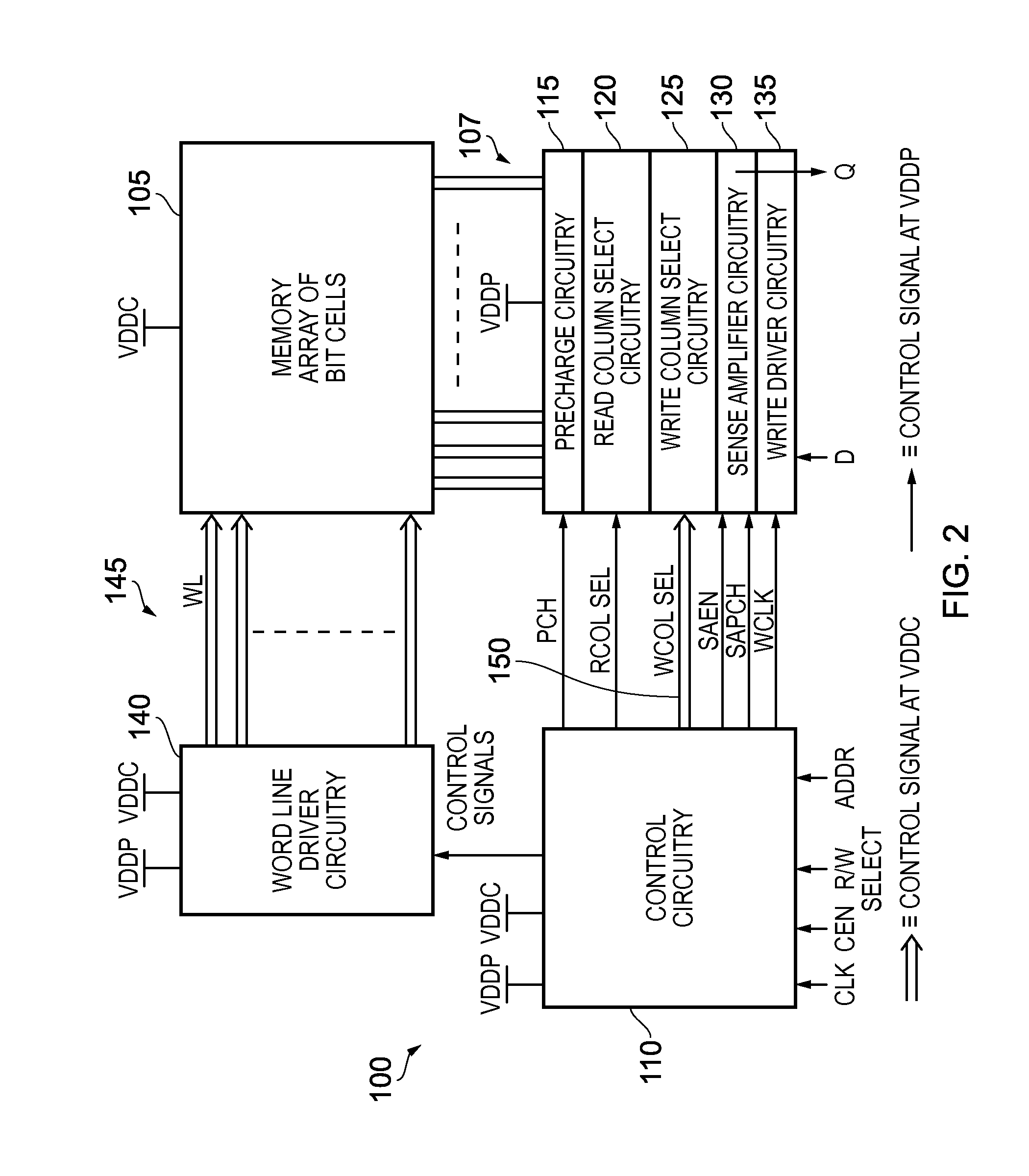
[0041]FIG. 2 is a diagram schematically illustrating a logical arrangement of a memory device in accordance with one embodiment. In particular, the memory device 100 includes a memory array 105 comprising an array of memory cells arranged in a plurality of rows and columns. A plurality of word lines 145 are provided through the array in order to allow individual rows of memory cells to be addressed by the word line driver circuitry 140 during write and read operations. In addition, a plurality of bit lines are provided in association with the columns of memory cells, in this embodiment each column having an associated pair of bit lines, to enable data to be written into an addressed memory cell of that column during a write operation, and for data to be read from an addressed memory cell of that column during a read operation.
[0042]Precharge circuitry 115 is used to precharge the voltage level on the bit lines under the control of control circuitry 110. Following the precharge opera...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com