Electro-enhanced solid-phase microextraction method
a solid-phase microextraction and enhanced technology, applied in the field of separation techniques, can solve the problems of affecting the health and reproduction system of both humans and wildlife, plasticizers that are easy to leach under harsh environmental conditions, and detection limits can reach parts per trillion (ppt) levels for certain compounds, so as to reduce the solubility of analytes and increase the ionic strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
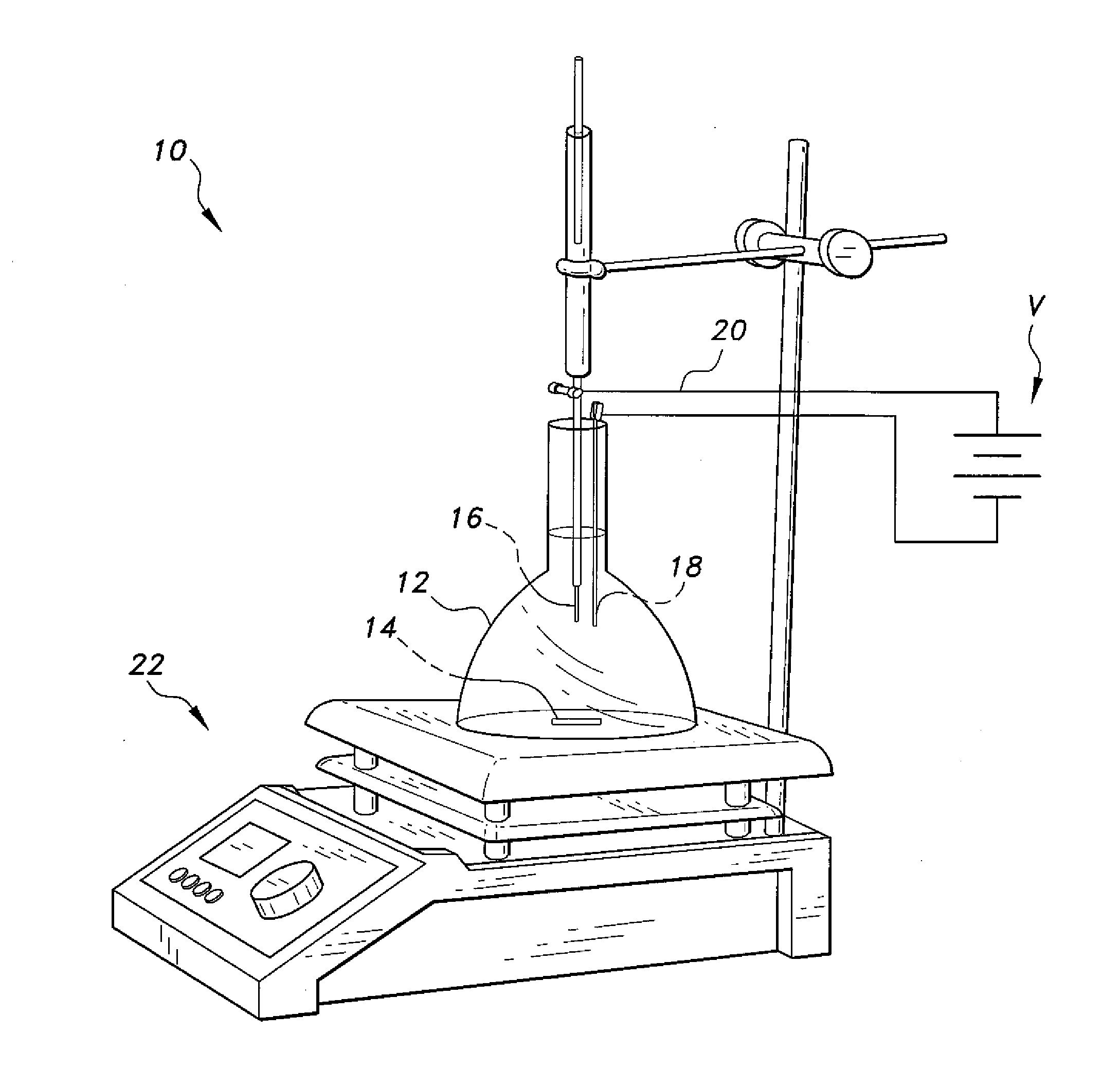
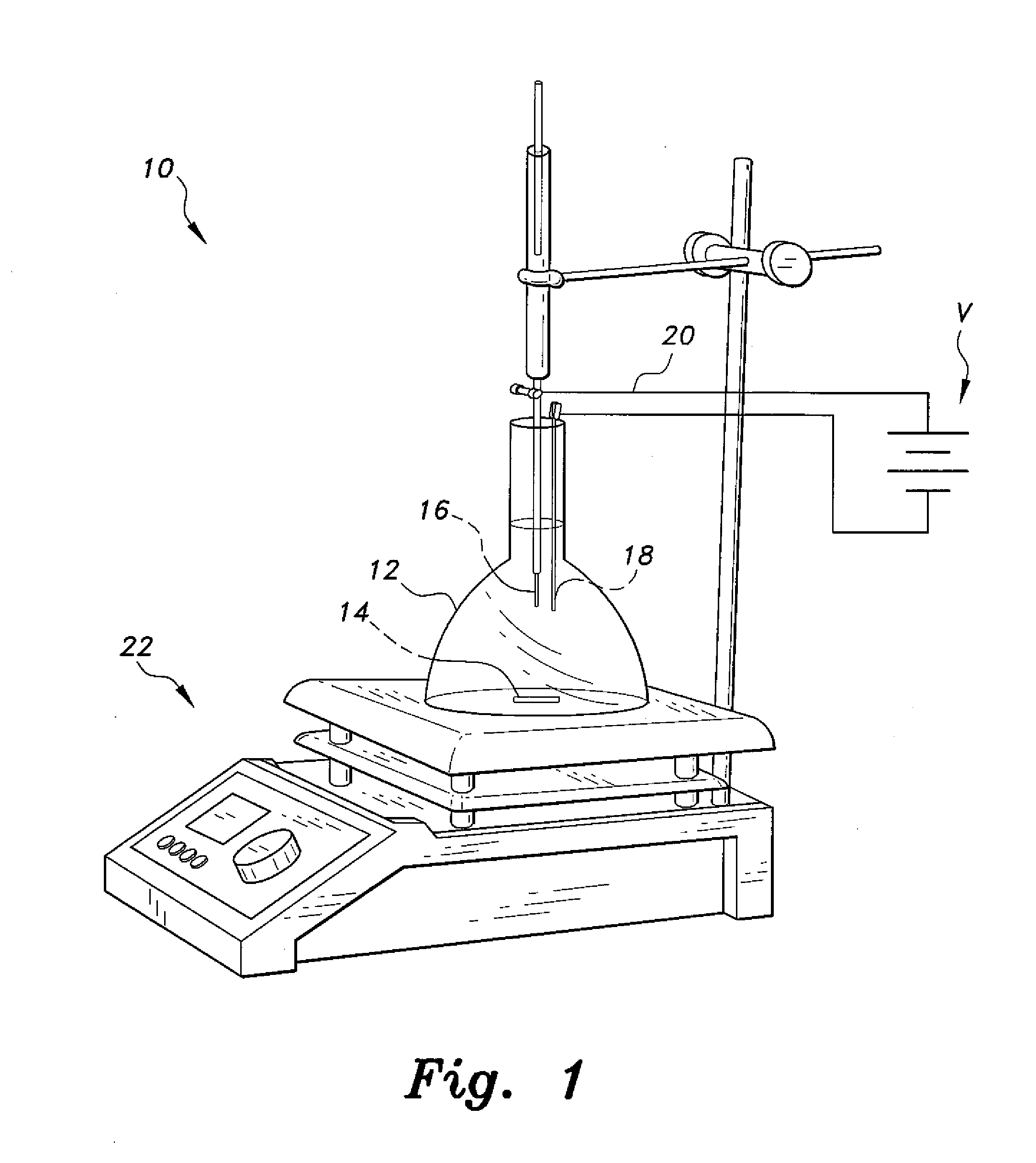
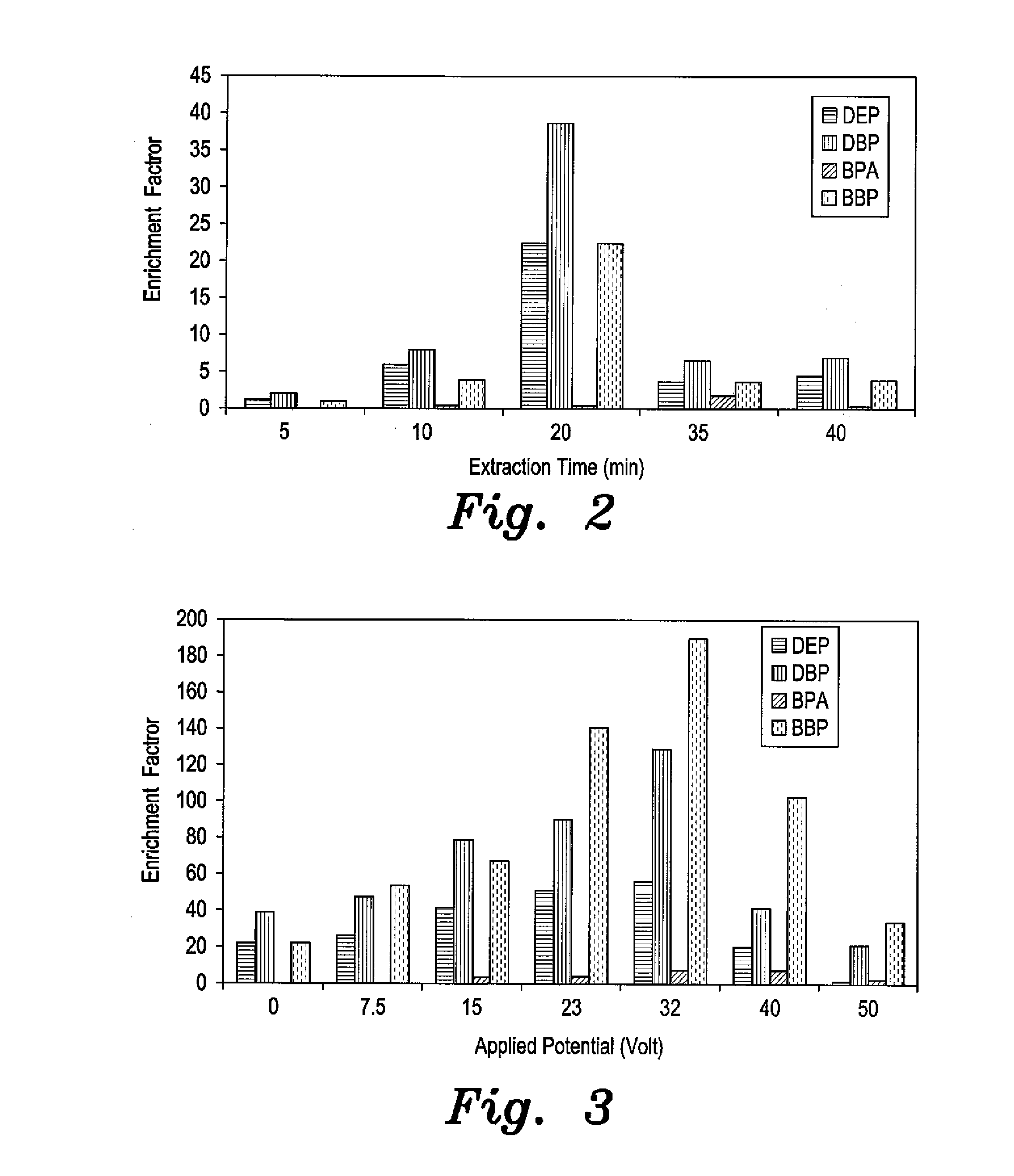
[0022]The electro-enhanced solid-phase microextraction (EE-SPME) method involves extraction that is performed with an SPME fiber, preferably made of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), in the presence of an applied electric potential for a predetermined period of time. Polar analytes are extracted onto the fiber, which is the stationary phase. The solid-phase microextraction fiber is then inserted into an injection port of a gas chromatograph coupled with a mass spectrometer. The polar analytes are desorbed in the injection port, and are analyzed by GC-MS to detect and quantify the individual components. The method is particularly useful for the detection of trace amounts of plasticizers, such as phthalate esters and bisphenol A, that are known to disrupt the endocrine system of humans and animals above known levels.
[0023]For purposes of laboratory testing, stored blood samples were collected from a blood bank of a local hospital in Al-Khobar, Saudi Arabia. Seawater samples were collected ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com