Method and apparatus for carding of staple fibers
a staple fiber and carding technology, applied in the field of method and apparatus of carding staple fibres, can solve the problems of high stress on the fibre, significant damage to the fibre, and weakened fibres, and achieve the effects of selective enhancement of fiber movement and trash movement in the entrained air, damage due to pin impact, and selective enhancement of fiber movement and trash movemen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
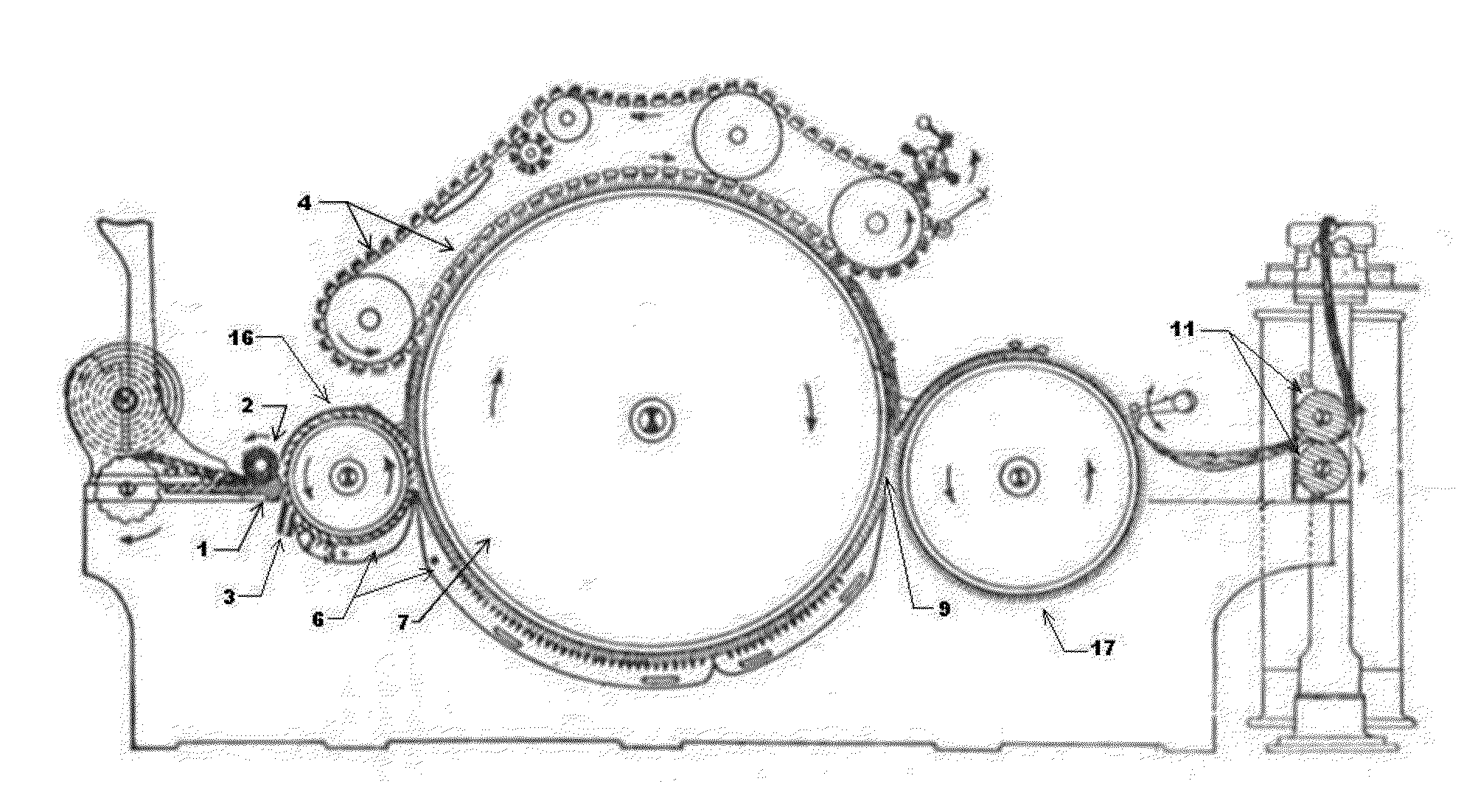
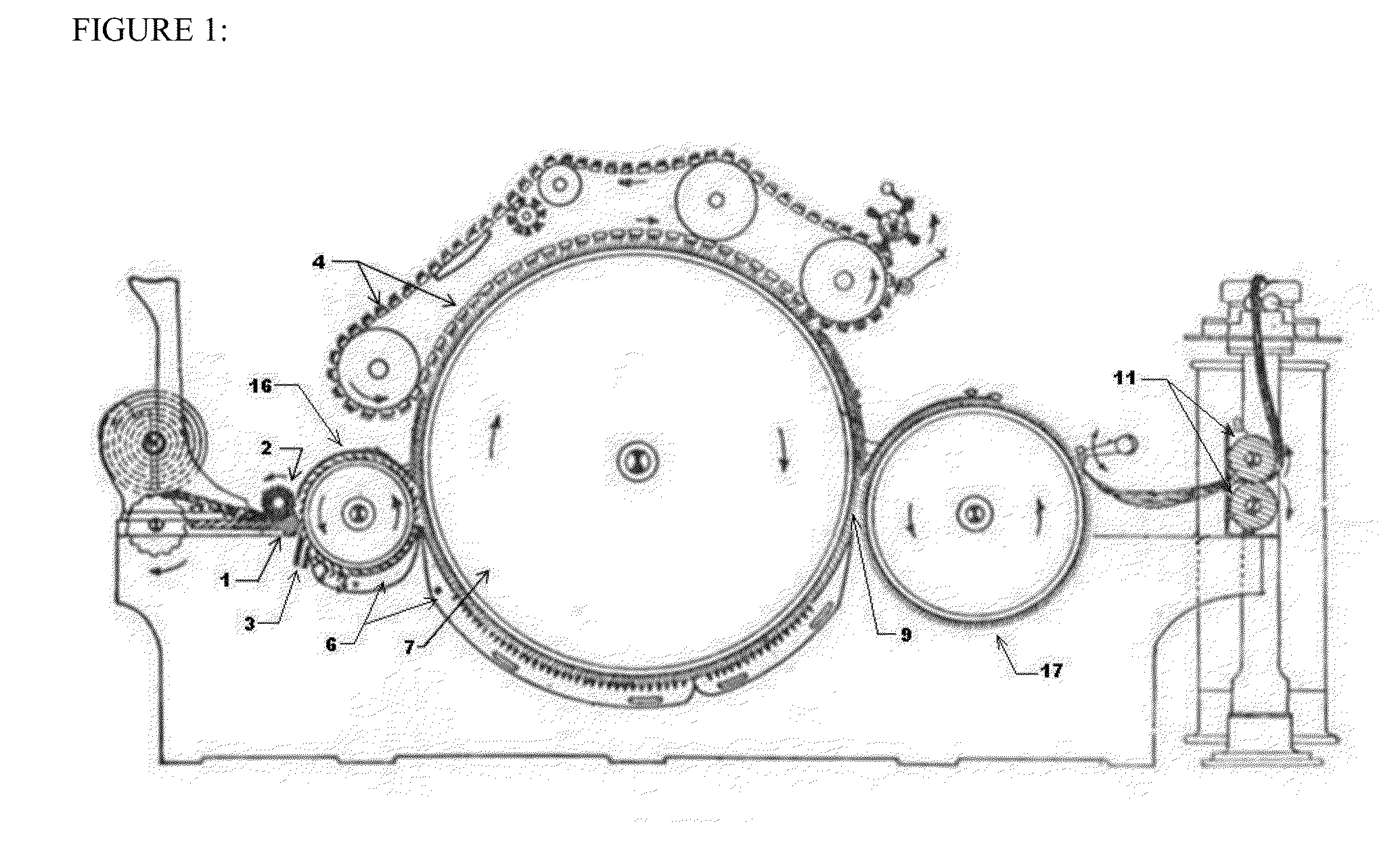
[0061]With respect to the drawings it is to be understood that only enough of the construction of the invention and the surrounding environment in which the invention is employed have been depicted therein, in order to simplify the illustrations, as needed for those skilled in the art to readily understand the underlying principles and concepts of the invention.
[0062]FIG. 1 shows, in schematic form, a prior art for the conventional carding apparatus. The tufts of fibres in the form of lap is guided by the feeding arrangement comprising stationary feed table 1 and rotatable feed roller 2 to a licker-in roller 16. The tufts of fibres that are firmly gripped between feed table 1 and feed roller 2 are stripped off by the pins of the licker-in cylinder 16 which rotates at a surface speed higher than that of the feed roller 2 resulting in opening of the tufts. The tufts are then passed on to the carding cylinder 7 from the licker-in cylinder 16. The revolving flats 4 in co-operation with ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com