Methods and Software for Screening and Diagnosing Skin Lesions and Plant Diseases
a skin lesions and plant disease technology, applied in the field of dermoscopy and software, can solve the problems of deficient image sampling, processing and texture analysis methods, algorithms and plug-in features in the early stages of the ar
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Methods
[0073]An image, such as skin lesion, can be acquired using a smartphone camera, with or without an external attachment that can provide illumination and magnification, or can be loaded from the photo library to provide the diagnosis in real time. The application can process images taken either with the iPhone® camera or taken with an external camera and uploaded to the image library on the phone. To test the application, images from a large commercial library of skin cancer images that were annotated by dermatologists (7) are uploaded to the phone. Intra-observer and inter-observer agreement could be low for certain criteria (8). All images were segmented manually to provide an evaluative level against which the automated techniques of the applications presented herein were compared. Prior to processing, if necessary, the images are converted from color to 256 level greyscale.
[0074]The iPhone 4® is a smartphone developed by Apple Inc., and features an Apple® A4 ARM® processor...
example 2
Non-Uniform Sampling for Bag-of-Features Classification
Dataset
[0078]A dataset with 645 epiluminescence microscopy (ELM) images, in which 491 lesions are benign and 154 lesions are melanoma, was used. The images are mainly collected from a commercial database (7). The total image size ranges from 712×454 to 1,024×768 pixels, while the lesion size ranges from 7,662 to 804,527 pixels.
Procedure
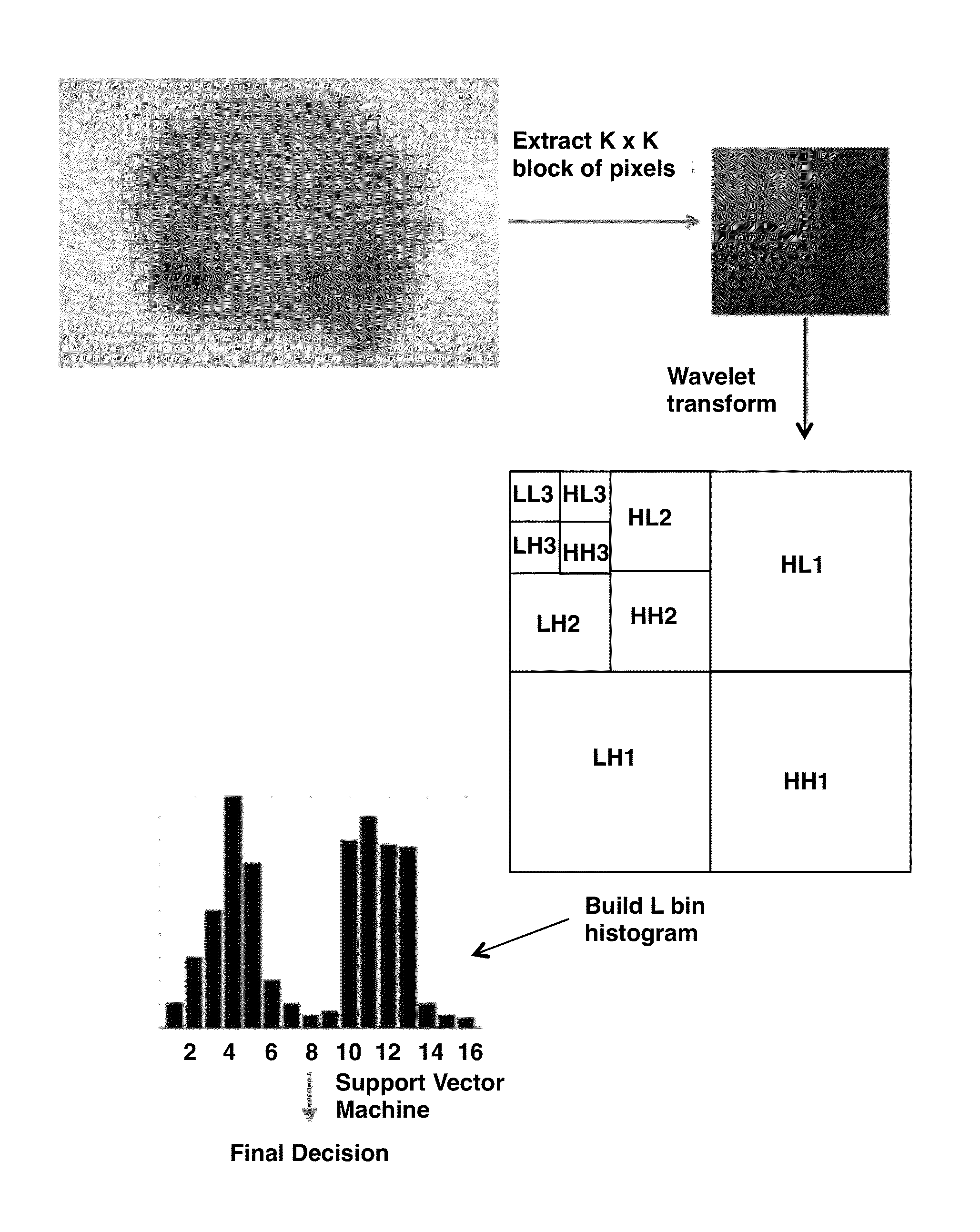
[0079]For bag-of-features-based classification, first, patches are extracted from every lesion, and then, for each patch, patch descriptors are generated using color moments and Haar wavelet coefficients, which capture the color and texture information. Then, each patch is assigned to a codeword from a pre-learned codebook, using hard assignment, as described herein. After that, a final feature vector is generated by pooling the assignments of all patches extracted from the lesion. For the classifier, support vector machines (SVMs) with a χ2 kernel are used, which currently represent state-of-art ...
example 3
Evaluation of Sampling Strategies of Dermoscopic Interest Points (DIPs) in Melanomas Dataset
[0094]A dataset with 1,505 epiluminescence microscopy (ELM) images, in which 1,098 lesions are benign and 407 lesions are melanoma were used. The image size ranges from 712×454 to 1,024×768 pixels, and lesion size ranges from 7,662 to 804,527 pixels. Manual segmentation of all lesions is used to ensure that evaluation of the various sampling strategies is not affected by possible differences in automated identification of the lesion boundary.
Procedure
[0095]The lesion classification procedure (9) consists of five main steps: image sampling, feature extraction, coding, pooling, and final classification (10). For a given image, identify DIPs inside the lesion are identified first and then a patch is extracted around each DIP. On each patch, several low level texture and color features were computed using Haar wavelets and color moments, which are important for melanoma detection. In the coding s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com