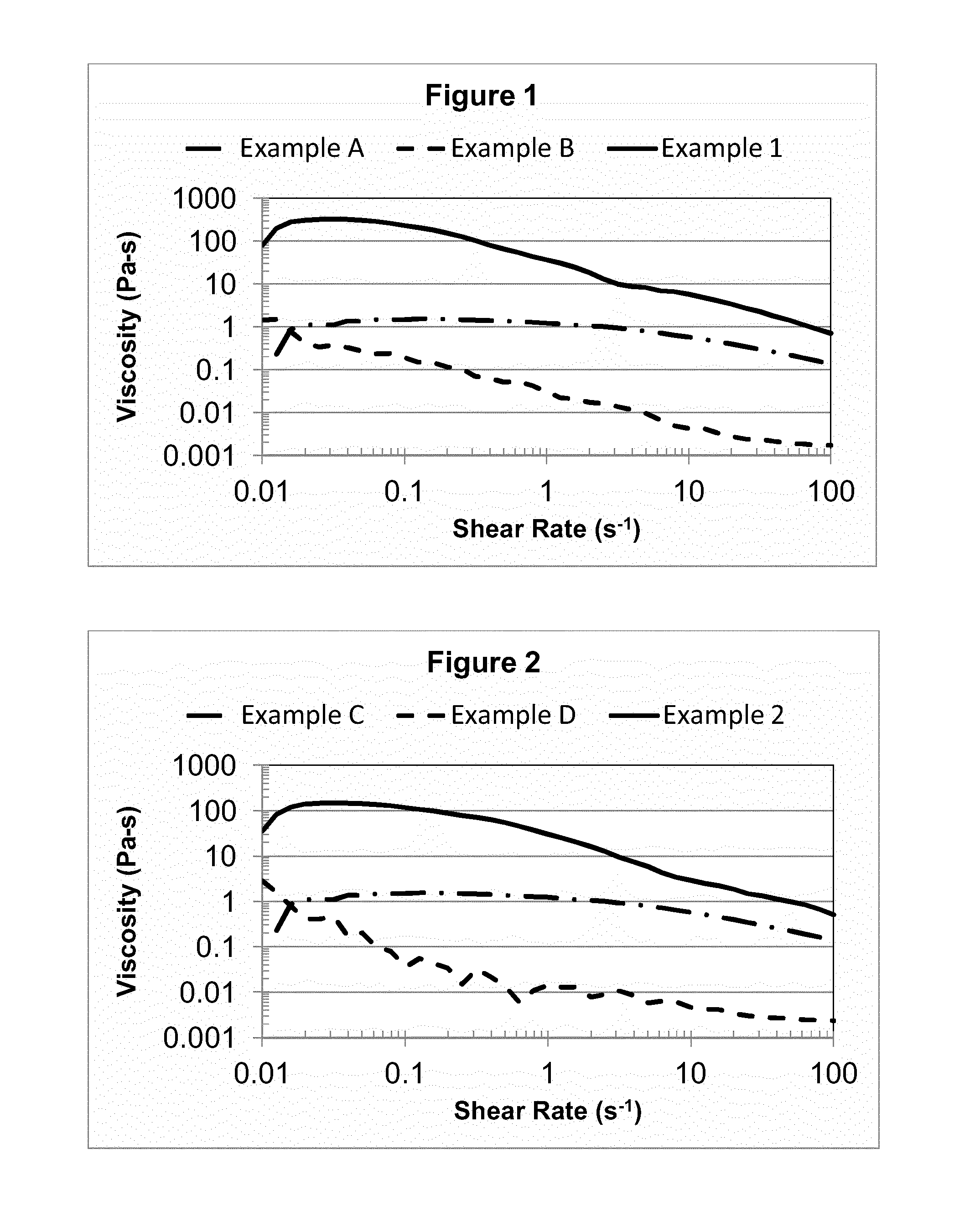
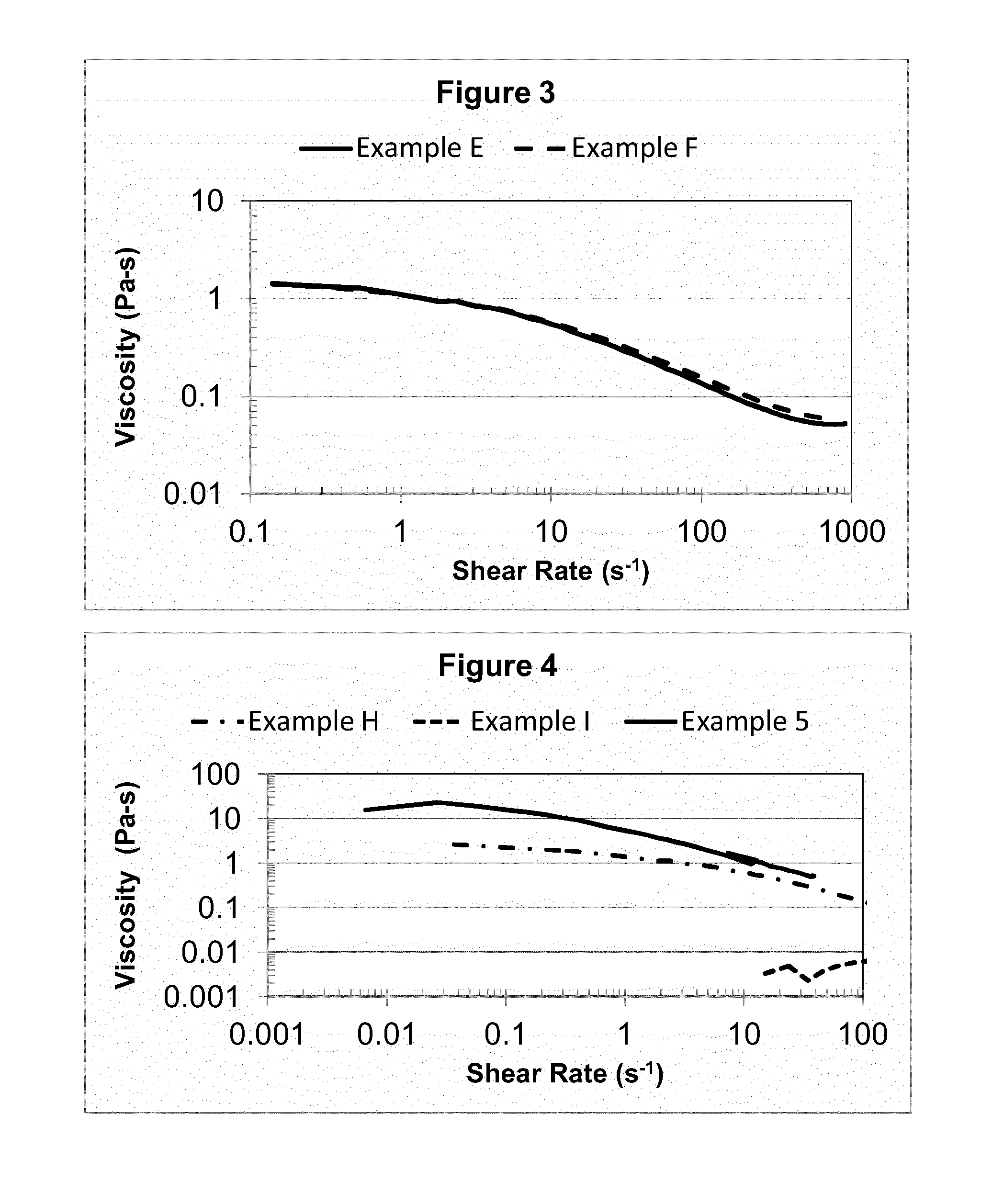
Personal care compositions including aqueous compositions of viscoelastic surfactants and hydrophobically modified polymers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 10
Stress Sweep and Elastic Modulus Measurement
Stress Sweep
[0150]Dynamic stress sweep were also evaluated using the Rheometric Scientific rheometer and same plate configuration as for steady state stress sweep. Measurement was carried out at a frequency of 1 Hz. These values allow us to investigate yield stress, storage (elastic) and loss (viscous) modulus. Figure below shows a typical example.
Elastic Modulus Results
[0151]Composition 1 containing 7.5% of surfactant, 3% Sodium Chloride, and 0% polymer was prepared and evaluated according to Example 10. Composition 2 containing 7.5% surfactant, 3% Sodium Chloride, and 0.2% R7-36-72 was prepared and evaluated according to Example 5.
[0152]The results are found in FIG. 9 showing Elastic Modulus as a function of Stress.
[0153]These data demonstrate that addition of the polymer of the present invention can dramatically increase the elastic modulus and yield stress of surfactant systems.
example 12
Foam Evaluation
[0154]Foam property was evaluated by creating a foam using a blender and the measuring the time taken for half of total liquid to drain from the foam matrix.
Procedure:
[0155]Prepare a 0.035% solution of each of the formulation by diluting with water. A total of 200 ml of the 0.035% solution were transferred to a blender (Oster Fusion, 3 speed blender). Blend the solution at medium speed for 30 sec. Transfer the resulting foam quickly into a 1000 ml cylinder and measure the volume of foam created.
example 13
Influence of Polymer on Foam Volume
[0156]Shampoo 1 containing 7.5% surfactant, 3% salt was prepared and evaluated for its foam height. Second, shampoo 2 containing 7.5% surfactant, 3% salt, and 0.25% polymer R7-36-72 was prepared and evaluated for its foam height. Finally, a Shampoo 3, a deep cleansing shampoo from a leading brand that is estimated to contain 15% total surfactants, was evaluated for its foam height. The results are summarized in Table 10 below.
TABLE 10Product NameFoam HeightStandard DeviationShampoo 1782 mL30 mL Shampoo 2845 mL2 mLShampoo 3802 mL3 mL
[0157]These data demonstrate that the polymers of the present invention enhance the foam characteristics of shampoo. Additionally, these data demonstrate that it is possible to exceed the foam characteristics of a shampoo with ˜15% surfactant with one that contains only 7.5% surfactant by addition of the polymer of the present invention.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com