Foam laminate product and process for production thereof
a technology of foam laminate and foam, which is applied in the field of foam laminate products, can solve the problems of relatively poor sound absorption, poor sound absorption properties, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing air flow resistance, avoiding scrim, and improving acoustic properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1-3
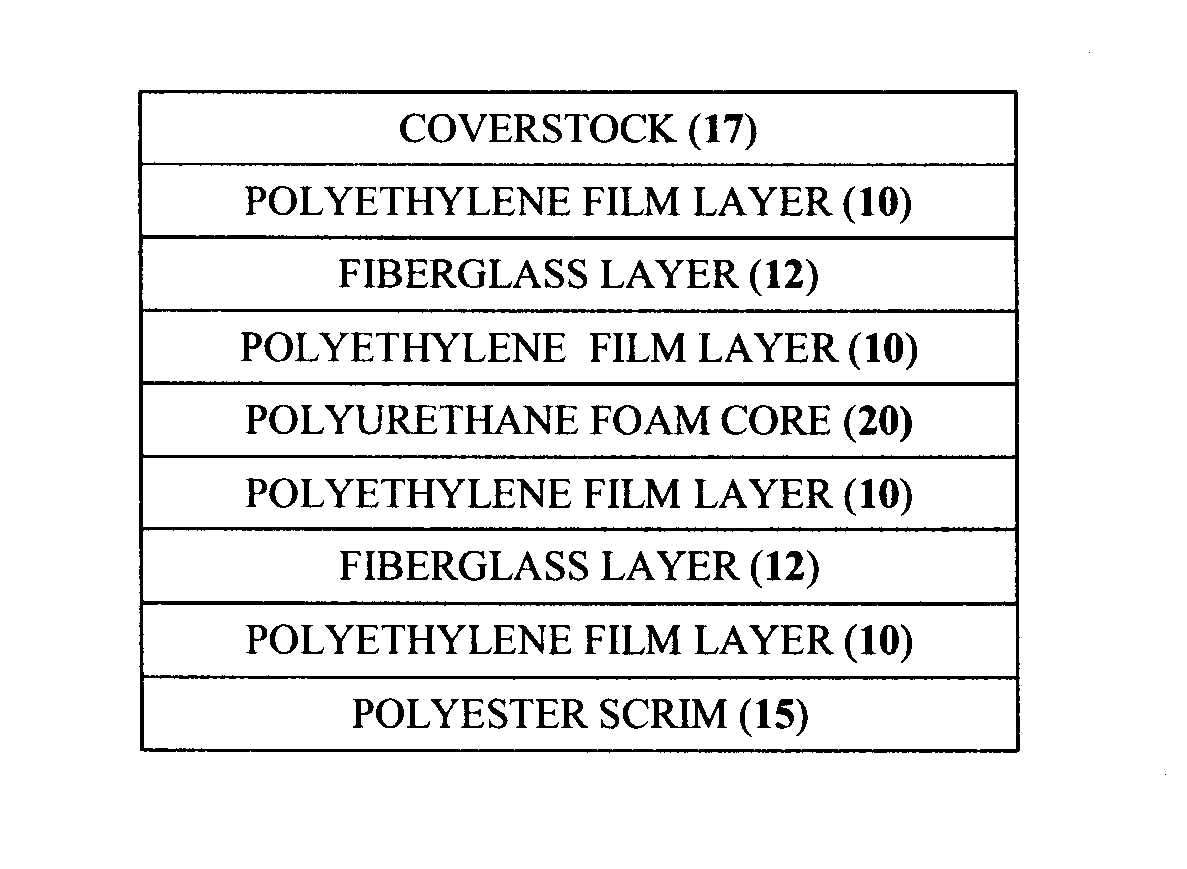
[0106]Example 1 was produced using a blank having the following lay-up:
PEFRLPEFCPEFRLPESCM
example 1
is provided for comparative purposes only and is outside the scope of the present invention.
[0107]Examples 2 and 3 were produced using blanks having the following lay-ups:
FPL#1FRLFPL#1FCFPL#1FRLFPL#1SCM
FPL#2FRLFPL#2FCFPL#2FRLFPL#2SCM
[0108]Each blank or stack was manually passed through a flat bed laminator, consisting of an adjacent heating zone and cooling zone. The process parameters for lamination were as follows:[0109]line speed: 9 m / min-12 m / min;[0110]hot Platens temp.: 175° C.-240° C.;[0111]pressure roller offset: 1.8 mm;[0112]plate height 5.2 mm; and[0113]cold platens temperature: 20° C.-45° C.
The resulting samples were conditioned for 24 hours.
[0114]Thereafter the samples were heated and shaped in a laminator such as the one described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,928,597 [Van Ert], U.S. Pat. No. 6,146,578 [Van Ert el al.] and U.S. Pat. No. 6,338,618 [Van Ert et al.] to produce the final form of the samples. The process conditions for this part of the process were as follows:[0115]inf...
examples 4-5
[0125]Typically, the foamed isocyanate-based polymer is produced from a reaction mixture which comprises an isocyanate and an active hydrogen-containing compound.
[0126]Examples 4 and 5 were produced using the methodology used in Examples 1-3 and blanks having the following lay-ups:
PEFRLPEPEFRLPEFCPEFRLPESCM
FPL#1FRLFPL#1FPL#1FRLFPL#1FCFPL#1FRLFPL#2SCM
[0127]Example 4 is provided for comparative purposes only and is outside the scope of the present invention.
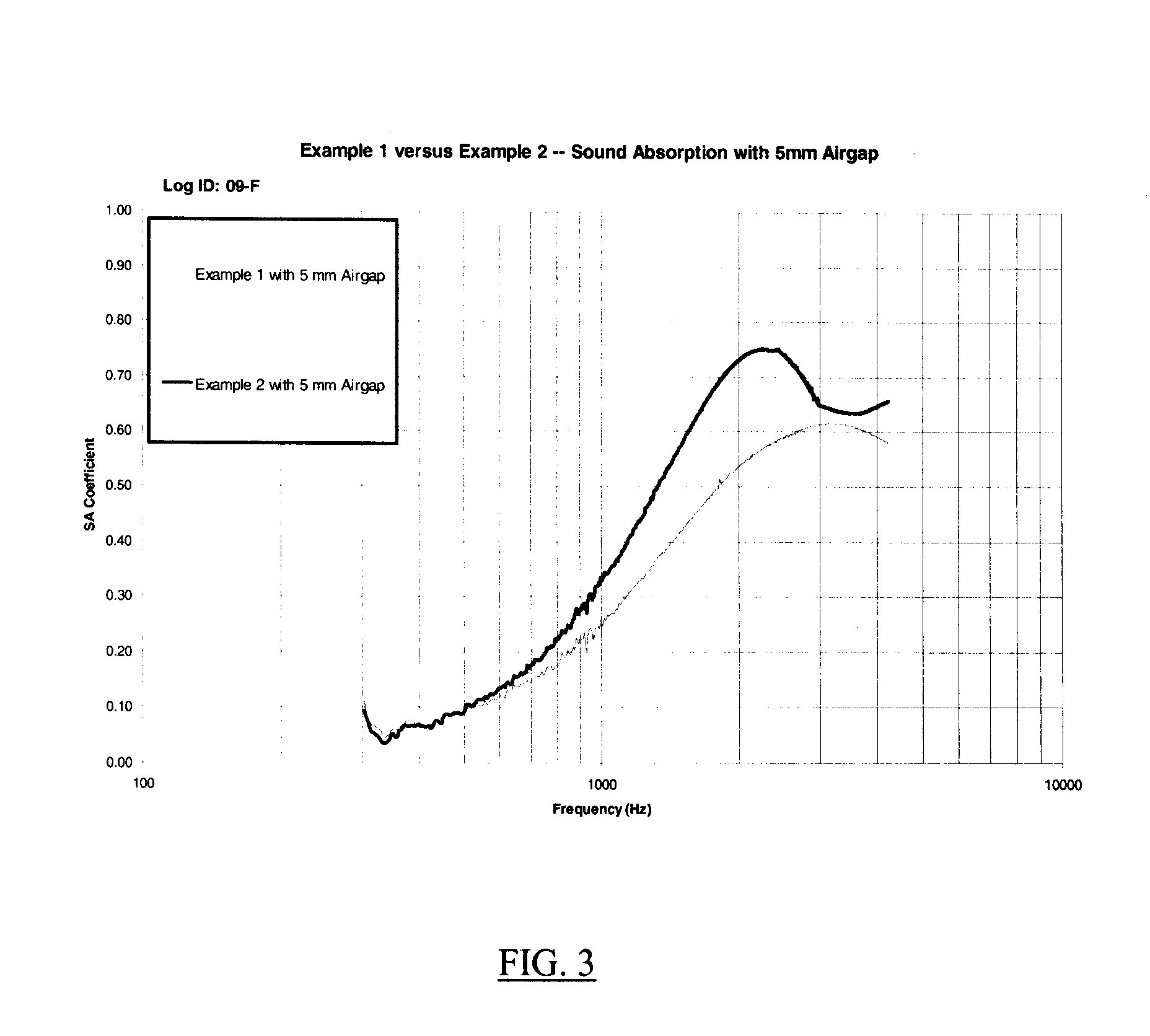
[0128]The result samples were subjected to the same physical testing reporting in connection with Examples 1-3 and the results are reported in Table 2 (weight, maximum load, strength and air flow resistance) and FIG. 4 (sound absorption). The same trends reported in connected with the results for Examples 1-3 are seen in the results for Examples 4-5.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com