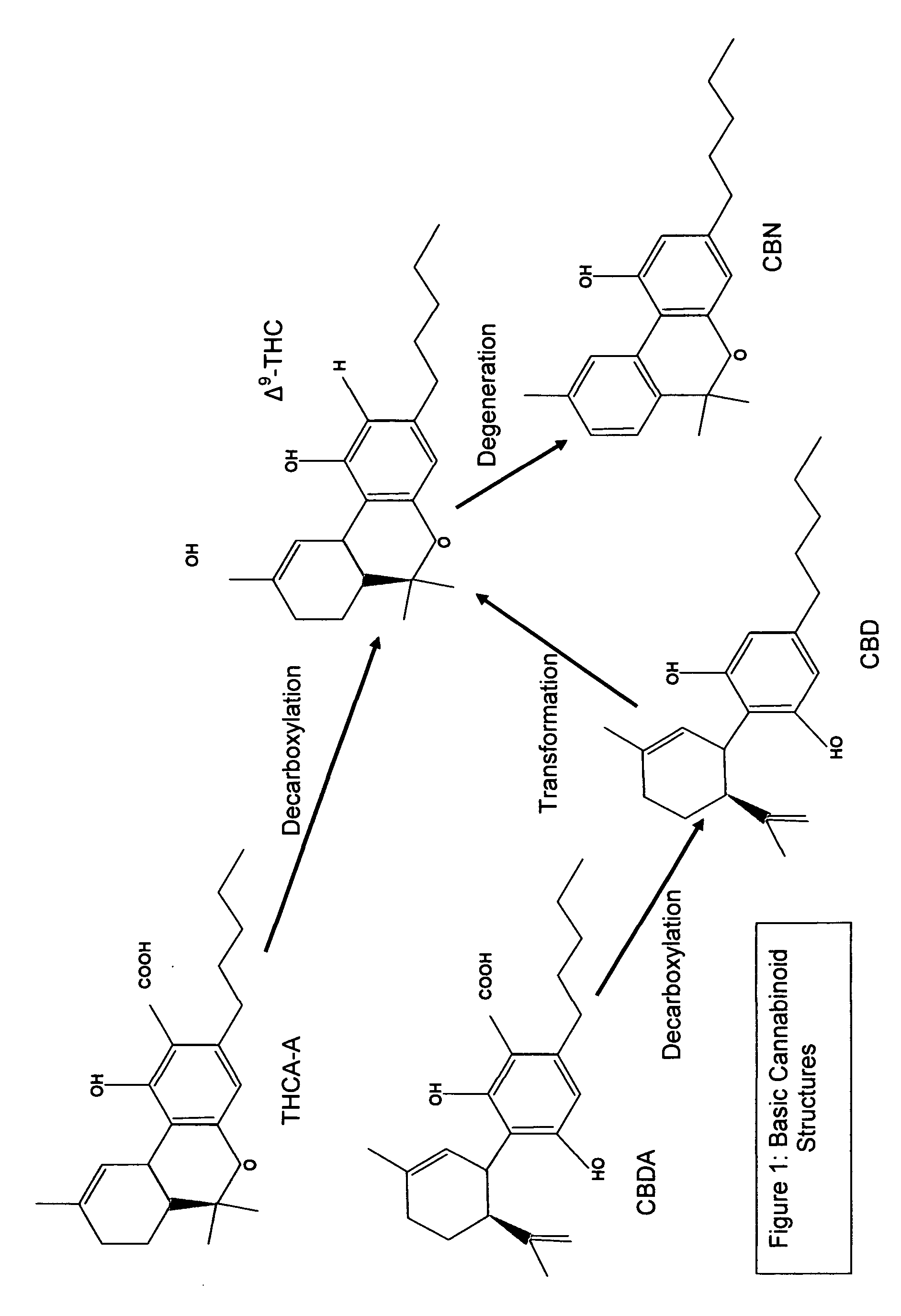
Medicinal cannabis added in food
a technology of cannabis and food, applied in the field of medical cannabis added in food, can solve the problem that the substance within cannabis will be lost to evaporation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
of Mixing Extracts:
[0081]Extract 1: Volume 2 fluid oz comprised of 40% flavonoids & waxy materials: 60% total cannabinoids (95% of total cannabinoids are Δ9-THC, and 5% of total cannabinoids are CBN)
[0082]Extract 2: Volume 4 fluid oz, comprised of 40% flavonoids & waxy materials: 60% total cannabinoids (58% of total cannabinoids are Δ9-THC, and 42% of total cannabinoids are CBN)
[0083]Mixed cannabinoid content: Volume 6 fluid oz; (95*0.33333+58*0.66666) Δ9-THC; (5*0.33333+42*0.66666) CBN=(31.67+38.67) Δ9-THC; (1.66+28) CBN=70.34% Δ9-THC; 29.66% CBN.
[0084]Please note that the extracts do not consist of 100% cannabinoids, in the example above only 60% of the extracts consist of cannabinoids and 40% of the extracts above consist of flavonoids and waxy materials. Please also note that the calculations above have been normalized to a total cannabinoid content of 100%.[0085]Therefore the total content of the mixed extract in Example 2 are 40% flavonoids and waxy materials; and 60% total ca...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com