Thin film coating pinning arrangement
a thin film coating and arrangement technology, applied in the field of pining regions, can solve the problems of the most expensive component of the photovoltaic solar collection system, the photovoltaic cell, and achieve the effect of significantly reducing the likelihood of cracking or delamination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
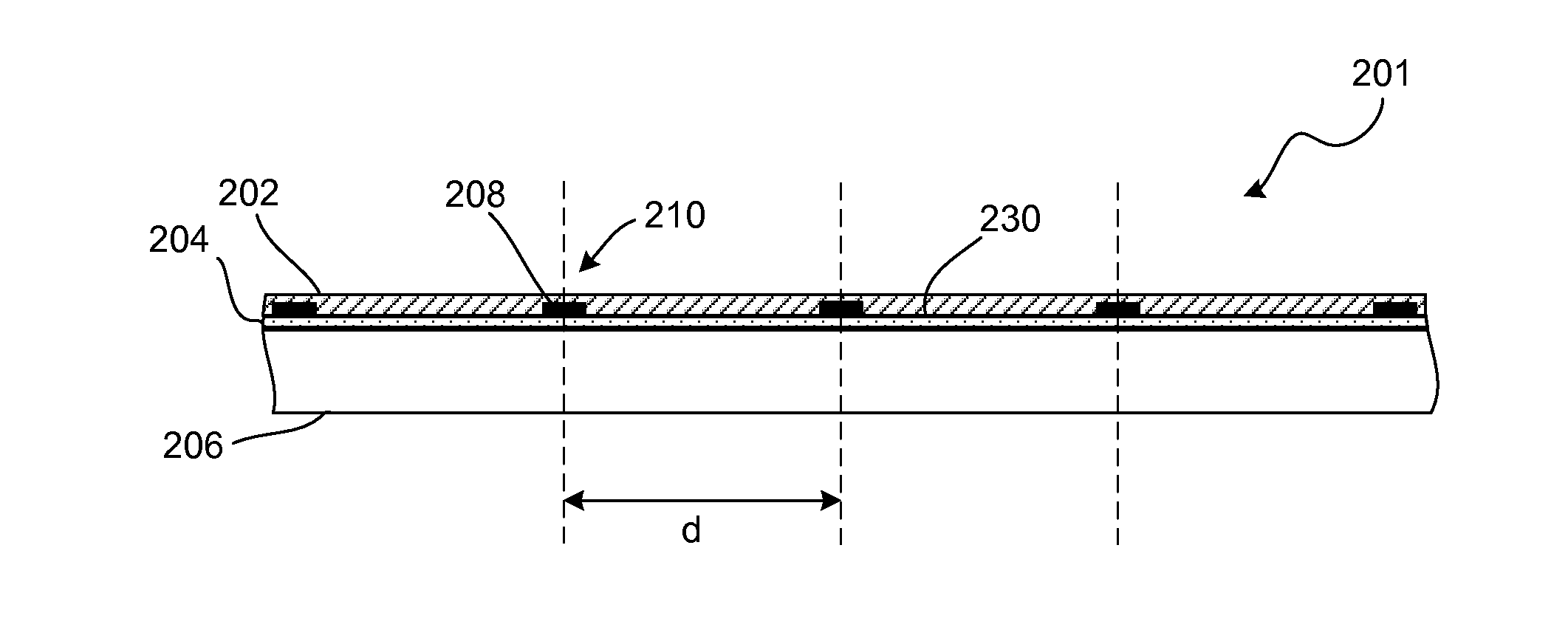
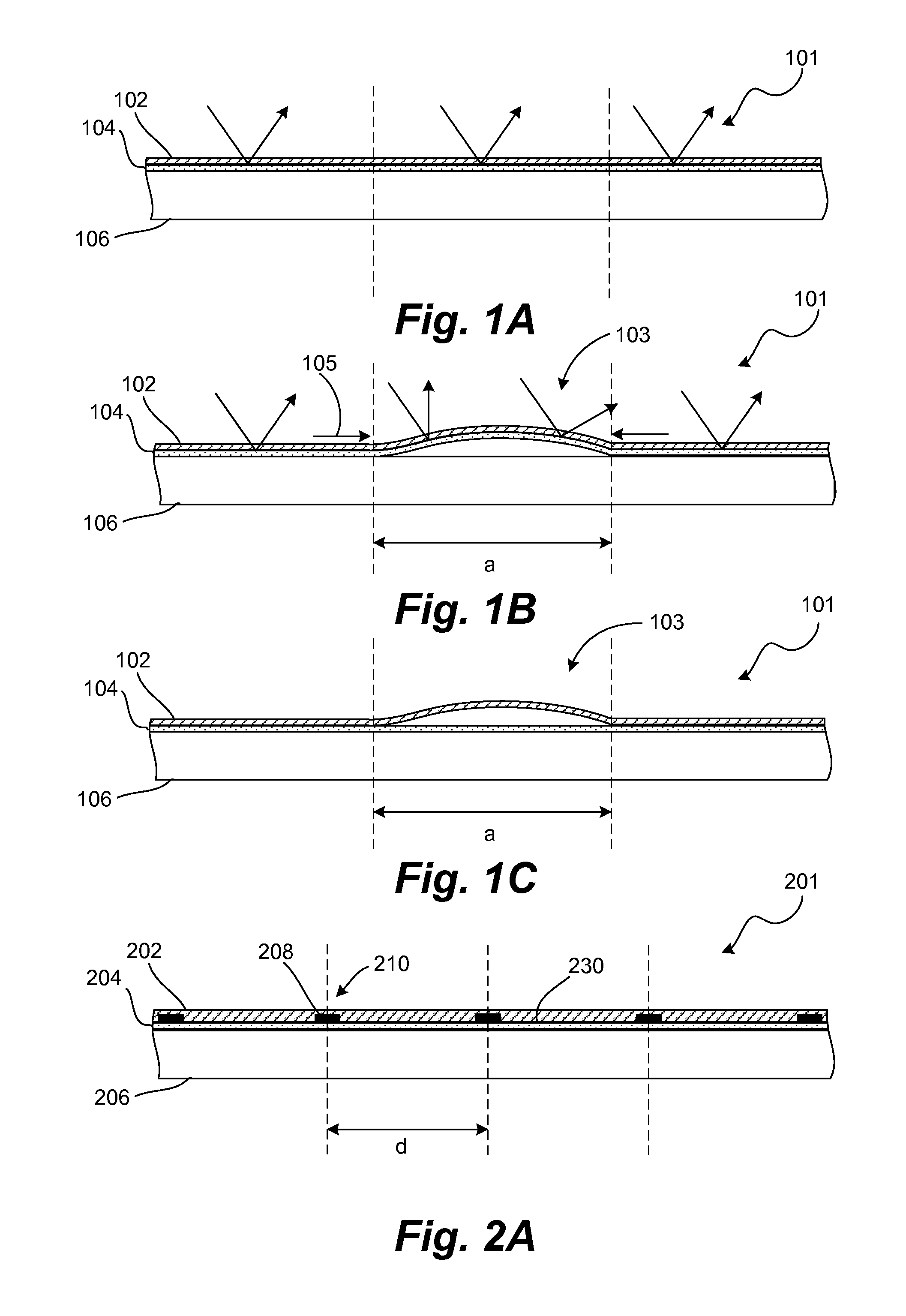
[0024]In some concentrating photovoltaic systems, a reflector is used to reflect incident light towards a solar receiver. Ideally, the reflector has a high quality optical surface. If the reflector surface is degraded, the incident light may be absorbed or scattered and never reach the solar receiver.
[0025]In operation, the reflector is exposed to the ambient environment and various environmental stresses, such as temperature fluctuation, ultraviolet light exposure, and moisture. These stresses can cause portions of the reflector to blister or crack. As a result, the light may be scattered or absorbed.
[0026]An example of this problem is diagrammatically illustrated in FIGS. 1A-1C. For purposes of comparison, FIG. 1A illustrates an example of an undamaged reflector 101. The reflector 101 includes a substrate 106, a reflective coating 104 and a protective layer 102. The protective layer 102, which is typically made of an optically transparent material, is formed over the other layers ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com