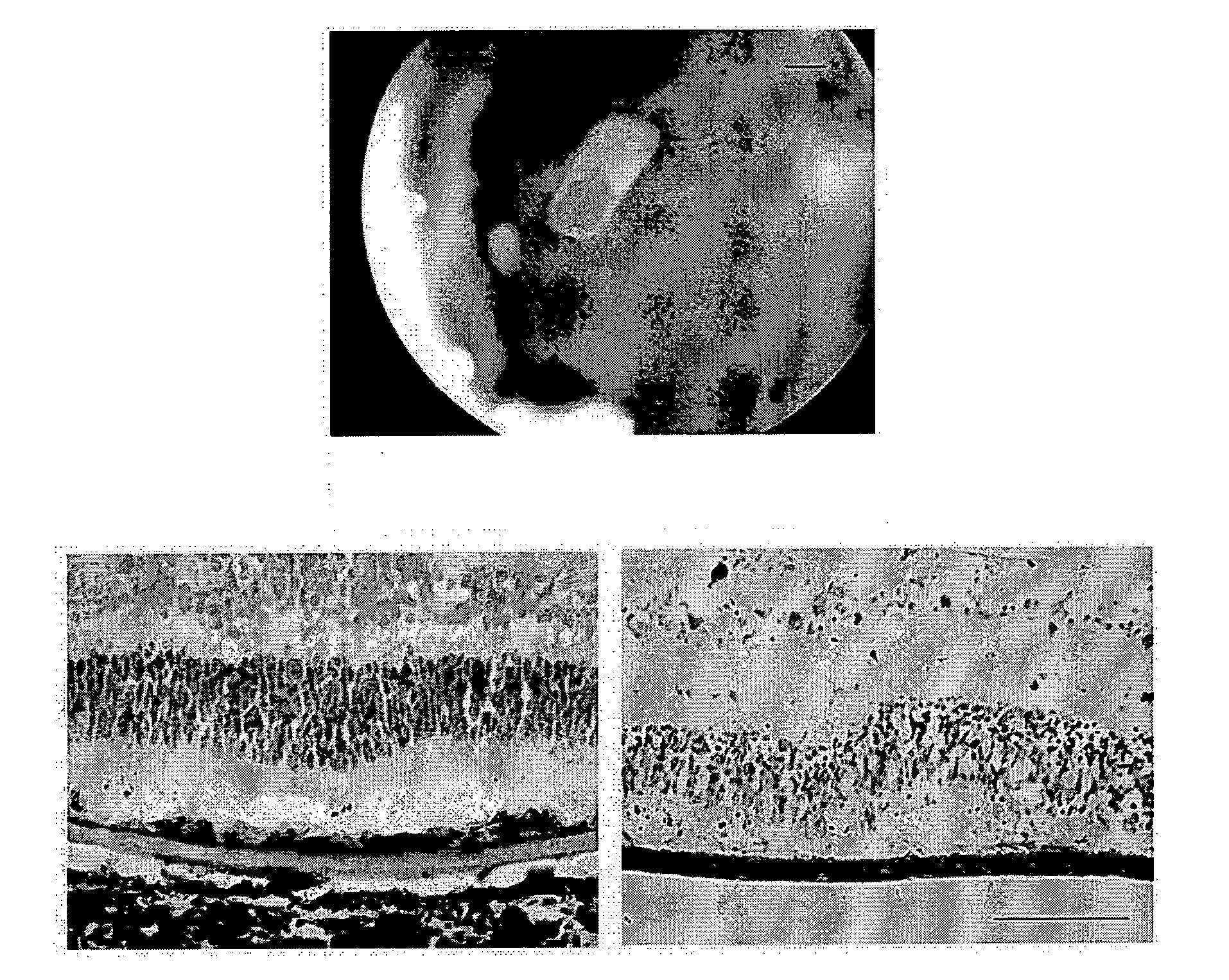
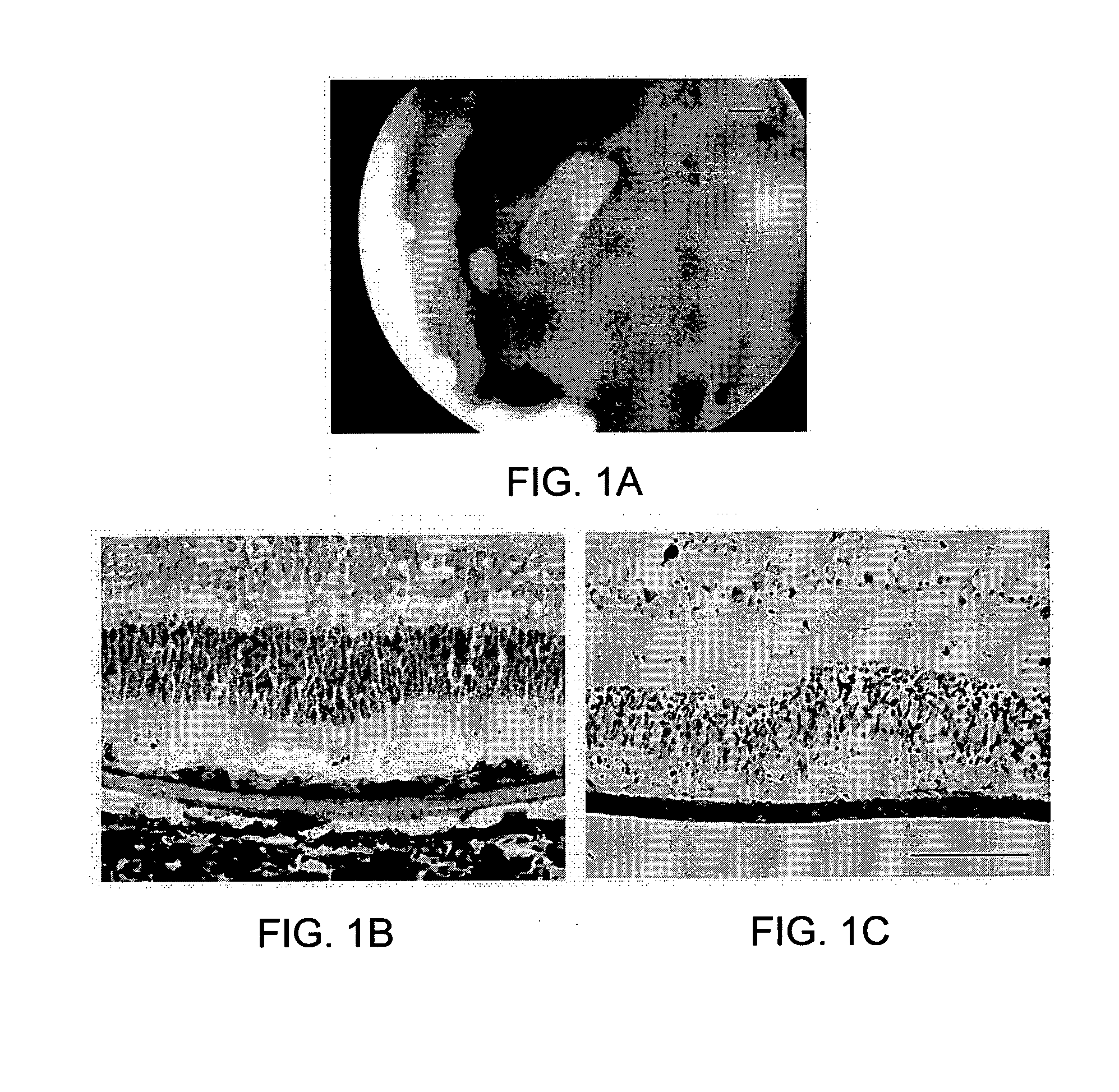
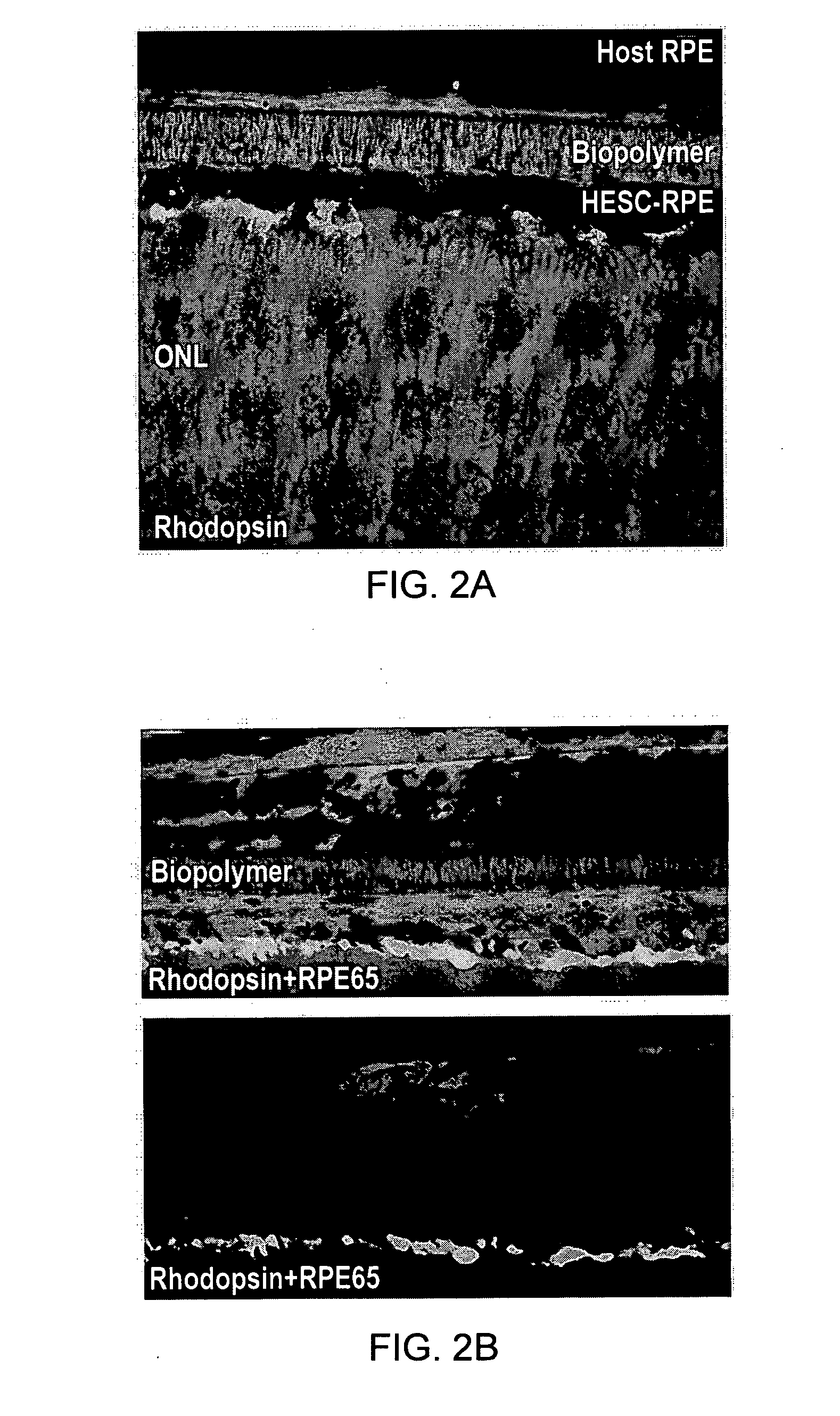
Membrane
a technology of membranes and membranes, applied in the field of membranes, can solve the problems of loss of vision in the central area of vision, more serious vision loss, inability to see fine details, read or recognise faces, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the likelihood of cells de-differentiating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of the Membrane
[0043]Thin polyester film is exposed to collimated, charged particles from a nuclear reactor. As these particles pass through the polyester material, they leave sensitized tracks. Next, the polymer tracks are dissolved with an etching solution to form cylindrical pores. Varying the temperature and strength of the etching solution, and the exposure time to it, produces precisely controlled pore sizes.
[0044]The resulting membrane is a thin, translucent, microporous polyester film with a smooth, flat surface containing pores of controlled diameter and number.
Production of Human Retinal Pigmented Epithelial Cells (hRPE) from Human Embryonic Stem Cells (hESC)
Cell Culture
[0045]The hESC are maintained in flasks coated with 0.1% Gelatine and seeded with mitomycin C inactivated mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) feeders (with seeding density of 1.2×104 / cm2) or equivalent human fibroblast feeders. Cells are maintained in basic HESC-medium which consists of the followi...
example 2
Seeding Membranes
[0057]RPE cells were seeded onto membranes at various densities to find the optimal density of seeding for highly differentiated cells. The cells were observed for the characteristics of RPE cells, such as pigmentation and cobblestone morphology. The results are shown in the following table:
Microscopic ExaminationNo. ofPigmentedRegularSeedingPigmentationcells per 40xMorphologyDensityAs seen withmicroscopic(Perfect Hexagon(cell / cm2)naked eyefieldis best = zero)*70,000Nil16Cells too sparse tocalculate212,000Light>4000.023270,000Dark (good)>4000.024391,000Darkest (best)>5000.0175
example 3
Growing Cells on Different Membranes
[0058]A number of different membranes were tested for ability to support cell growth. The results are given in the following table:
TeflonPoly-TC PolystyrenePLGA(PTFE)urethanesDacron PolyesterProsExcellent wellGoodStrong,Strong,Strong, flexible,characterisedgrowthflexible,flexibe,sufficiently porousgrowth surfacesurfaceporousporousexcellent growthsurface. Pore sizesmall enough toexclude cellmigration of bothdonor and hostimmune cells.Excellent surgicalhandling propertiesdespite being verythin (see thickness)ThicknessThin film700-90090-150 μm60-200 μm5-12 μmunavailableμm†Pore sizeN / A17-50 μmApprox.20-200 μm0.4 μm0.3-0.5 μmPoreN / AHighHighLow1 × 10{circumflex over ( )}8 per cm2densityHydro-NoNoStrongNoNophobicityCellHighHighVery LowLow-HighaffinityMedium
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com