Pet/mri device, pet device, and image reconstruction system
a technology of image reconstruction and pet devices, applied in the field of pet/mri devices and pet devices, can solve the problems of longer pet measurement time and insufficient sensitivity of pet devices, and achieve the effect of short time and higher sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
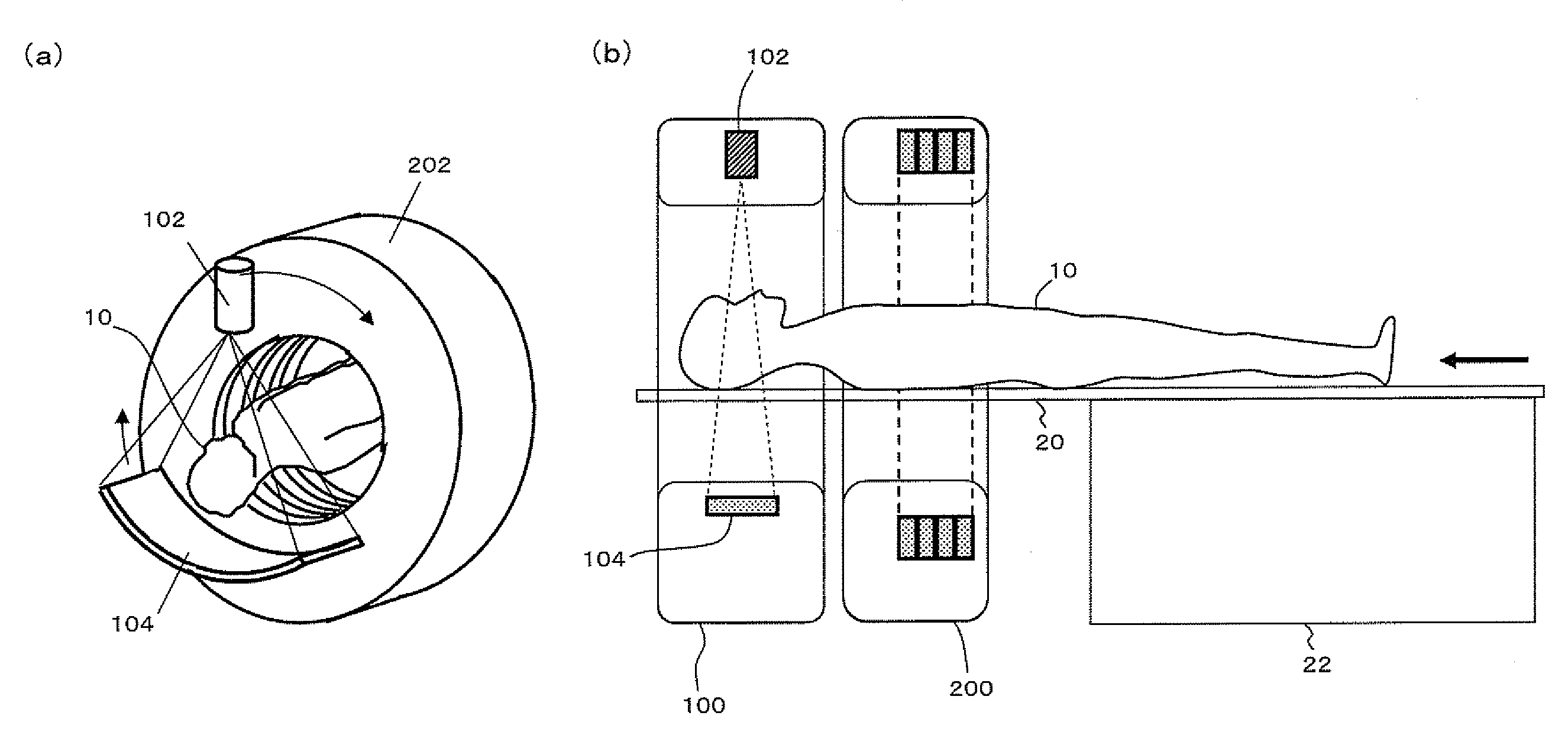
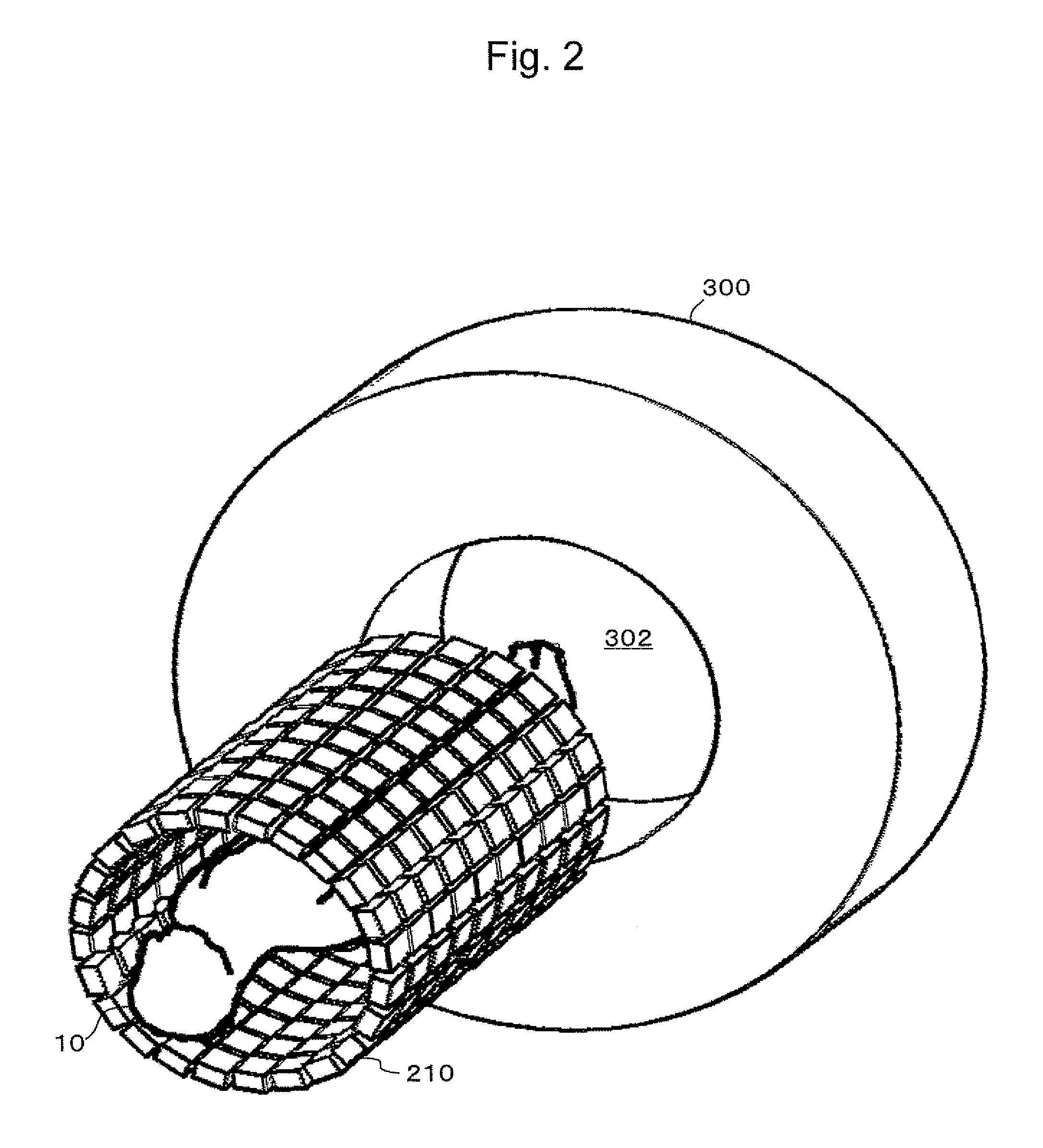
[0092]As shown in FIG. 2 (a perspective view for overview), FIG. 3A (a front view), and FIG. 3B (a sectional view seen from a side), the present invention includes an MRI device 300 and a PET detector 210. The MRI device 300 has a measurement port (here, a patient port) 302. The PET detector 210 has an outer diameter smaller than the inner diameter of the patient port 302, and can move through the patient port 302 with a measurement object (here, a patient) 10. The PET detector 210 has an effective measurement field of view (referred to as a PET field of view) P wider than the effective measurement field of view (referred to as MRI field of view) M of the MRI device 300, thereby allowing MRI measurement during PET measurement. In the diagrams, 24 denotes a cushion for protecting the patient 10, and 304 denotes an RF coil for the MRI device 300. The RF coil 304 may be integrated with the cushion 24 at the back side of the patient.
[0093]The MRI field of view M is determined by the are...
sixth embodiment
[0120]As in a sixth embodiment shown in FIG. 13 (a perspective view) and FIG. 14 (a sectional view seen from a side), the technology of the open PET device may be used to form an open area in the head PET device 212 in the vicinity of the field of view so as to alleviate the sense of confinement on the head.
seventh embodiment
[0121]As in a seventh embodiment shown in FIG. 15, the body PET detector 214 may be made of noncircular (in the diagram, elliptical) rings so that the PET detector comes closer to the patient's body.
[0122]FIGS. 16A to 16C show the configuration of essential parts where the detector rings can be changed in size according to the body type of the patient 10. FIG. 16A shows an example where normal-sized detector rings 214a are used.
[0123]FIG. 16B shows an example where large-diametered detector rings 214b are used for the abdomen. FIG. 16C shows an example where the large-diametered detector rings 214b are used not only for the abdomen but for the entire body.
[0124]FIGS. 17A to 17C show the cross sections of FIGS. 16A to 16C. FIG. 17A shows a PET detector layout for slender type, FIG. 17B shows a PET detector layout for stout type, and FIG. 17C shows a PET detector layout for the head. In the PET detector layout for stout type of FIG. 17B, the arched half portion of the detector on the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com