Sequence hopping method, wireless communication terminal apparatus and wireless communication base station apparatus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0040]With the present embodiment, different amounts of hopping are given to a plurality of ZC sequences of varying sequence lengths.
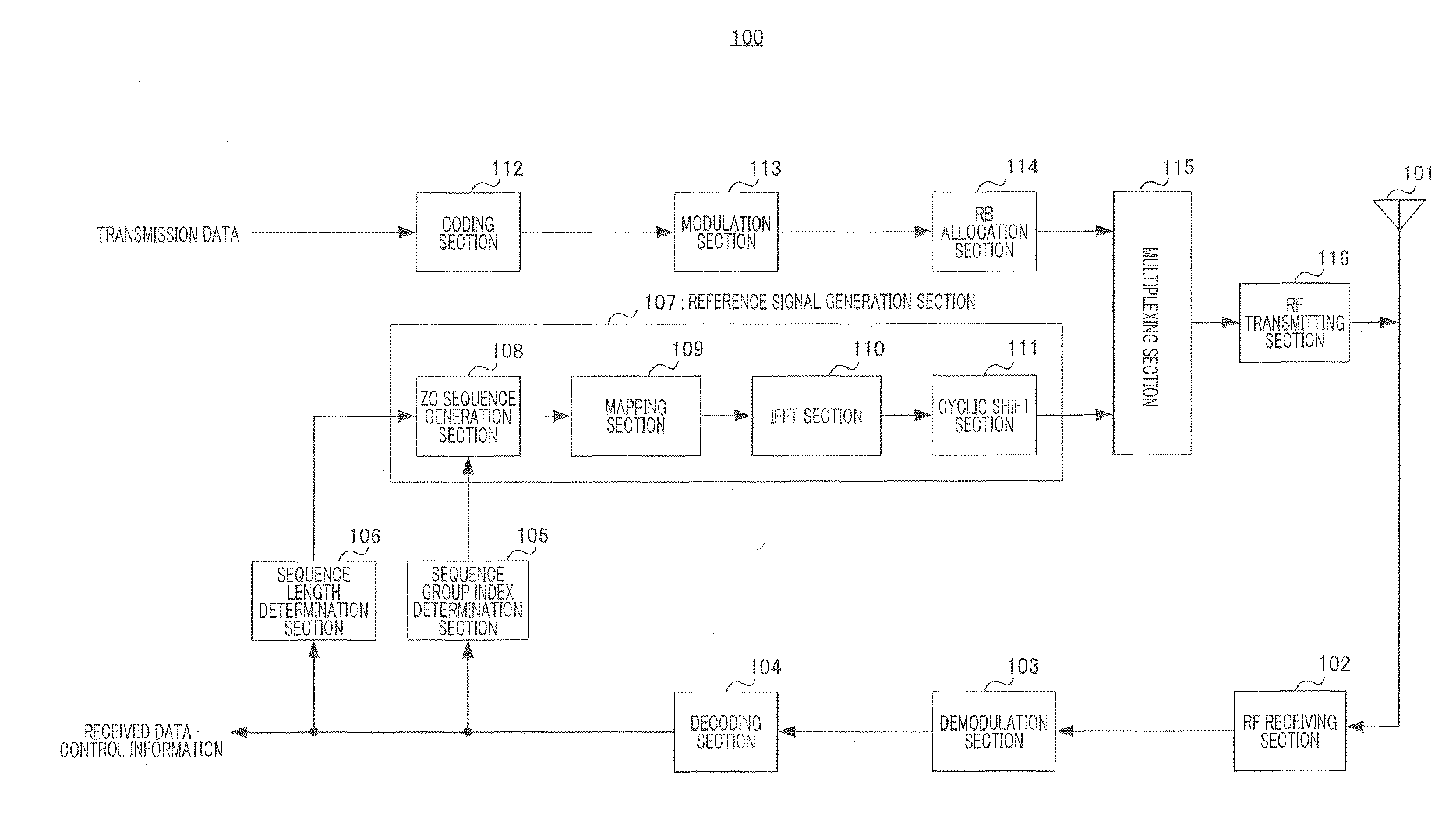
[0041]The configuration of terminal 100 according to the present embodiment will be described using FIG. 9.
[0042]RF receiving section 102 of terminal 100 shown in FIG. 9 performs receiving processing including down-conversion and A / D conversion on a signal received via antenna 101, and outputs the signal subjected to receiving processing to demodulation section 103.
[0043]Demodulation section 103 performs equalization processing and demodulation processing on the signal received as input from RF receiving section 102, and outputs the signal after these processing to decoding section 104.
[0044]Decoding section 104 decodes the signal received as input from demodulation section 103, and extracts received data and control information. Then, decoding section 104 outputs the sequence group index among the extracted control information to sequence index determ...
embodiment 2
[0100]With the present embodiment, in addition, different offsets between ZC sequences of varying sequence lengths are given to ZC sequences to use for reference signals in slot #1 (i.e. reference signals before hopping) in one subframe.
[0101]Now, an example of setting offsets and the amount of hopping of sequence indexes in sequence index determination section 105 of terminal 100 (FIG. 9) and sequence index determination section 164 of base station 150 (FIG. 10) will be explained.
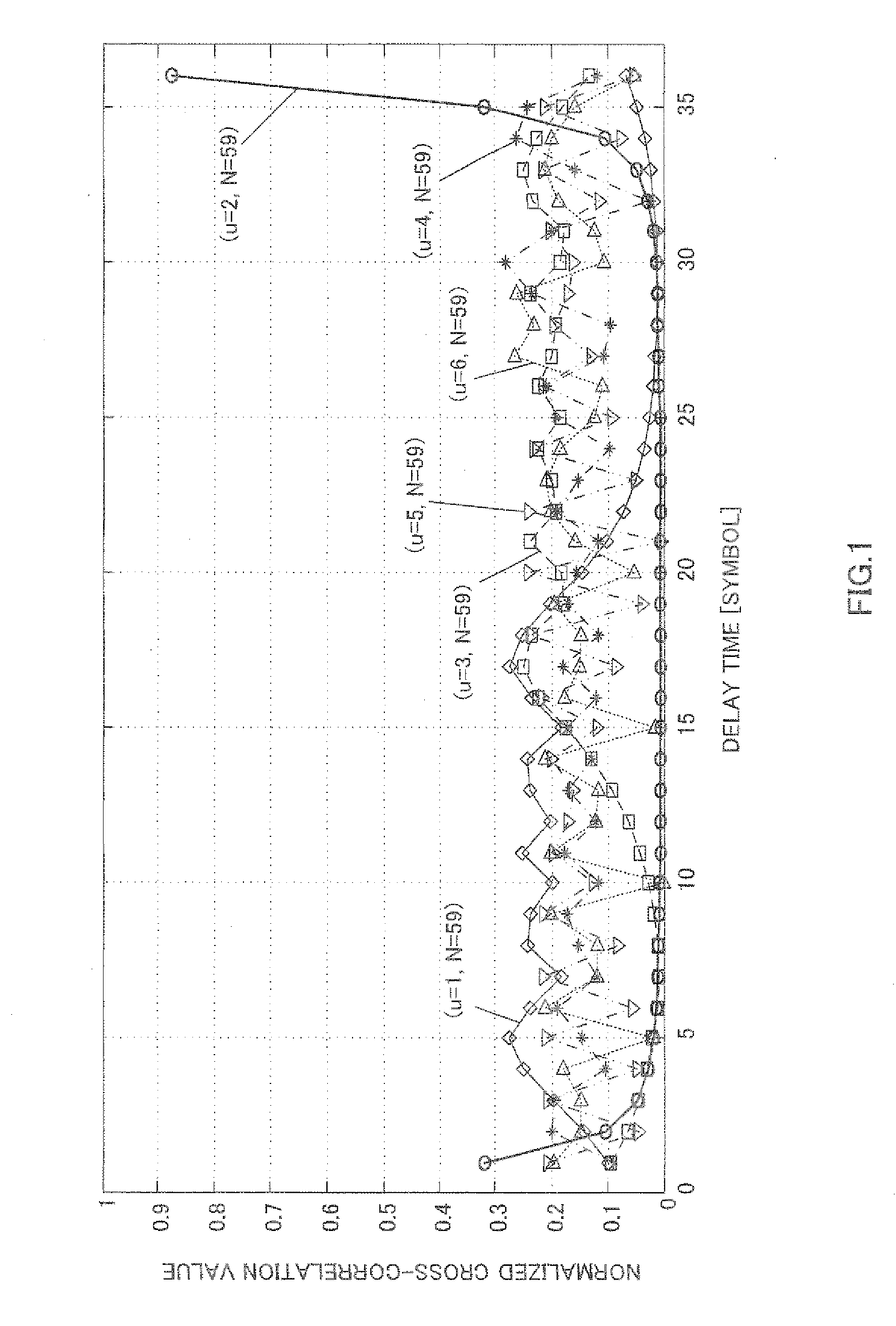
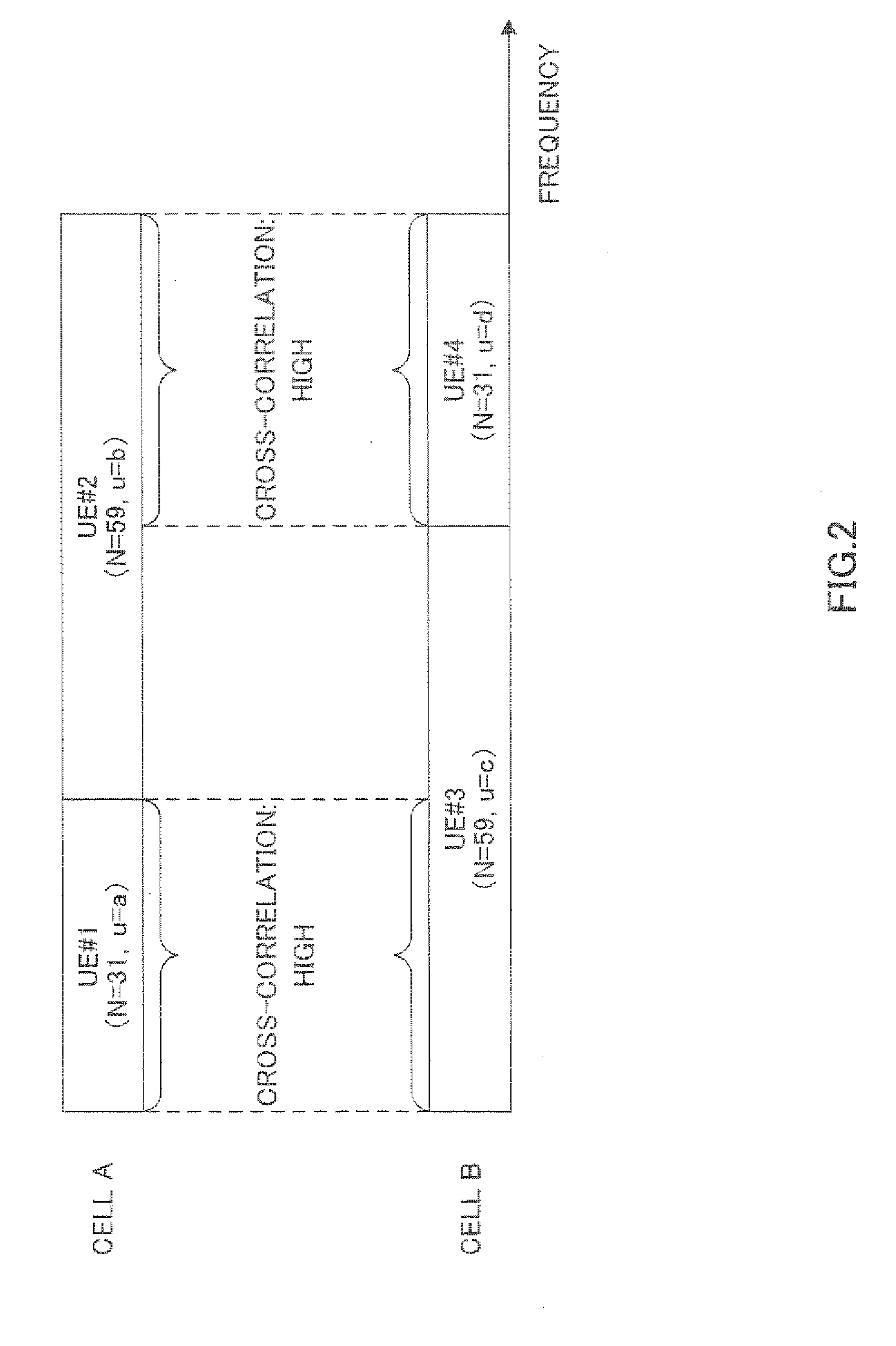
[0102]Here, the same transmission bandwidths (i.e. the same numbers of RBs), sequence lengths N and sequence groups are used as transmission bandwidths (i.e. the numbers of RBs), sequence lengths N and sequence groups shown in FIG. 11 of Embodiment 1. Further, here, when the difference in u / N between ZC sequences is equal to or more than 0.05 (the cross-correlation characteristics shown in FIG. 8 are equal to or less than 0.7), it is assumed that the cross-correlation between the ZC sequences is low.
[0103]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com