Substrate bonded MEMS sensor
a technology of mems sensor and glass substrate, applied in the field of mems sensor, can solve the problems of difficult to define the opposing distance of glass substrate with high precision, difficult to provide an appropriate movable clearance (margin) between the movable electrode portion and the glass substrate, and difficult to form a sealing layer with a fine pattern
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
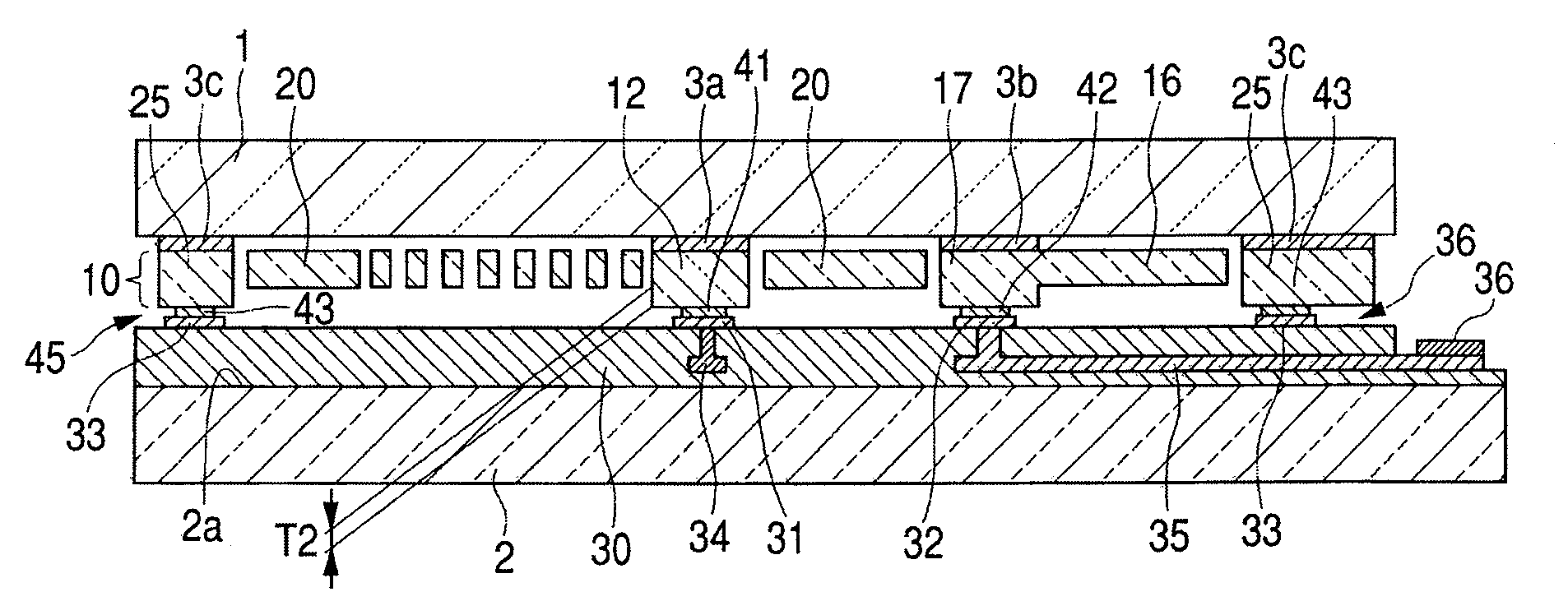
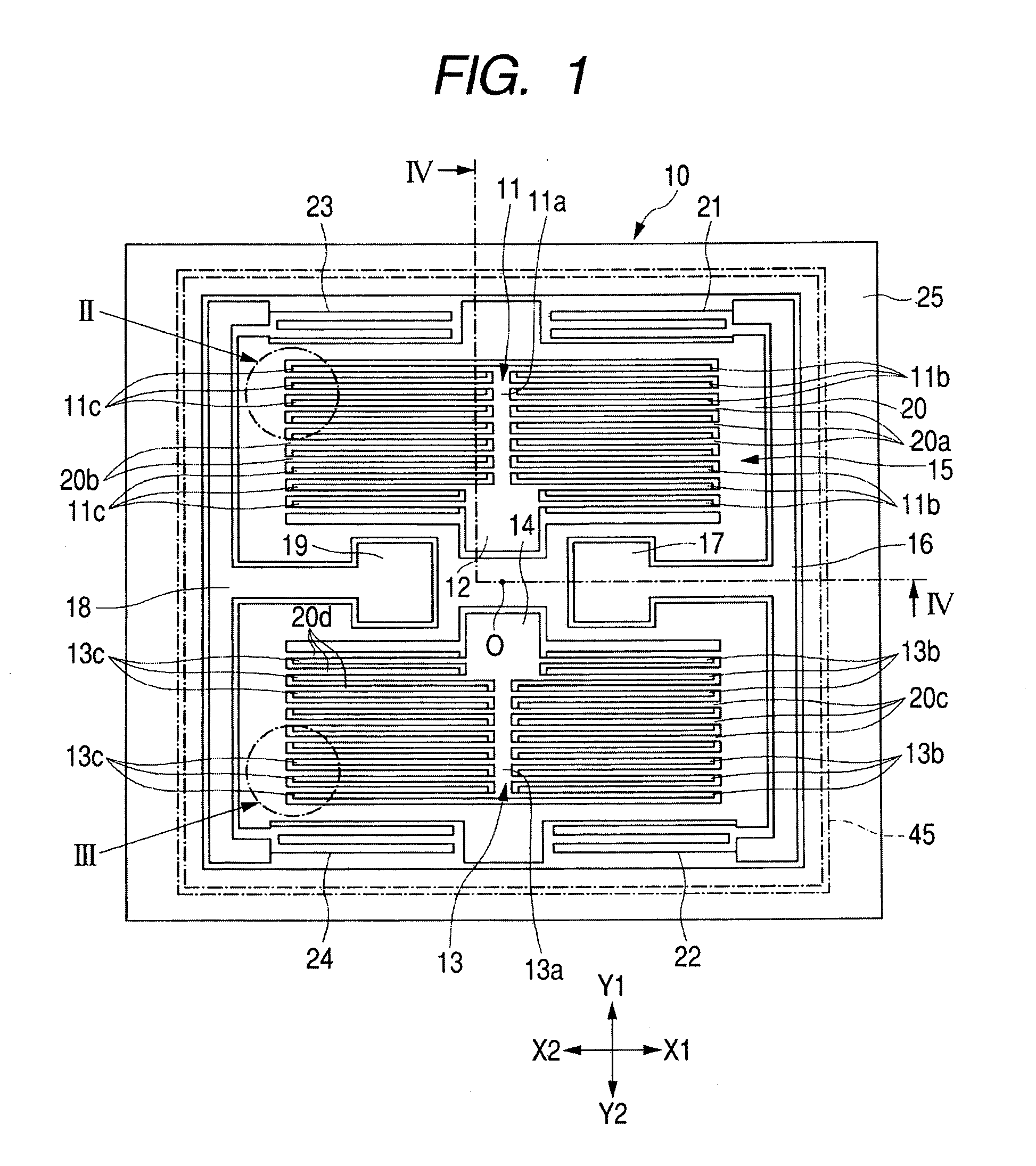
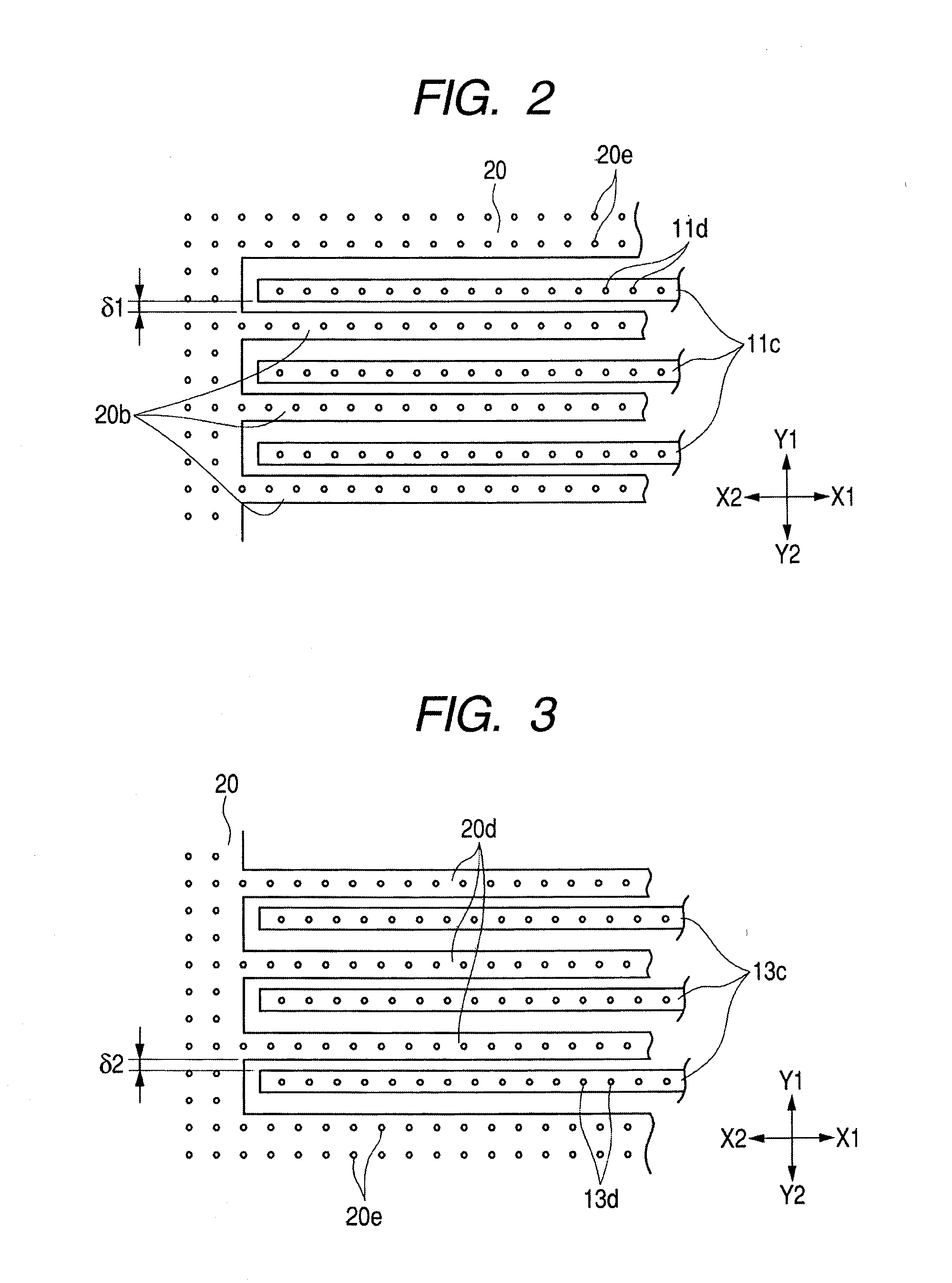
[0032]FIG. 1 is a top plan view of a MEMS sensor according to the first embodiment of the invention, illustrating movable electrode portion, a fixed electrode portion, and a frame layer. In FIG. 1, the illustrations of a first substrate and a second substrate are omitted. FIG. 2 is an enlarged view of the II portion in FIG. 1, and FIG. 3 is an enlarged view of the III portion in FIG. 1. FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view illustrating the overall structure of the MEMS sensor, taken along the IV-IV lines in FIG. 1. FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view for describing the method for fabricating the MEMS sensor. In FIGS. 4 and 5, the arrangements of respective layers are reversed upside down.
[0033]As illustrated in FIG. 4, the MEMS sensor has such a configuration that a functional layer 10 is sandwiched between a first substrate 1 and a second substrate 2. The respective portions of the functional layer 10 and the first substrate 1 are bonded together via a first insulating layer 3a, 3b, or 3c...
second embodiment
[0075]FIGS. 6A and 6B are cross-sectional views of a MEMS sensor according to the second embodiment of the invention, illustrating the VI portion in FIG. 4 in the enlarged views.
[0076]In the embodiment illustrated in FIG. 6A, on the surface of the conductive supporting portion 17 of the movable electrode portion 15, a groove 51 is formed so as to surround the bonding portion in which the metallic connection layer 42 and the connection electrode portion 32 are bonded together by eutectic bonding or diffusion bonding. The groove 51 may be continuously formed so as to surround the entire circumference of the bonding portion or may be discontinuously formed at intervals so as to surround the bonding portion.
[0077]In the embodiment illustrated in FIG. 6B, on the surface of the conductive supporting portion 17 of the movable electrode portion 15, a groove 52 is formed so as to surround the bonding portion of the metallic connection layer 42 and the connection electrode portion 32. The gro...
third embodiment
[0080]FIG. 7 is a cross-sectional view illustrating the MEMS sensor according to the third embodiment of the invention.
[0081]The MEMS sensor uses an IC package 100 instead of the second substrate 2. The IC package 100 incorporates therein a detection circuit, or the like, capable of detecting a change in the electrostatic capacitance between the counter electrodes and the movable counter electrodes.
[0082]The second insulating layer 30 is formed on an upper surface 101 of the IC package 100, and the connection electrode portions 31 and 32 and the sealing electrode portion 33 are formed on the surface of the second insulating layer 30. The connection electrode portions 31 and 32 are electrically connected to electrode pads that appear on the upper surface 101 of the IC package 100 via connection layers 134 and 135 such as through-holes configured to penetrate through the second insulating layer 30 and are connected to an electric circuit incorporated into the IC package 100.
[0083]In t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com