Non-imaging tracking tools and method for hip replacement surgery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
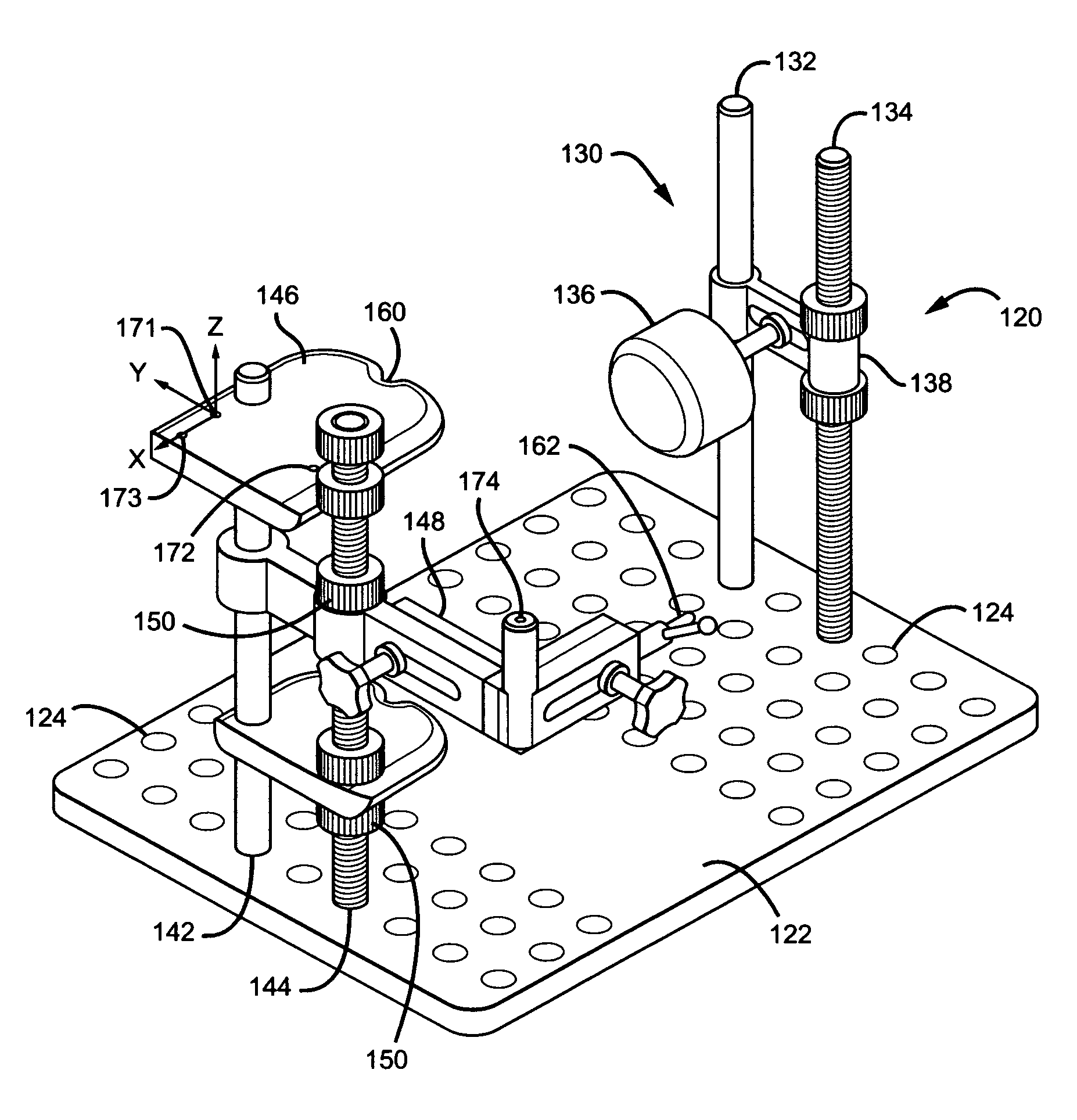
[0027]FIG. 1 shows a system-level block diagram of a system or apparatus 20 which provides the environment in which the present invention operates. The system or apparatus 20 is generally a computer aided system for navigating orthopedic surgery. A physician or other professional 22 performs a hip surgery (for example, total hip replacement) on a patient 24. An optical or equivalent locator or locating system 26 is disposed near the patient, so that the operating field is encompassed substantially within the field of view 28 of the locator 26. A suitable optical locator is available commercially, for example the “Polaris” available from Northern Digital Inc., in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. Optical trackers or markers 30 are used during the operation, as more fully described in related application U.S. Ser. No. 10 / 075,796. The markers 30 allow the locator 26 to acquire the positions and orientations of tools and anatomical reference points, as described below.
[0028]The optical locator...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com