System and Method for Planning and Generating Queries for Multi-Dimensional Analysis using Domain Models and Data Federation
a domain model and query technology, applied in the field of data integration and data analysis, can solve the problems of increasing complexity of the product itself, lack of visibility across the product life cycle, and increasing complexity of the it environment in the industrial manufacturing sector
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
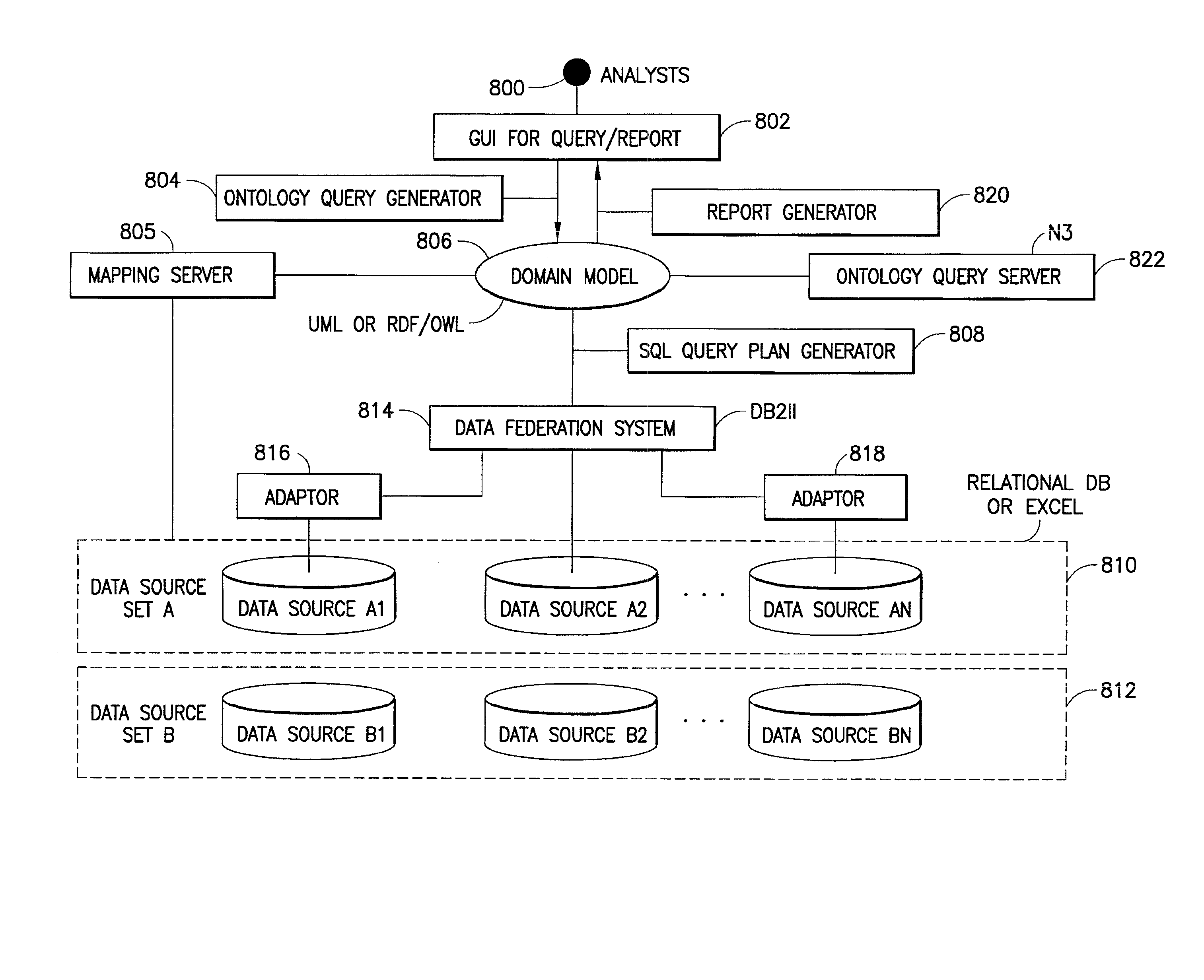
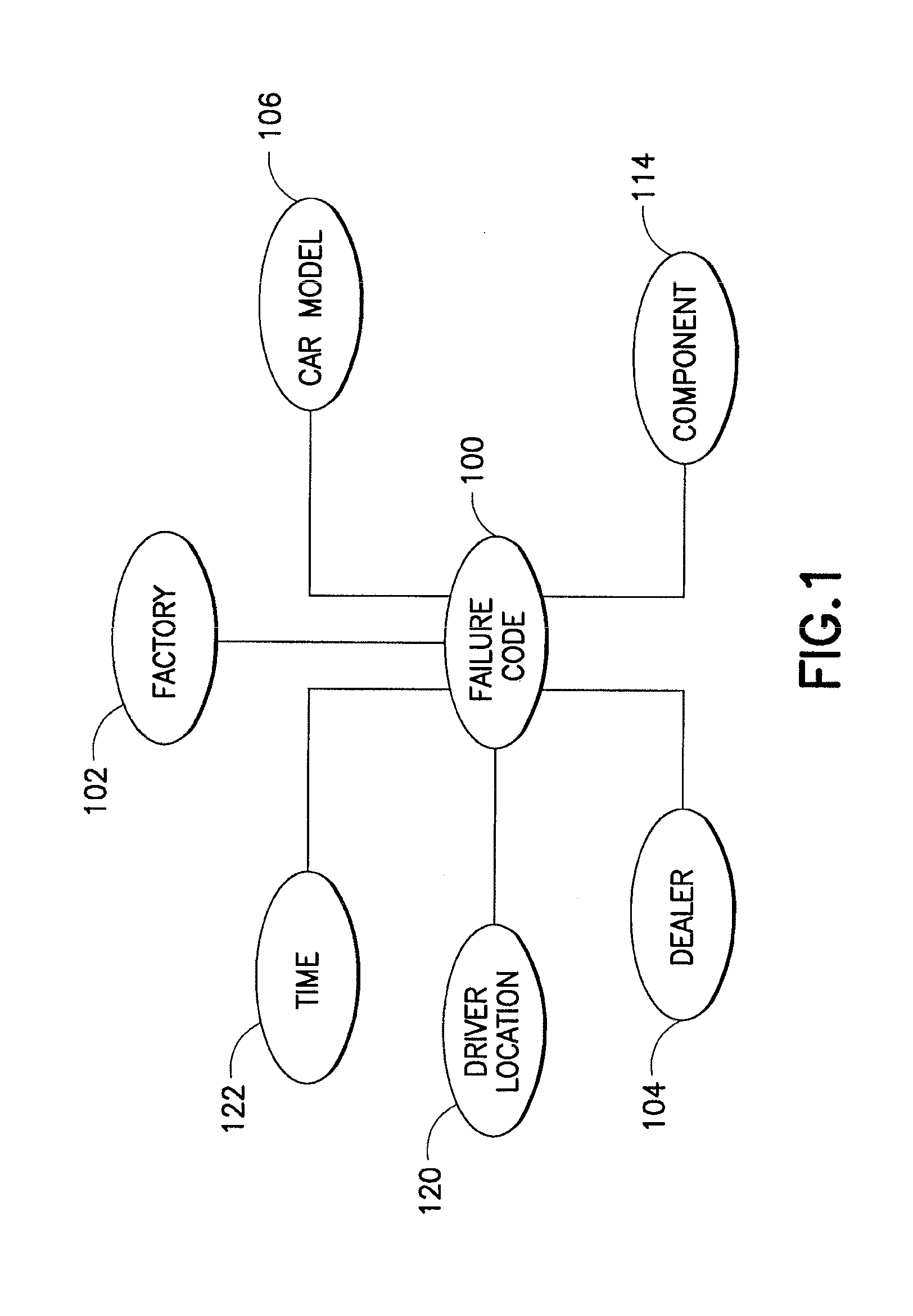
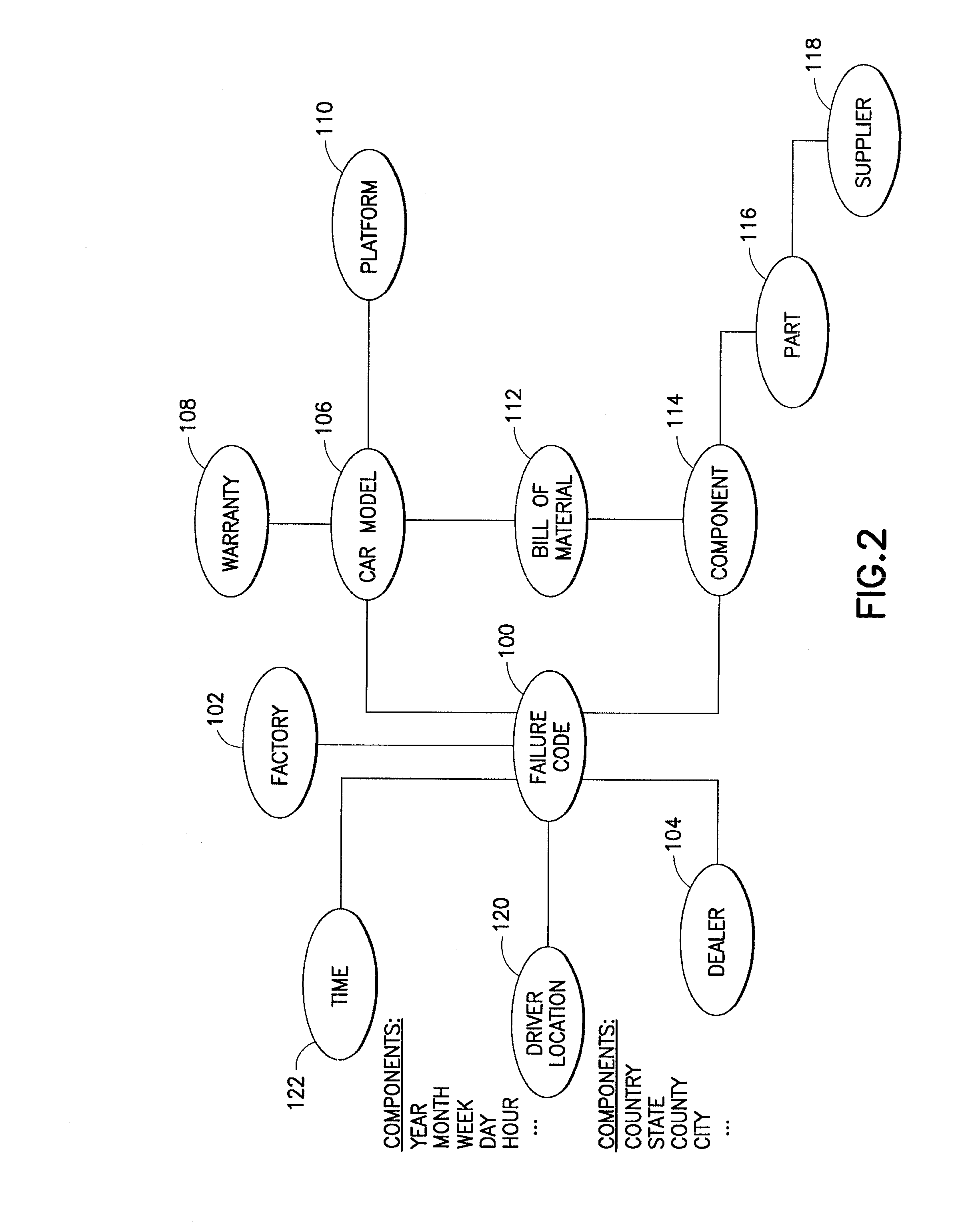
[0041] Referring now to the figures and specifically to FIGS. 1 and 2 there are shown a semantic model for automotive diagnostics and an expanded semantic model, respectively. A semantic model (ontology) is a formal explicit description of classes, i.e., concepts in a domain of discourse (e.g., automotive), properties of each class describing its attributes, relations with other classes being a special kind of properties (e.g., subclass, equivalentClass, etc.), properties of relations (e.g., transitive, symmetric, inverse, etc.), and constraints on properties (e.g., cardinality, etc.). Knowledge base often indicates a semantic model together with a set of individual instances of classes. The theoretical foundation of semantic models and technologies include logic (First Order Logic and Description Logic), knowledge representation of artificial intelligence (AI), and symbolic computation. The advantages of using semantic models include: (1) the models provide a means to express rich ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com