Absorbent member and a method of producing an absorbent member
a technology of absorbent members and absorbent pads, which is applied in the field of absorbent members, can solve the problems of inability to exhibit absorption capability, difficult to monitor the position of scattering patterns on the production line, and high cost of performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
(1) Preparation of Absorbent Member
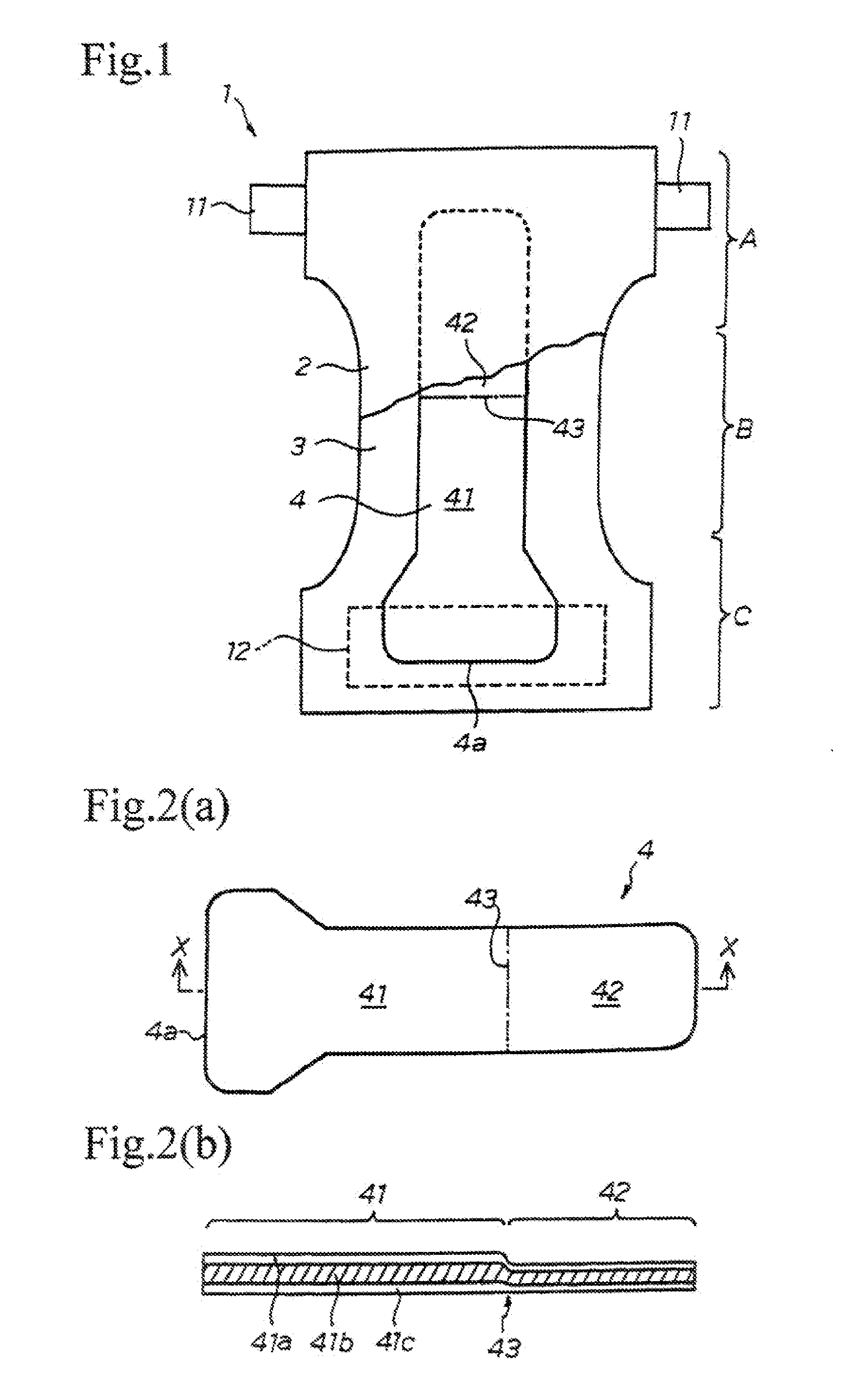
[0104] Absorbent members having the structure shown in FIGS. 2(a) and 2(b) were produced from a superabsorbent polymer and pulp fiber using an apparatus having the configuration shown in FIG. 3.
[0105] The shape of forming recesses and arrangement of first and second suction regions in each recess were as shown in FIG. 4(a). The open area ratio of the first suction region 51 and that of the second suction region 52 were 56% and 5%, respectively. The diameters of suction holes provided in both the first and second suction regions all fell within a range of 0.1 to 0.3 mm and averaged 0.2 mm in both regions. Each chamber provided behind the regions 54 to 56 of the drum 5 was maintained at a vacuum pressure lower than atmospheric pressure by 8 to 11 kPa, and this vacuum pressure was exerted to the first and second suction regions 51 and 52.
[0106] The area, etc. of the first and second suction regions are shown in Table 1, in which “front” and “rear”...
examples 2 and 3
[0107] Absorbent members were produced in the same manner as in Example 1, except for changing the open area ratio of the second suction region 52 to 10% (Example 2) or 18% (Example 3).
example 4
[0110] Absorbent members were produced in the same manner as in Example 1, except for changing the arrangement of the first and second suction regions as illustrated in FIG. 5. In Table 1, “T” and “Y” correspond to the first and second suction regions, respectively.
(2) Absorbent Member
[0111] The absorbent members obtained in Examples 1 to 4 and Comparative Examples 1 and 2 were measured for the pulp and the polymer contents in each of the portion corresponding to the first suction region (i.e., the high basis weight portion 41, represented by “front” or “T” in Table 1) and the portion corresponding to the second suction region (i.e., the low basis weight portion 42, represented by “rear” or “Y” in Table 1). The weights and specific contents (contents per unit area) of the pulp fiber and the polymer in each portion, and the like are shown in Table 1.
(3) Evaluation of Absorbent Member
[0112] Disposable pull-on diapers were produced using the absorbent members prepared in the Exam...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com