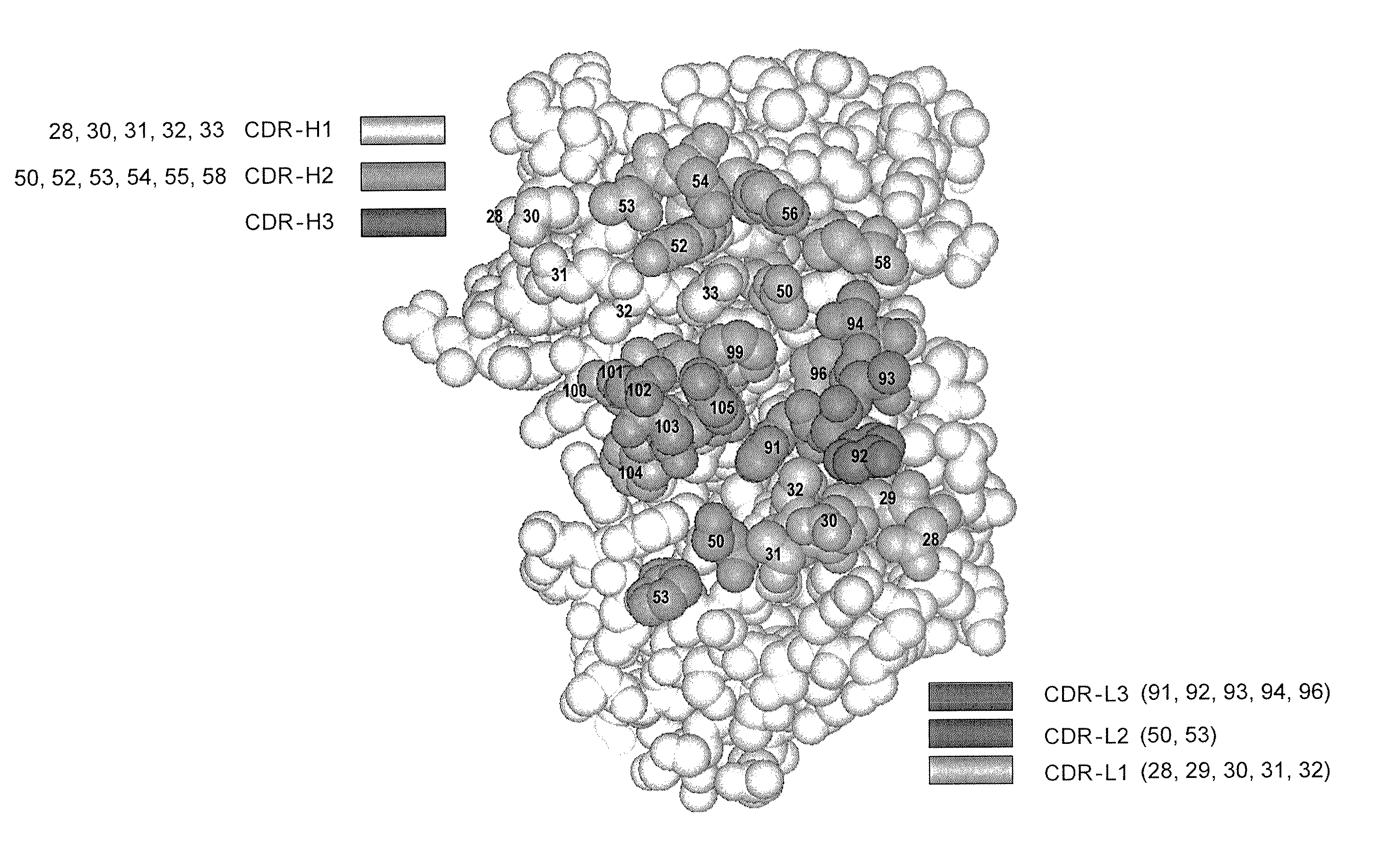
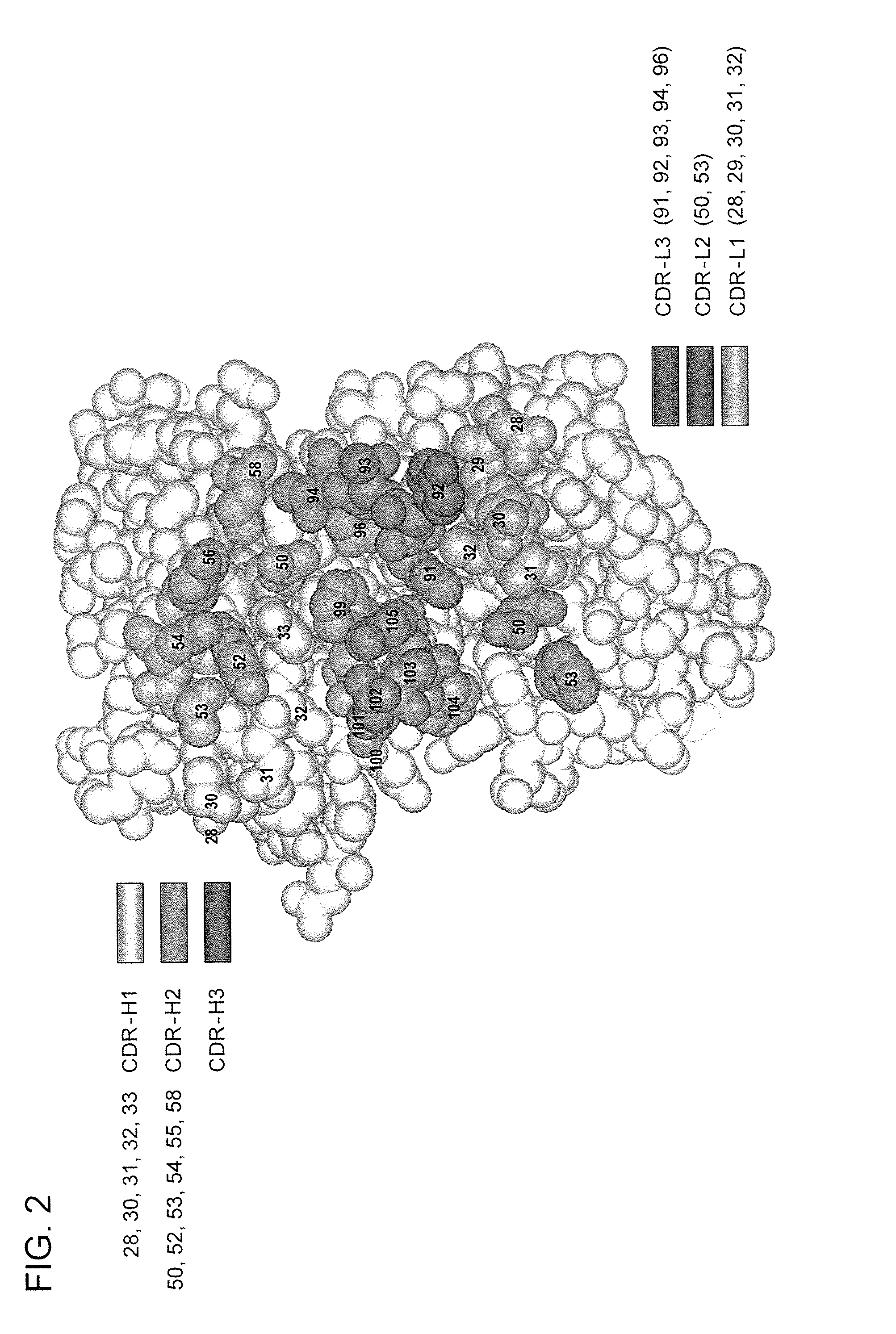
Binding polypeptides with restricted diversity sequences
a polypeptide and diversity technology, applied in the field of variable cdrs, can solve the problems of inability to apply systematic and quantitative methods, limited diversity of these libraries, and inability to meet the needs of patients,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Construction of Phage-Displayed Fab Libraries with CDR Residues Enriched in Tyr or Ser
[0686] Phage-displayed Fab libraries were constructed using the “Fab-C” phagemid vector that resulted in the display of bivalent Fab moieties dimerized by a free cysteine inserted between the Fab heavy chain and the C-terminal domain of the gene-3 minor coat protein (P3C). This vector was constructed as described in U.S. Patent Application Publication No. US20050119455 and in Lee et al., J. Immunol. Meth. 284: 119-132 (2004). The vector (schematically illustrated in FIG. 5) comprises the humanized antibody 4D5 variable domains under the control of the IPTG-inducible Ptac promoter. The humanized antibody 4D5 has mostly human consensus sequence framework regions in the heavy and light chains, and CDR regions from a mouse monoclonal antibody specific for Her-2. Methods of making the anti-Her-2 antibody and the identity of the variable domain sequences are provided in U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,821,337 and 6,05...
example 2
Selection of Specific Antibodies from the Naïve Libraries YS-C and YS-D
[0692] Phage from library YS-C or YS-D (see Example 1) were cycled through rounds of binding selection to enrich for clones binding to human VEGF. The binding selections were conducted using previously described methods (Sidhu et al., supra).
[0693] NUNC 96-well Maxisorp immunoplates were coated overnight at 4° C. with 5 μg / mL human VEGF and blocked for 2 h with a solution of PBT (phosphate buffered saline additionally containing 0.2% BSA and 0.05% Tween-20) (Sigma). After overnight growth at 37° C., phage were concentrated by precipitation with PEG / NaCl and resuspended in PBT, as described previously (Sidhu et al., supra). Phage solutions (about 1012 phage / mL) were added to the coated immunoplates. Following a two hour incubation to permit phage binding, the plates were washed ten times with PBT. Bound phage were eluted with 0.1 M HCl for 10 minutes and the eluant was neutralized with 1.0 M Tris base. Eluted ph...
example 3
Construction of Phage-Displayed Fab Libraries with CDR Residues Enriched in Tyr, Ser, Gly, and Arg
[0698] Phage-displayed Fab libraries were constructed using a phagemid vector, Fab-C, that resulted in the display of bivalent Fab moieties dimerized by a free cysteine inserted between the Fab heavy chain and the C-terminal domain of the gene-3 minor coat protein (P3C), as previously described in Example 1.
[0699] Four libraries were constructed: YSGR-A, YSGR-B, YSGR-C, and YSGR-D. The libraries were constructed with randomized residues in all three heavy chain CDRs and light chain CDR3. Each library was randomized at positions 91-94 and 96 of CDRL3, positions 28 and 30-33 of CDRH1, positions 50, 52-54, 56, and 58 of CDRH2, and positions 95-100, 100a, 100b, and 100c of CDRH3. The type and ratio of the amino acids allowed at each of the randomized positions is described in FIG. 11. In addition, the length of CDRH3 was varied by using oligonucleotides that replaced the seven wild-type c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com