Virtual heart valve
a heart valve and virtual technology, applied in the field of virtual heart valves, can solve the problems of difficult experimental measurement of leaflet strains for validation, inability to perform experimental measurements of leaflet strains, and inability to meet the requirements of clinical trials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
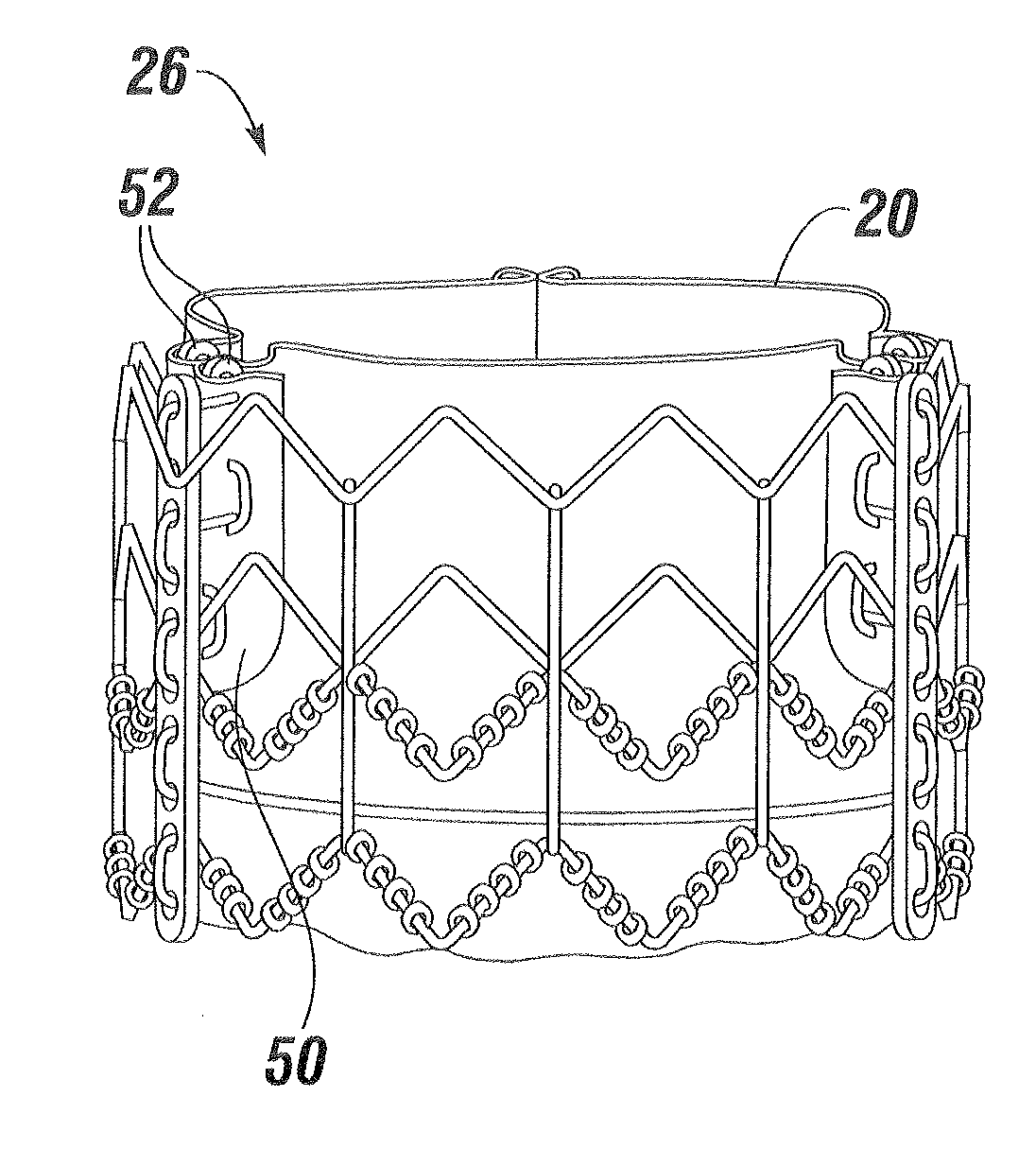
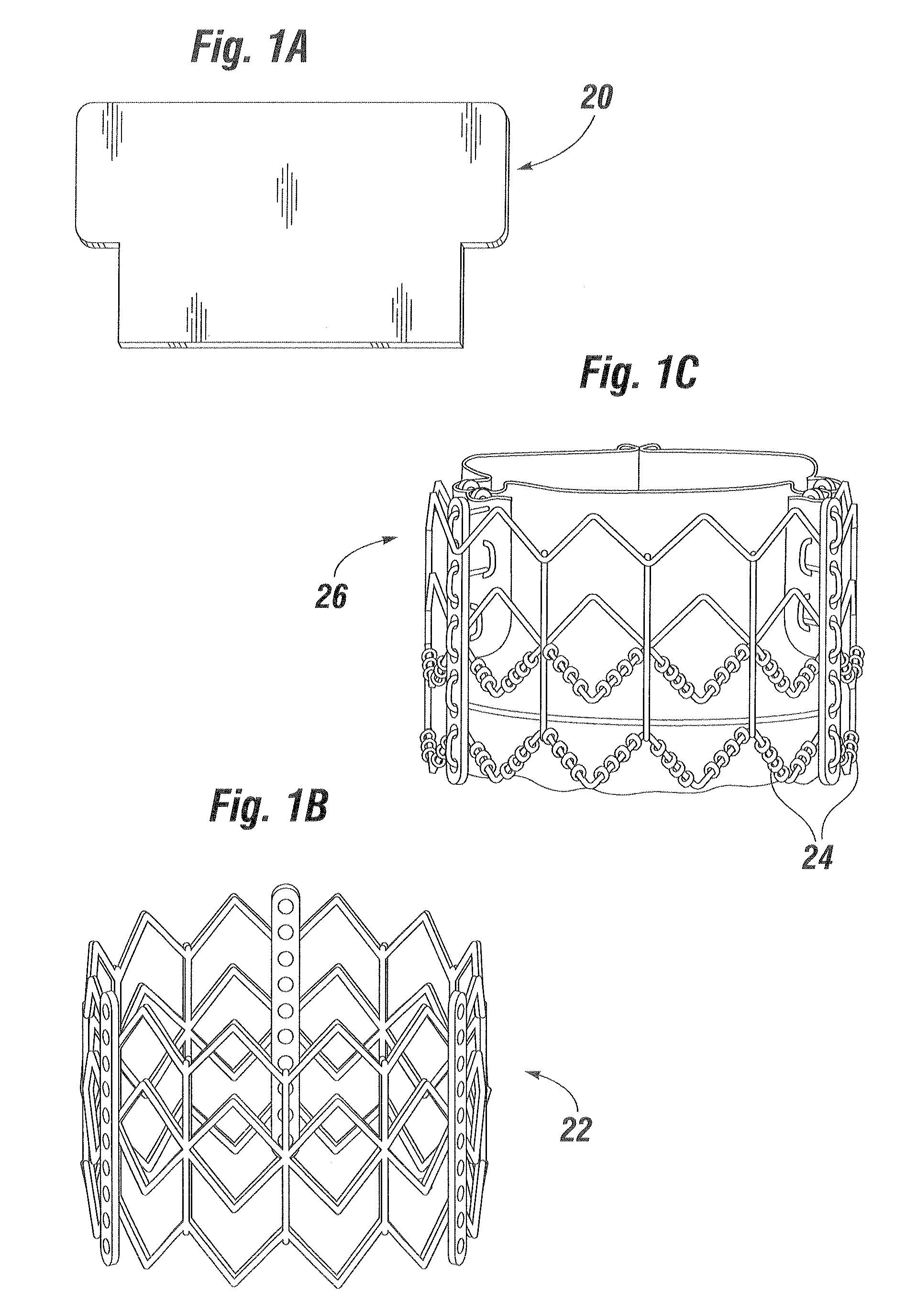
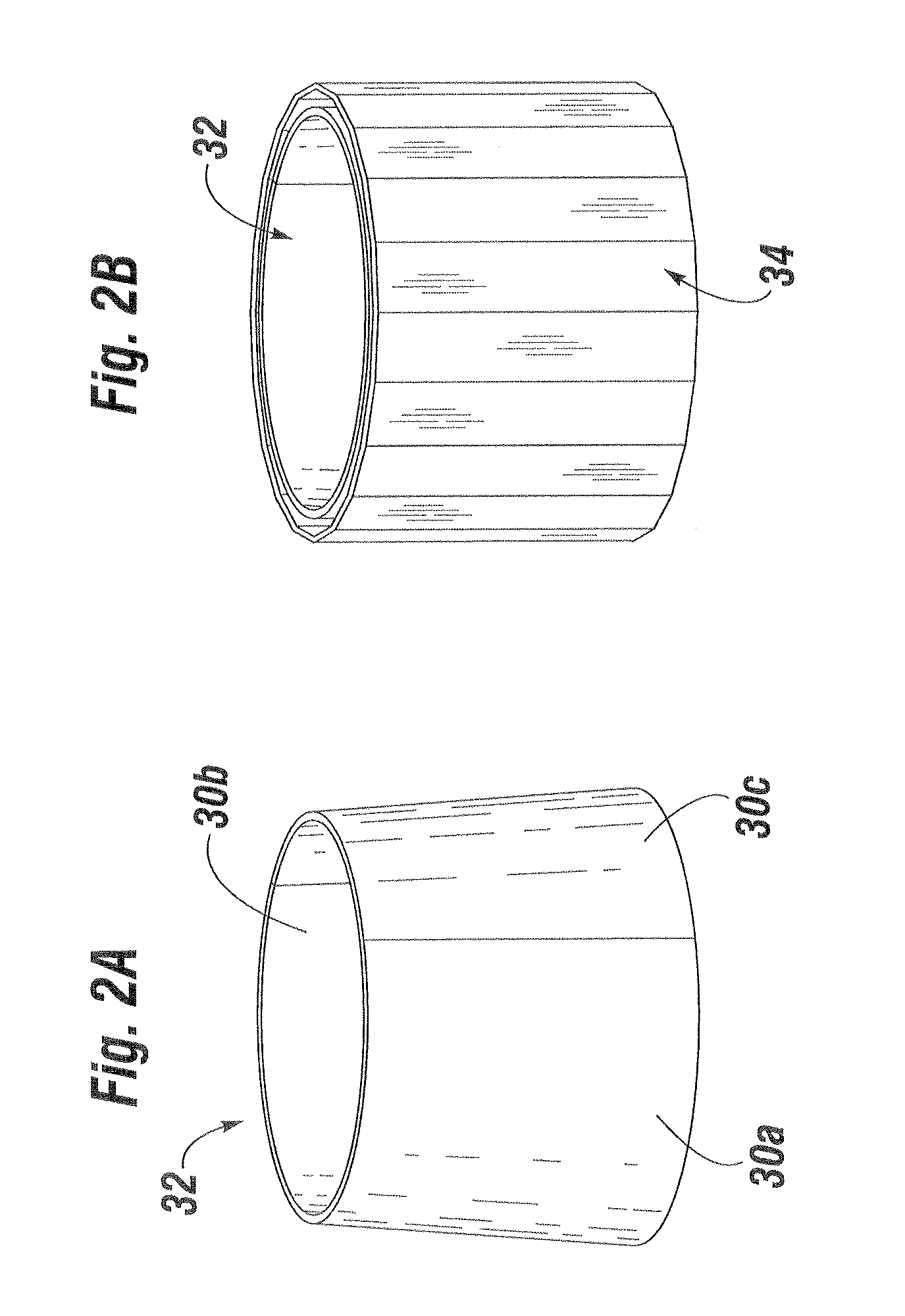
[0033]The present invention is an improved software-based technique for constructing a virtual three-dimensional heart valve. Such a virtual heart valve is useful for testing purposes prior to prototype or development model build. In particular, the methods described herein are desirably performed between the design and prototype stages. An accurate model for simulating heart valves and their operation in three dimensions is an extremely valuable tool for experimental purposes. At present, there is a great deal of interest in new collapsible much expandable heart valves that are delivered via minimally-invasive surgical or percutaneous approaches. However, this effort involves the design of new heart valve geometries that have not been clinically proven. Therefore, a computational model that produces an accurate virtual heart valve and can simulate dynamic conditions saves a great amount of time and money.
[0034]Performance of stress analysis and evaluation of flexible leaflet valve ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com