Microflow System for Particle Separation and Analysis
a microflow system and particle technology, applied in chemical microanalysis, material testing goods, open gradient mangetic separators, etc., can solve the problems of high dilution of desired cell samples, low speed and sterility, and cell sorting by flow cytometry suffers, etc., to achieve the highest resolution of detection, easy integration, and high susceptibility sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
[0175] Further, the micro flow system used in Example 1 has also been tested by utilising it for separation of Human T-lymphocytes (JURKAT cells). Magnetically stained and unstained JURKAT cells were used to form a heterogeneous cell sample. For magnetic staining of the cells, a CD4-magnetic surface marker from Miltenyi Biotech was used. JURKAT cells were suspended in 1% PBS / BSA to a concentration of 107 / ml. Biotin-conjugated CD4 magnetic microbeads were added at 2 μl stock / 107 cells following the manufacturer instruction.
[0176] The magnetically stained cells (107 cells / ml) flowed through the microchip for 10 min. and fluids were collected at the two outlets. Three experiments at different flow rates (5, 25, 50 μl / min) were performed. The same experiments were performed using magnetically unstained cells.
[0177] An aliquot of the collected samples was analysed under a microscope and the particles were counted using a Neubauer microscopy chamber. For each experiment 1 μl sample was ...
example 3
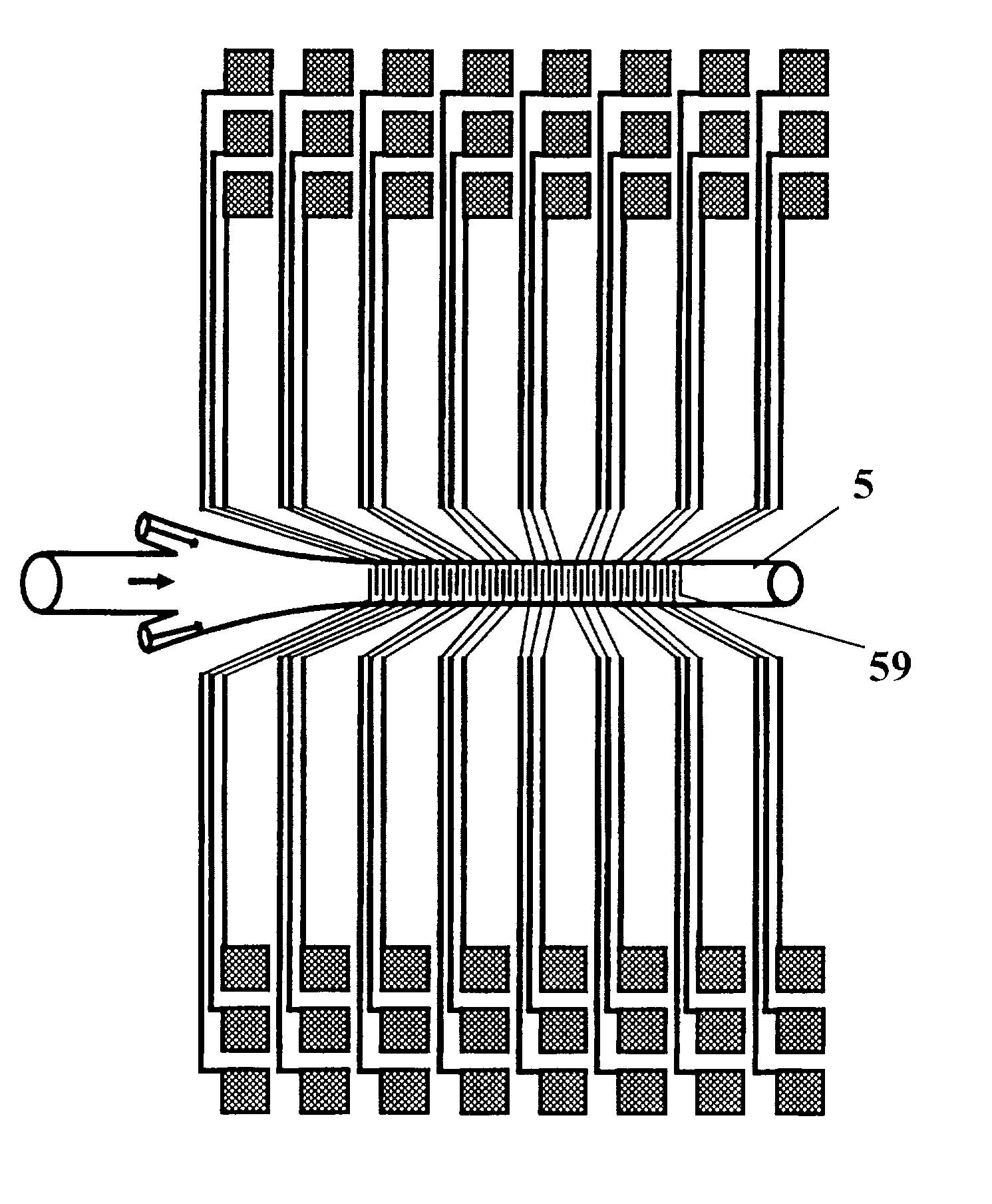
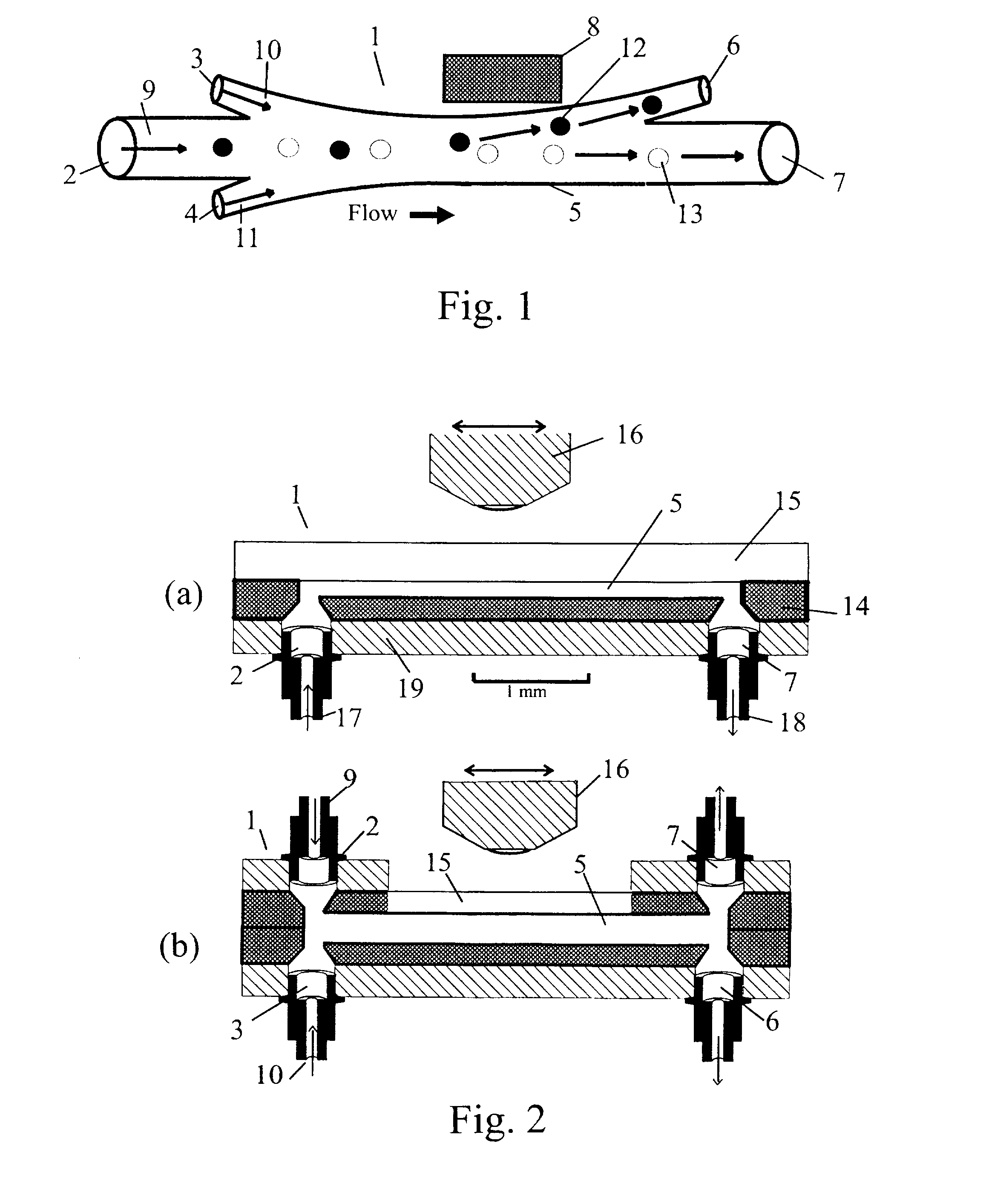
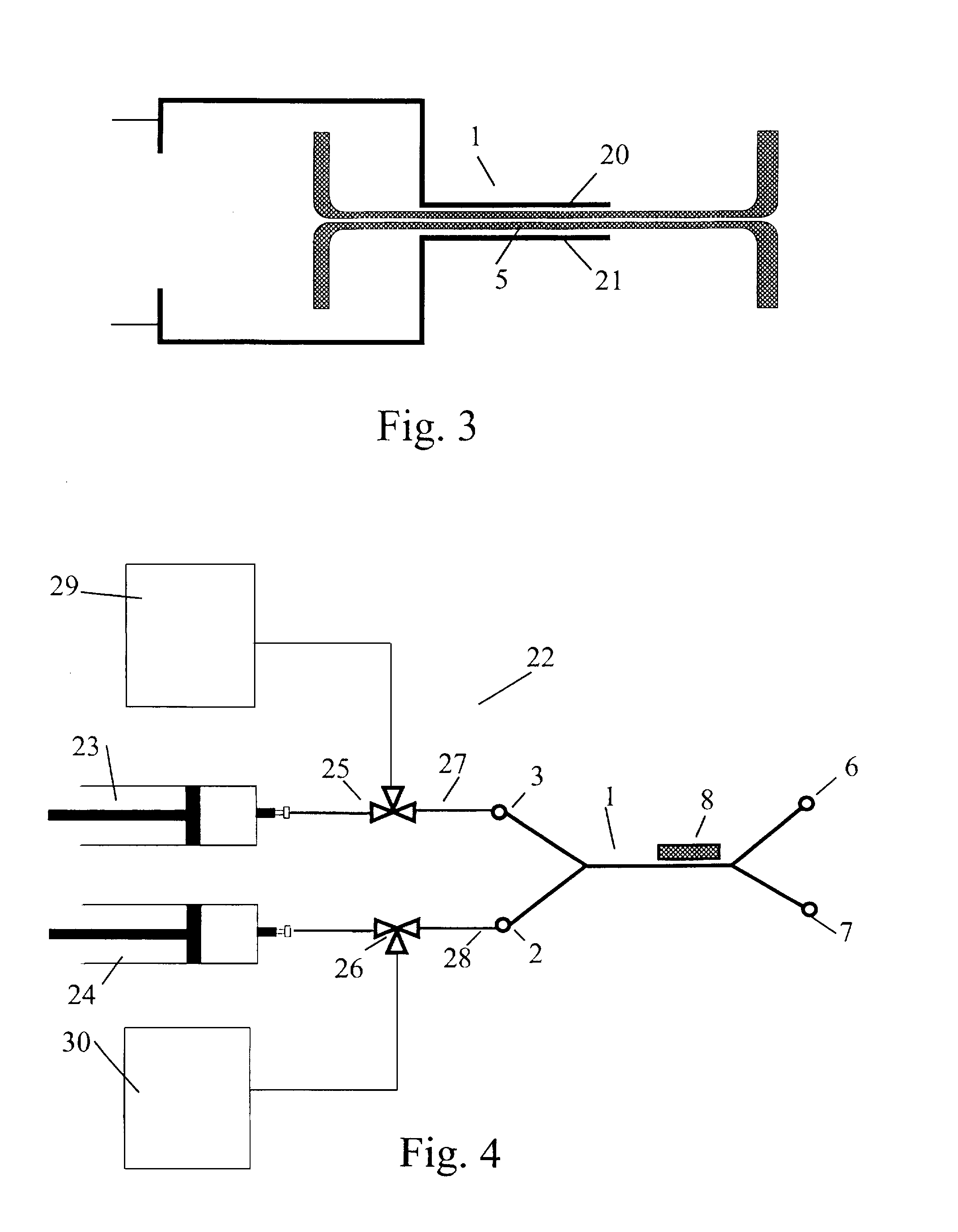
[0178] The system employed for separation of magnetisable particles from a sample is shown in FIG. 4. It comprises two syringe infusion pumps (Harvard Apparatus, Southnatik, Ariz.) that provides constant flow rates of 0.1 to 100 μl / min using a 0.5 ml micro syringe (Hamilton, Bonaduz, Switzerland), a separation flow channel of silicon for the separation of the magnetisable particles, and a collecting unit for collecting of the sorted particles. Two 3-way microvalves (Lee, Parameter AB, Sweden) were integrated into the apparatus for sterile solution handling. All components were interconnected with fused silica capillaries (340 μm id., Supelco, U.S.A.). The SFC was placed under an inverted microscope (Axiovert 100, Zeiss, Germany) for visualisation of the separation procedure. All micro channels and tubing were deactivated by silanisation as described in Blankenship, G. Scampavia L, Branebjerg J, Larsen U D, Ruzicka J (1996): Flow switch for analyte injection and cell / particle sorting...
example 4
[0180] This example concerns enrichment of fetal cells in a sample for magnetic activated cell sorting. A combination of the embodiment of the invention as shown in FIGS. 7 and 10 (upper), optical cytometry, and FIGS. 4 and 10 (lower), magnetic cell separation, provides a powerful apparatus for efficient enrichment of fetal cells in a sample.
[0181] The process for increasing the concentration of fetal cell in maternal blood samples involves the following steps (see FIG. 18): (i) A first selection step for removal of the majority of the maternal blood cells based upon their volume, size and density; (ii) A second sorting step for isolation of the fetal blood cells from the remaining maternal blood cells based on immuno-fluorescent separation using a device as described in FIG. 7 and / or based on immuno-magnetic separation using a device as described in FIG. 4. In the examples shown in FIG. 9(b), the magnetic blood sample is first separated in a magnetic separation chamber, followed b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Reynolds number | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com