Method and apparatus for controlling reactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
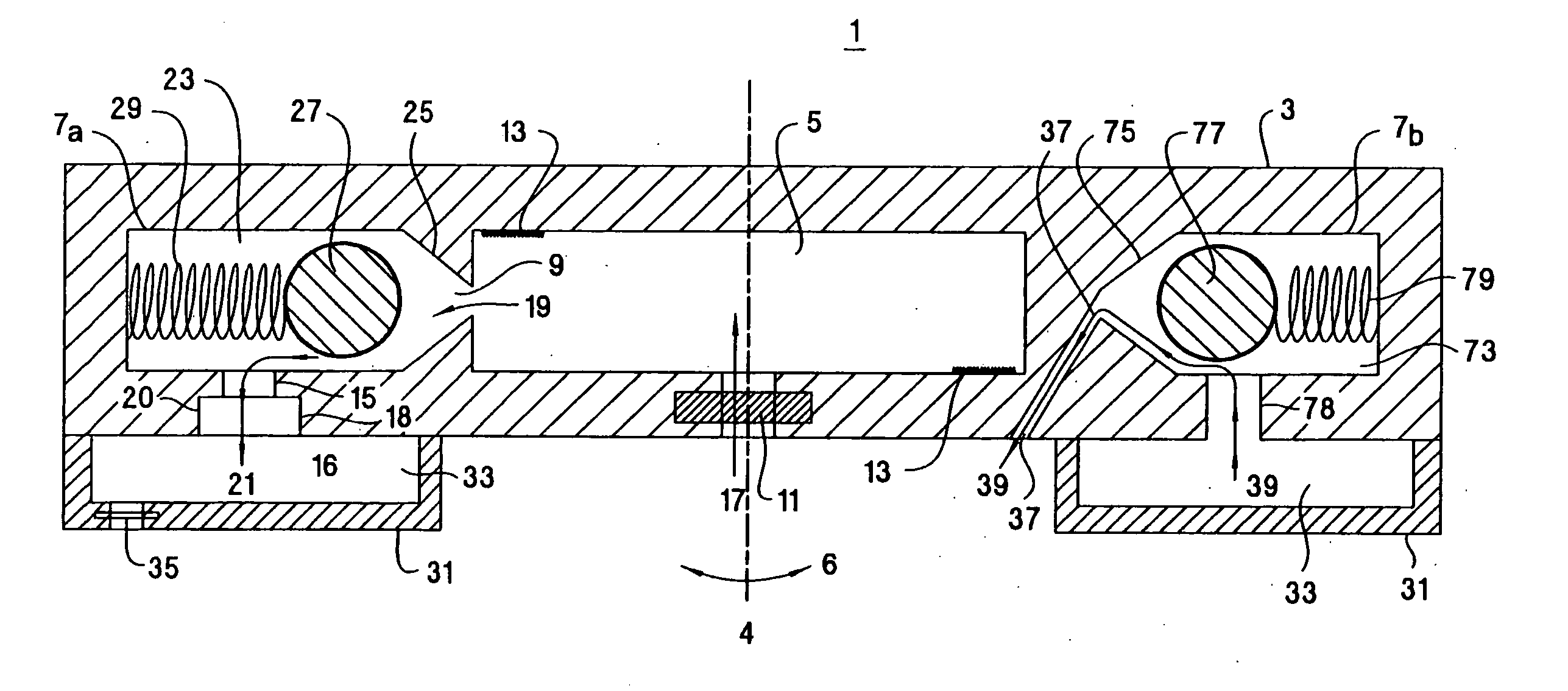
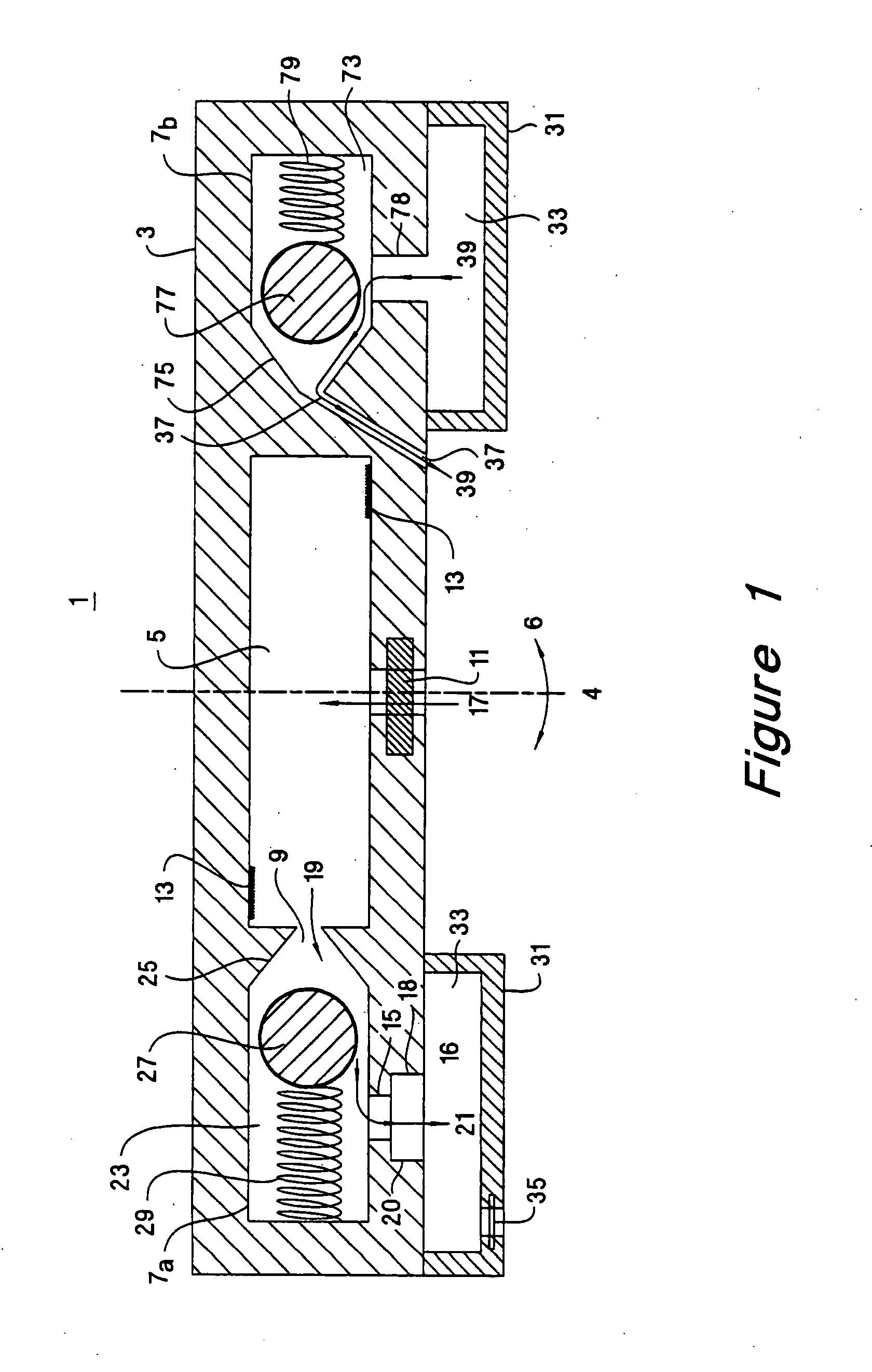
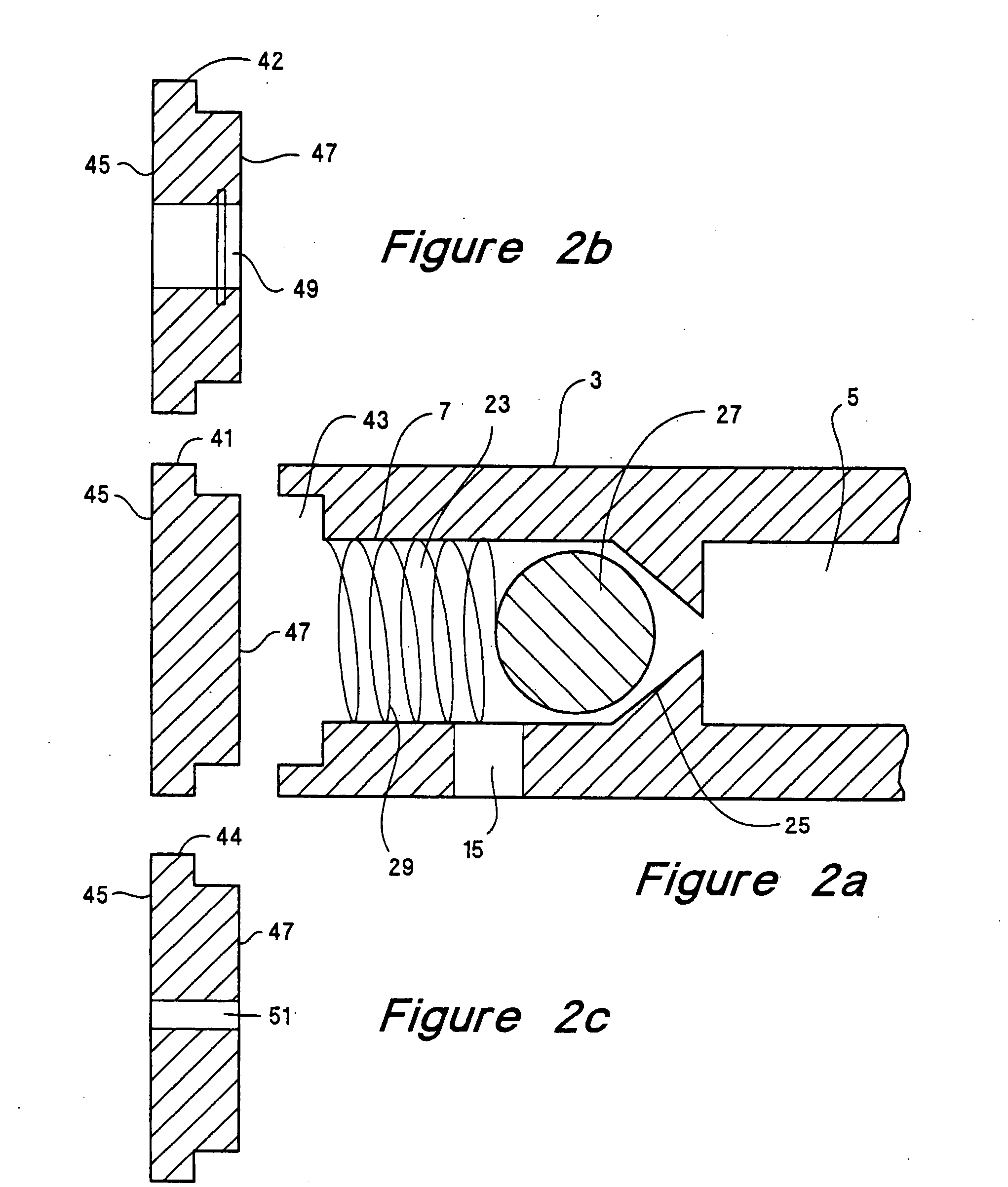
[0033] In the following detailed description and in the several figures of the drawings, like elements are identified with like reference numerals.
[0034] As shown in the drawings for purposes of illustration, the invention is embodied in an analytical device having an assay chamber for fluid reactions and at least one centrifugal force-activated valve in fluid communication with the assay chamber. The valve provides positive control of fluid contained in the assay chamber and allows for multiple, fluid reaction steps, mixing steps, and washing steps to occur in the assay chamber. The analytical device of the present invention is easy to use, can be manufactured at low cost, is adaptable to automation, provides predictable fluid control that can be tuned over a wide range of rotational speeds, and can be disposed of after use to prevent contamination from repeated use of the same analytical device. Previous apparatus for controlling reactions have incorporated complex fluid control ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com