Method and device for locating magnetic implant source field
a magnetic implant and source field technology, applied in the field of magnetic implant methods, can solve the problems of difficult without proper imaging guidance to provide even a reasonable guess, the determination of this movement can be a problem, and it is difficult to accurately and reliably locate the magnetic surgical implant, and achieve the effect of accurately and reliably locating the magnetic surgical implan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
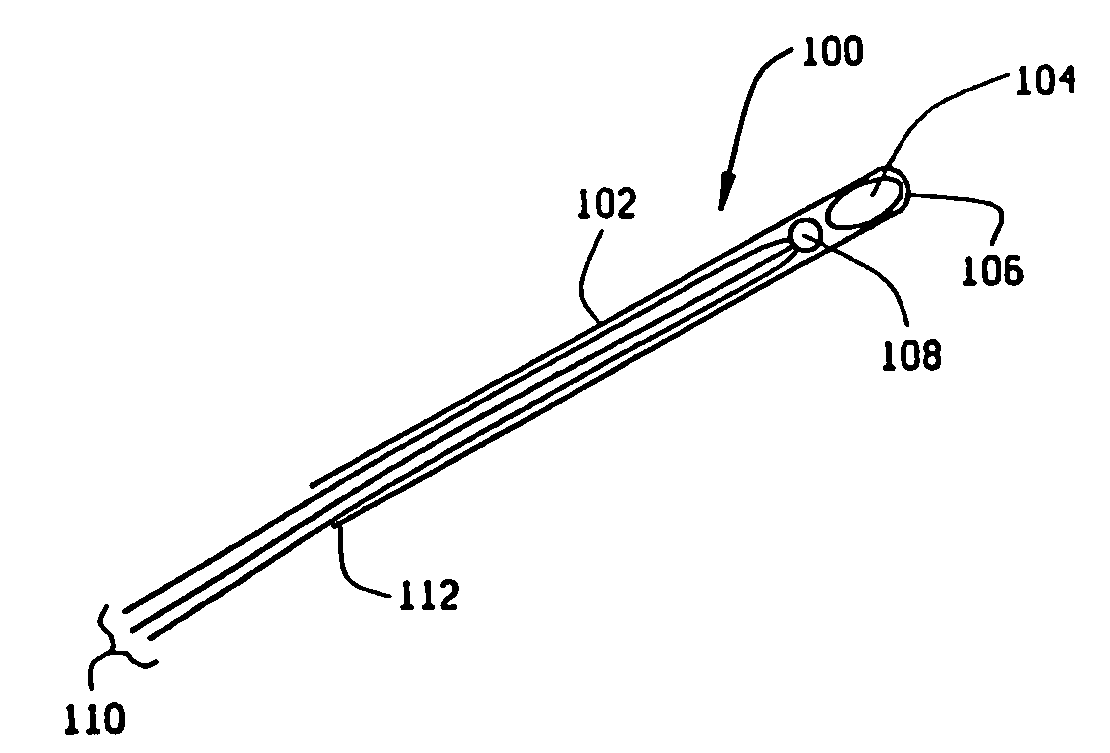
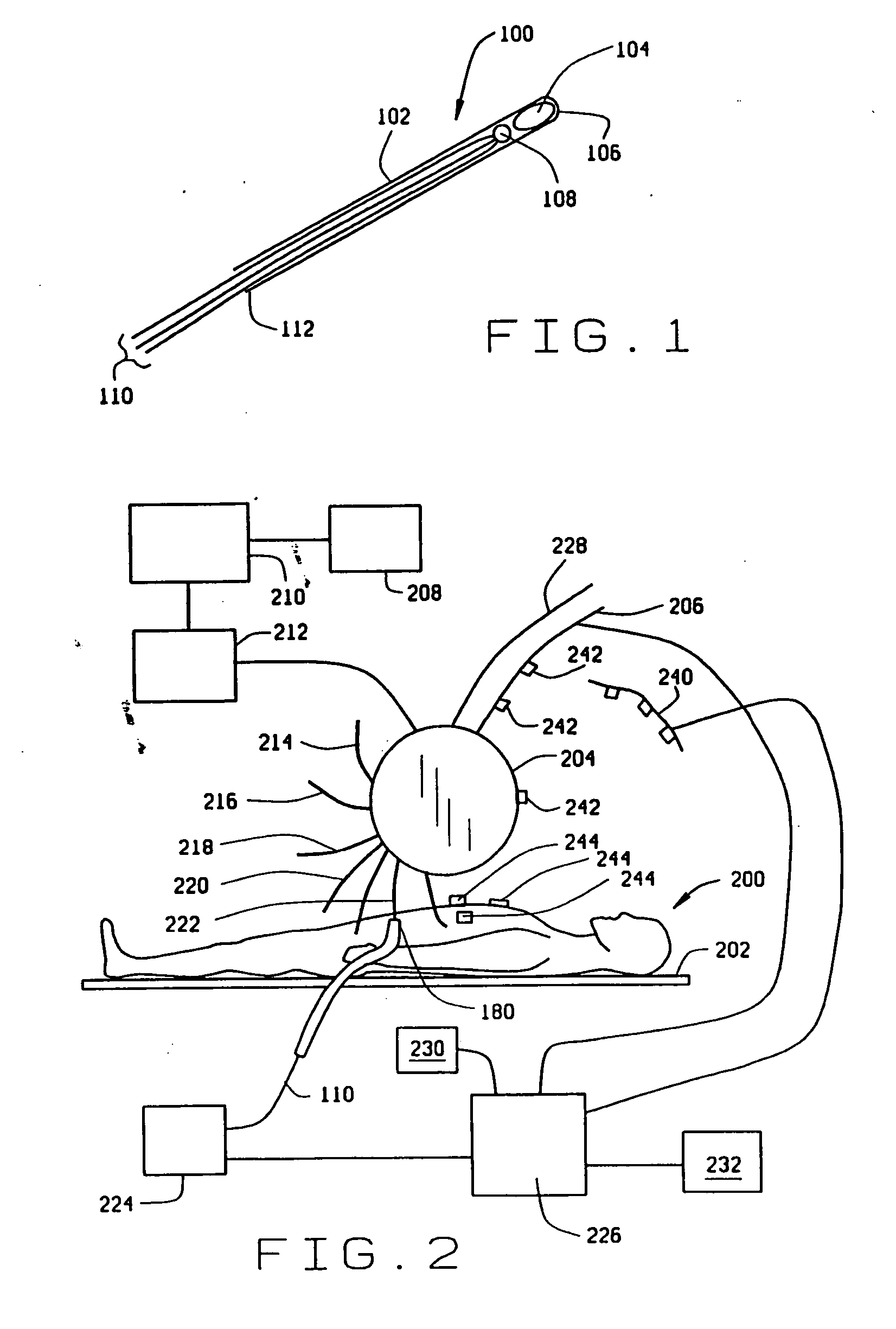
[0021]FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating an embodiment 100 of an inventive device in accordance with a first aspect of the invention. This device comprises a flexible probe 102, which may be an endoscope or a catheter tube. A magnetic seed 104 of permanent magnetic, or at least a permeable material, is located near an end 106 of the flexible probe. Seed 104 preferably comprises a samarium-cobalt (SmCo) permanent magnet, or even more preferably a neodymium-boron-iron (NdBFe) permanent magnet. Typically, seed 104 may be about 0.7 mm in diameter and length, but may range up to about 4-5 mm in diameter and up to 7-10 mm long, depending upon the surgical application of probe 102. It is not intended to exclude seeds of other sizes, whether larger or smaller, from the scope of the invention. Preferably, seeds 104 of the sizes given as examples would have magnetic fields in the immediate vicinity of seed 104 of no more than 0.4 T. It is contemplated that the magnetic seed 104 is fixedly held ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com