Fiberglass pool edge coping system
a technology of fiberglass pool and coping system, which is applied in the direction of gymnasium, construction, buildings, etc., can solve the problems of non-rigid shell structure generally involves a degree of trial and error, the top edge of the pool liner is out of true relative to typical construction tolerance, and the pool is difficult to install with precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
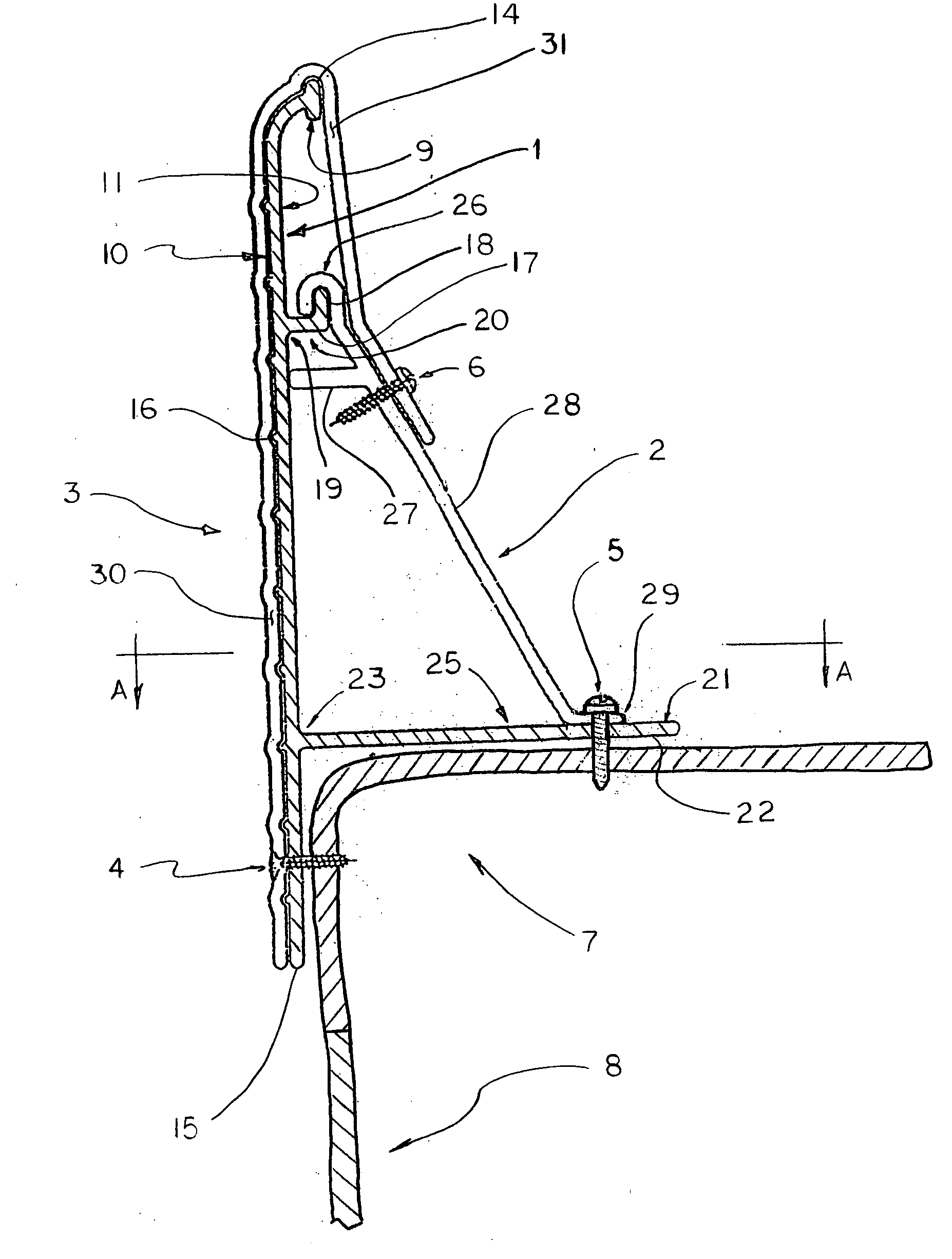
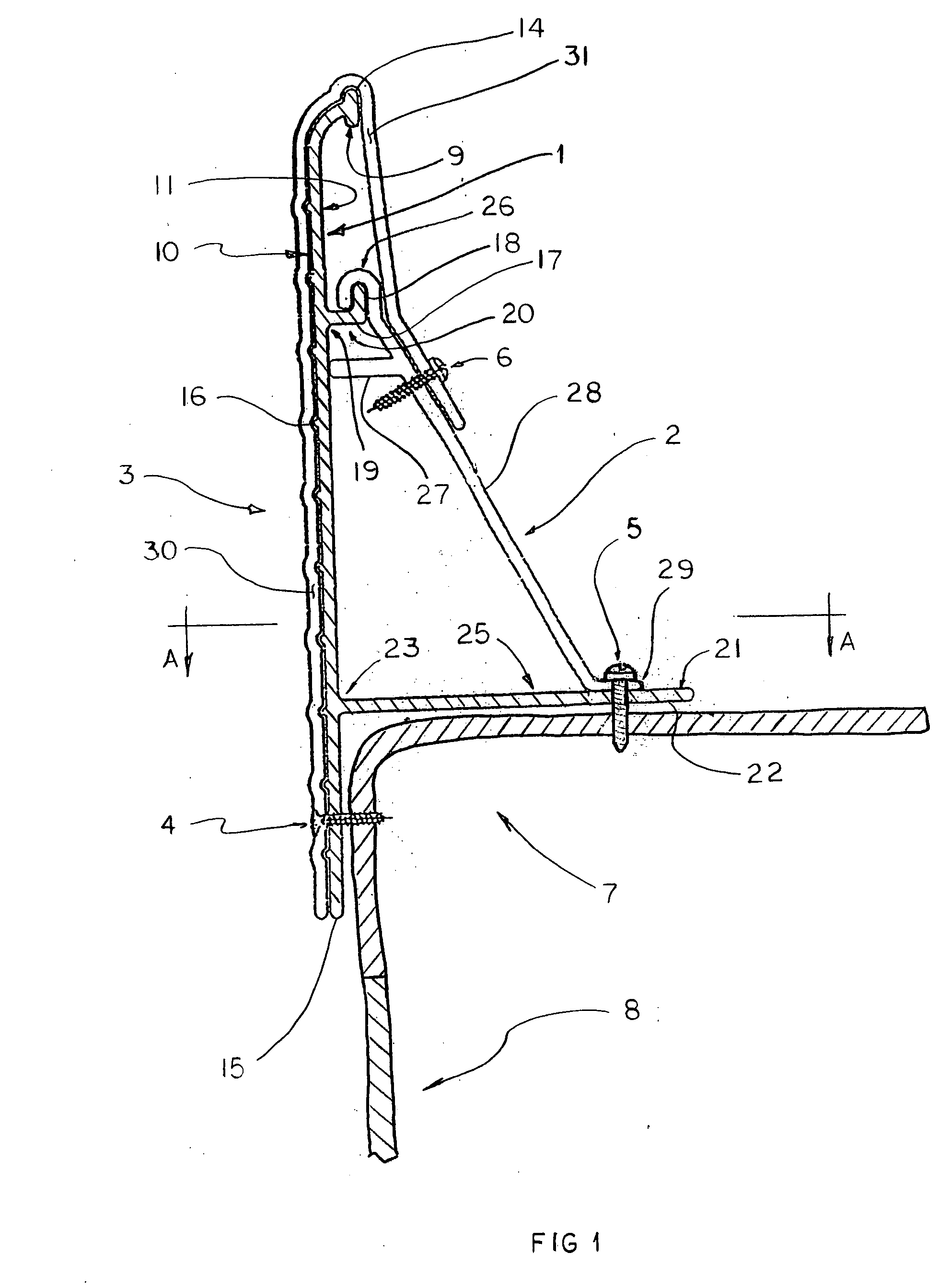
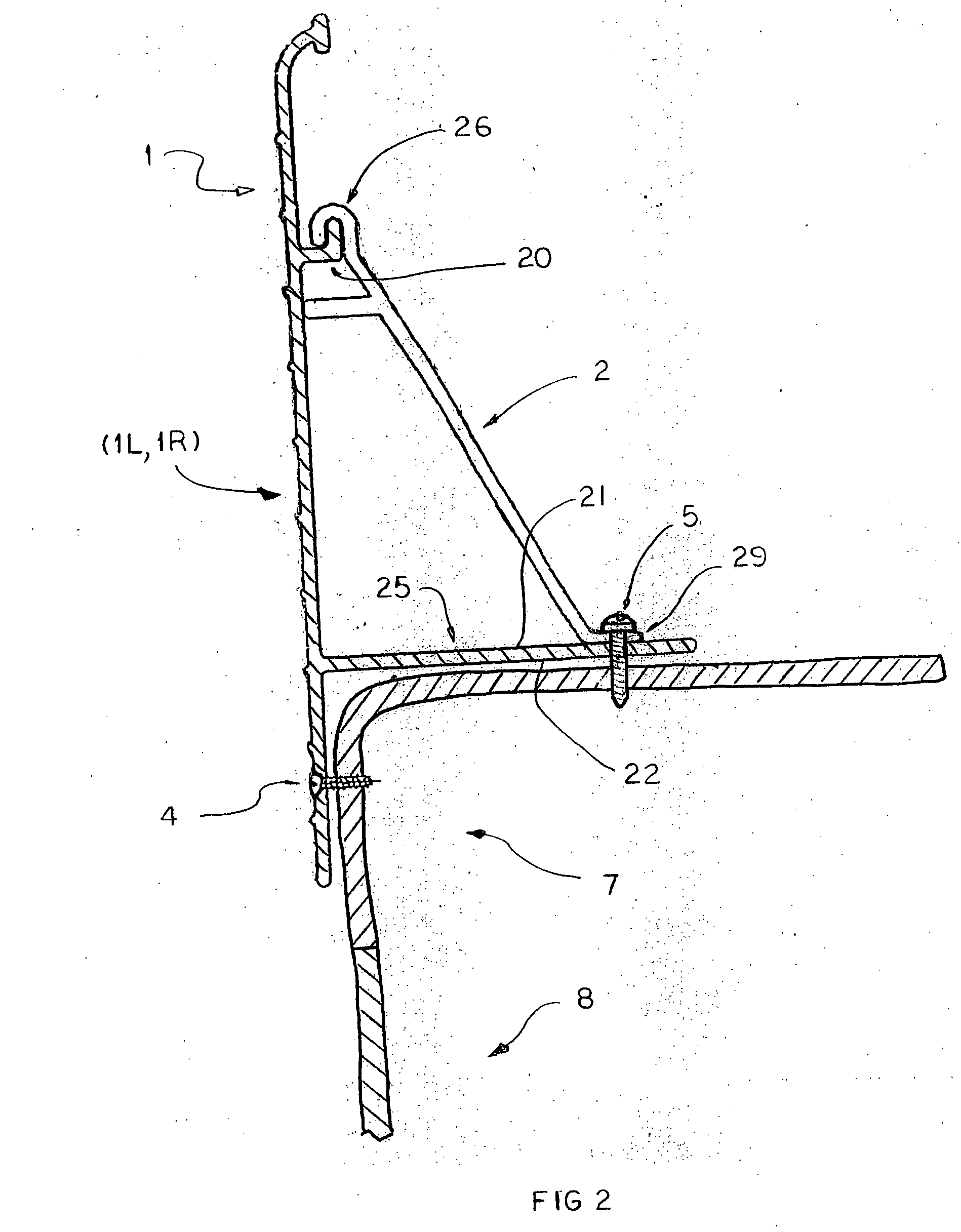
[0042] The installation process of the first embodiment continues, placing additional edging bands, intermediate anchors, joint anchors and joint clips, finishing with a final edging band (not shown) being cut to length and fit to the left end of the first edging band 1L (not shown) in a final butt joint (not shown), until the entire top corner of the pool is edged with the edging band. This creates a continuous edging band (not shown) around the entire perimeter of the pool.
[0043] Once the continuous edging band is ready, additional known preparation of a concrete placement area is completed. Said concrete placement area comprises a prepared surface beginning at said continuous ending band and projecting away from back side 11 of all edging bands comprising said continuous band to a known limit. Concrete is then placed in said concrete placement area, utilizing said continuous edging band as a retaining wall (a concrete form) to prevent a flow of wet concrete into the pool, and sim...
third embodiment
[0046] In a third embodiment, front side 10 may be decorated with paint or a pattern.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com