Mutants of streptococcal toxin a and methods of use
a technology of streptococcal toxin and mutants, which is applied in the field of mutants of streptococcal toxin and methods of use, can solve the problems of large problem of severe gas infection, abnormally high level of circulating cytokines, and inability to protect animals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Cloning and Expression of SPE-A Wild Type
[0138] The gene encoding wild type SPE-A toxin (speA) was cloned from E. coli as described in Johnson et al., Mol. Gen. Genet. 194:52-56 (1984). Briefly, the speA gene was identified by cloning of a HindIII digest of Phage T12 DNA in pBR322 in E. Coli RR1. Transformants were selected by identifying those positive for toxin production using polylconal neutralizing antisera to A toxin. A nucleotide sequence for A toxin is reported in Weeks et al, Inf. Imm. 52: 144 (1986).
[0139] A DNA sequence including the speA gene was subcloned and then expressed in S. aureus. The speA carried on a E. coli plasmid was digested with restriction enzymes HindIII and SalI. The fragments were purified and ligated into HindIII-SalI sites of pMIN 164 (available as described previously). The vector pMIN 164 is a chimera of the staphylococcal plasmid pE194 (carrying erythromycin resistance) and the E. coli vector pBR328 (carrying Amp and Tet resistance). Cloning of ...
example
Administration and Immunization of Rabbits with Recombinantly Produced SPE-A (wt)
[0141] Administration of recombinantly produced SPE-A to animals induces STSS. Immunization of animals with recombinantly produced SPE-A reduces the death rate when animals are challenged with M3 or M1 streptococci and protects animals against STSS.
[0142] Administration of SPE-A induces STSS in rabbits. A rabbit model for STSS has been established by administration of SPE-A in subcutaneously implanted miniosmotic pumps. Lee et al., Infect Immun. 59:879 (1991). These pumps are designed to release a constant amount of toxin over a 7-day period, thus providing continuous exposure to the toxin. Recombinantly produced SPE-A was administered to rabbits at a total dose of 200 μg / in 0.2 ml over a 7-day period. The results indicate that animals treated with SPE-A developed the criteria of STSS with nearly all animals succumbing in the 7-day period (data not shown). The symptoms of STSS in rabbits include weigh...
example 3
Site Directed Mutagenesis of a DNA Sequence Encoding SPE-A
[0153] Locations in the SPE-A molecule important for biological activity were identified using site directed mutagenesis. Single amino acid changes were introduced into various regions of the molecule as described below.
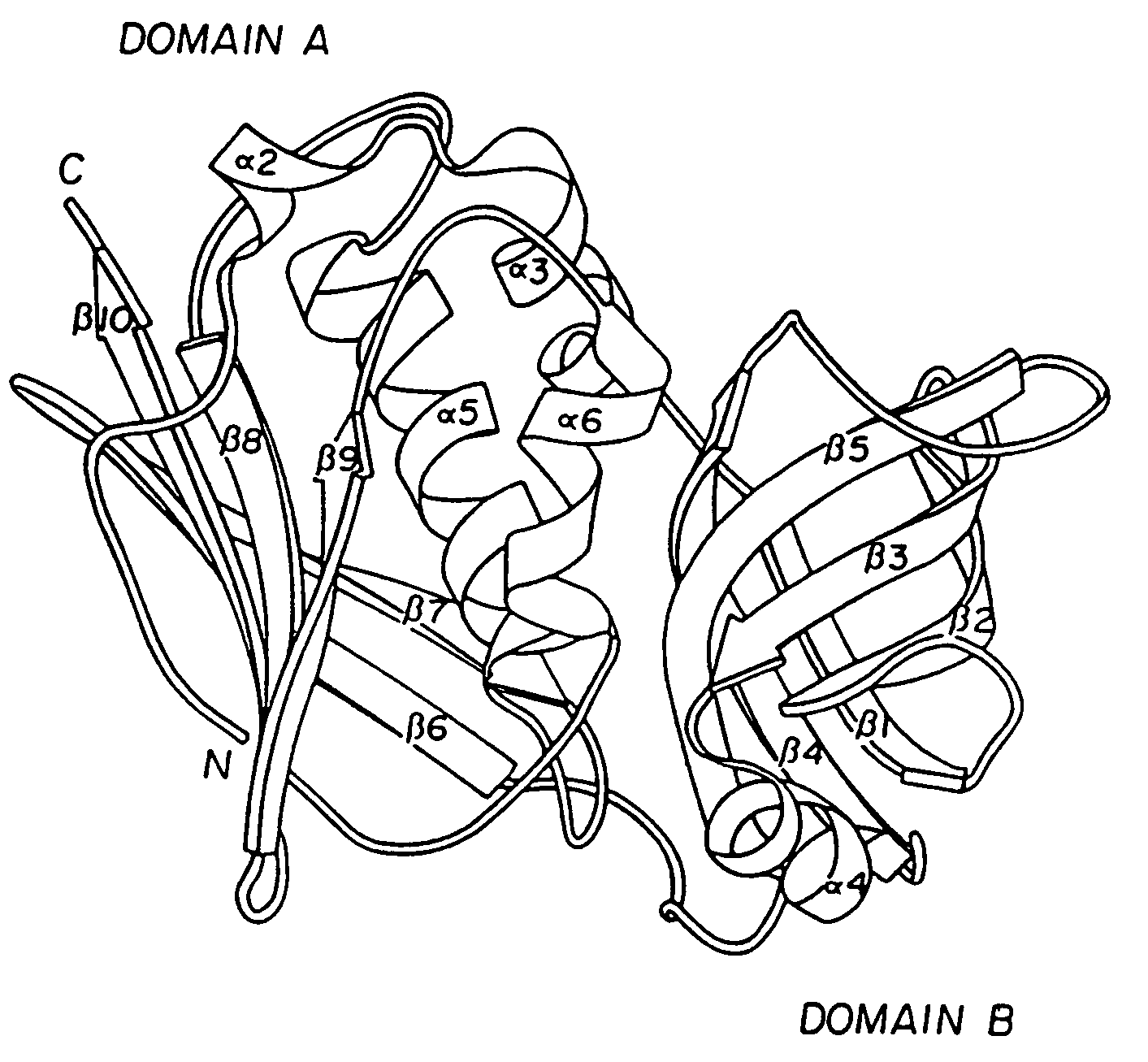
[0154] The model of the three dimensional structure of SPE-A is shown in FIG. 1. This model structure was constructed by Homology using an Insight / Homology program from BioSym Corp., San Diego, Calif. This molecule has several domains identified as:
CorrespondingDomainAmino AcidsHelix 211-15N terminal α-helix, helix 318-26Domain B - β strandsstrand 130-36strand 244-52strand 355-62strand 475-83strand 5 95-106Central α-helix, helix 5142-158Domain A - β strandsstrand 6117-126strand 7129-135strand 8169-175strand 9180-186strand 10213-220Helix 464-72Helix 6193-202
[0155] Amino acid number designations are made by reference to the sequence in FIG. 3.
[0156] Amino acids were selected in each of the domains and to al...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compositions | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com