Fabrics of mixed-polyester-ratio bi-component fibers
a technology of polymer ratio and fibers, applied in the field of yarns comprising mixed polymer ratio bicomponent fibers, can solve problems such as non-uniform areas of fabrics, and achieve the effect of avoiding follow-the-leader crimping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0024] A first yarn was produced by commingling two yarns. Each yarn contained fibers of a unitary weight ratio of components for all filaments in the yarn. One yarn was a 150 denier PTT / PET yarn, which was then commingled with a 100 denier PTT / PET yarn. Each yarn was spun with 34 filaments. Thus, the resulting commingled yarn had a total of 68 filaments, with a denier per filament (dpf) of 250 divided by 68, or about 3.7. Tenacity for the commingled yarn was about 4 g / denier, with a maximum elongation of about 20%. Crimp contraction of the commingled yarn was about 60%.
example 2
[0025] A second yarn was produced in the same manner as generally described above, except that this 34 filament yarn included a mixed filament ratio from 70 / 30 to 30 / 70 weight percent of PET and PTT. The overall weight percent of PET to PTT in the yarn was about 50 / 50. The yarn was drawn 3.75×. Tenacity for the mixed filament ratio yarn was about 3.5 g / denier, with a maximum elongation of about 20% Crimp contraction was measured at about 45%.
example 3
[0026] A third yarn was produced in a manner identical to the yarn of Example 2, with the only exception that the yarn was drawn 4×. Tenacity, elongation and crimp contraction were all measured at about the same value as the yarn of Example 2.
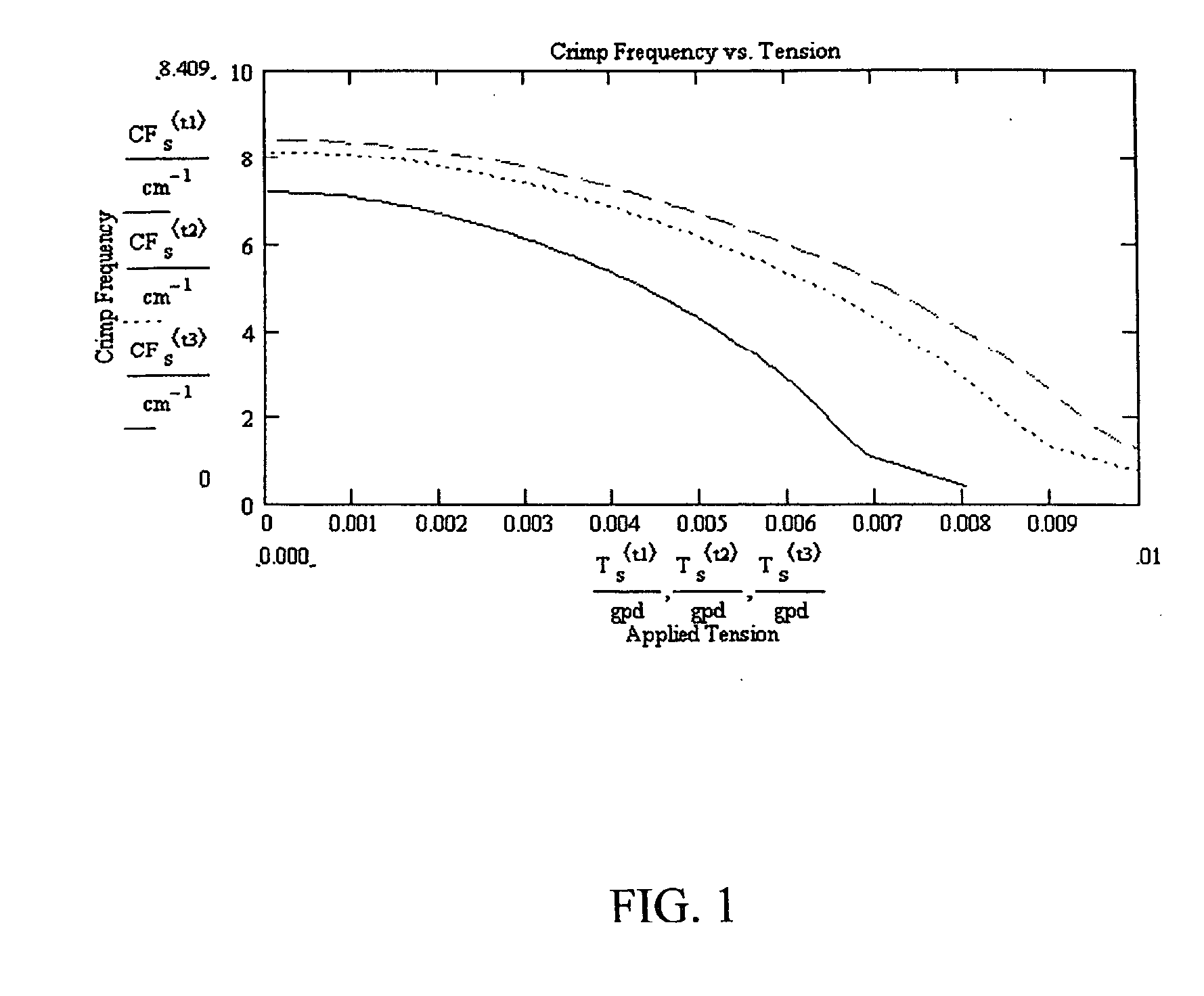
[0027] To evaluate yarns of mixed ratios, the crimp frequency of individual filaments having varying weight ratios was charted versus applied tension as shown in FIGS. 1 and 2.
[0028]FIG. 1 shows an analysis of three filaments comprising PET and PTT. The weight ratios vary between 30 / 70, 40 / 60, and 50 / 50. Crimp frequency, measured in the number of crimps per inch, is plotted on the y-axis as measured against increasing tension from 0 to .01 g / denier, in 1 mg / denier increments. Tensions typically seen in fabrics tend to be about 2 to 4 mg / denier. Over this range, the difference in crimp frequency between the 40 / 60 and 50 / 50 versions are about 4-5%, while the difference between the 30 / 70 and 50 / 50 mixture filaments is about 16-27%.
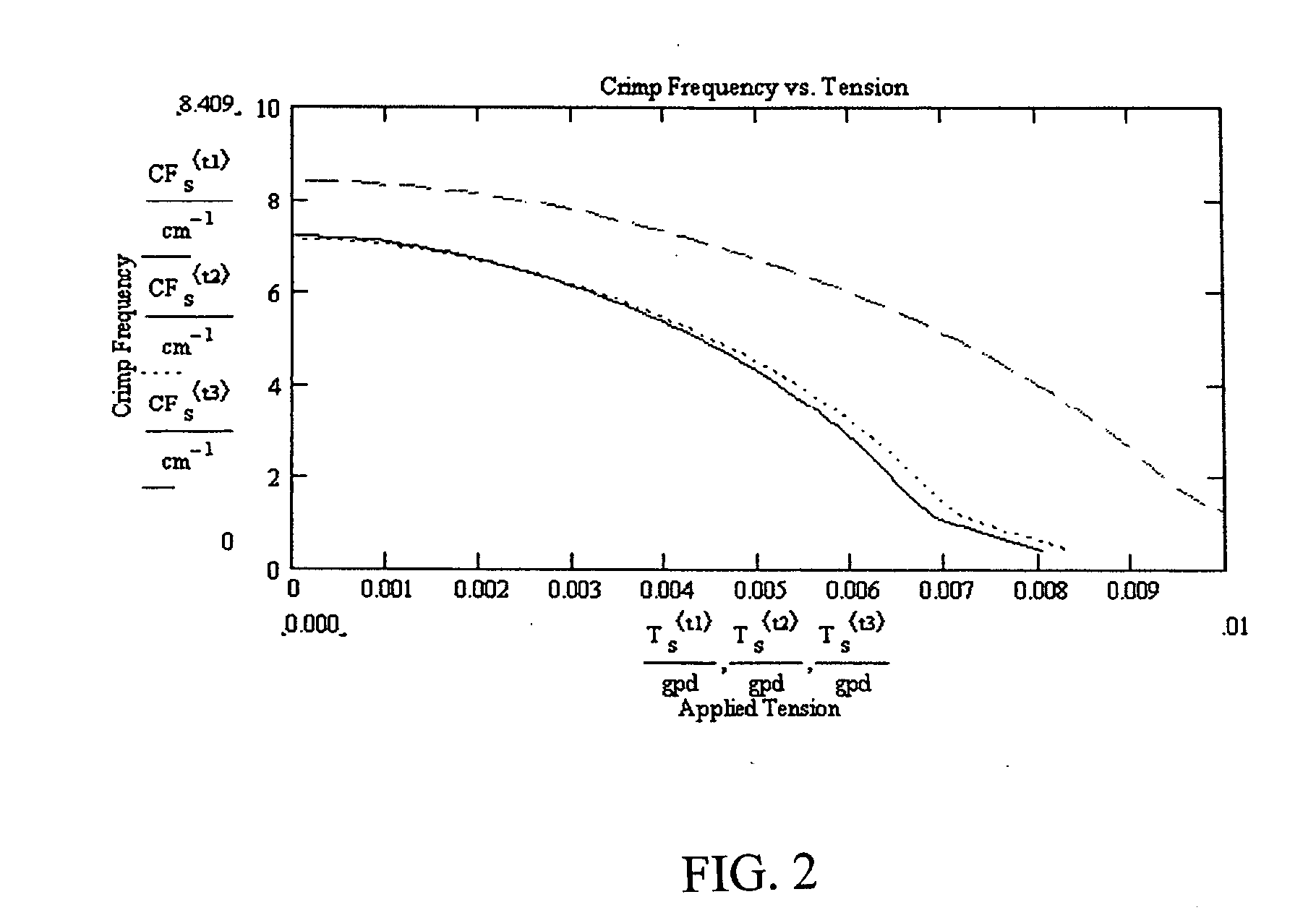
[0029]FIG. 2...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com