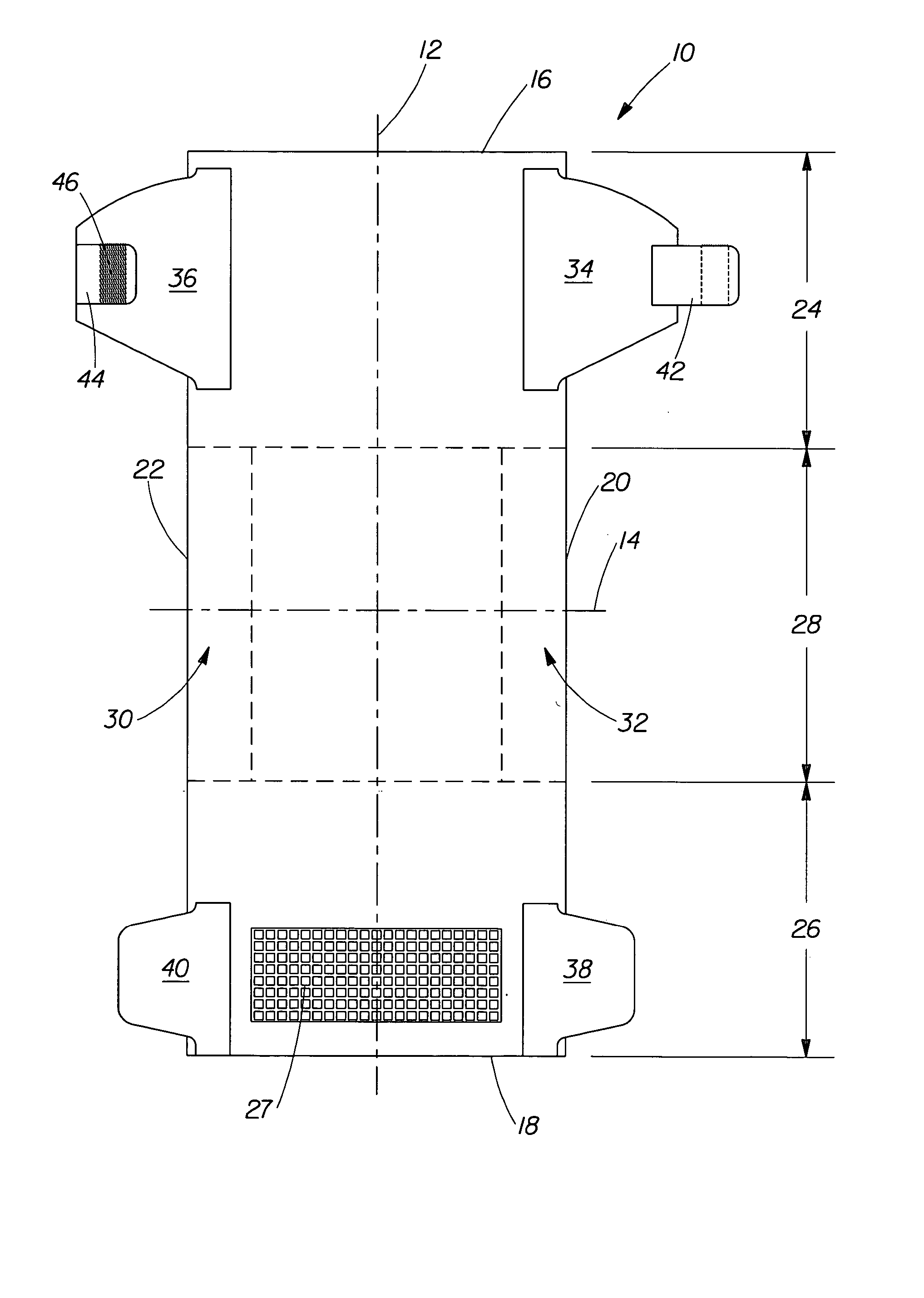
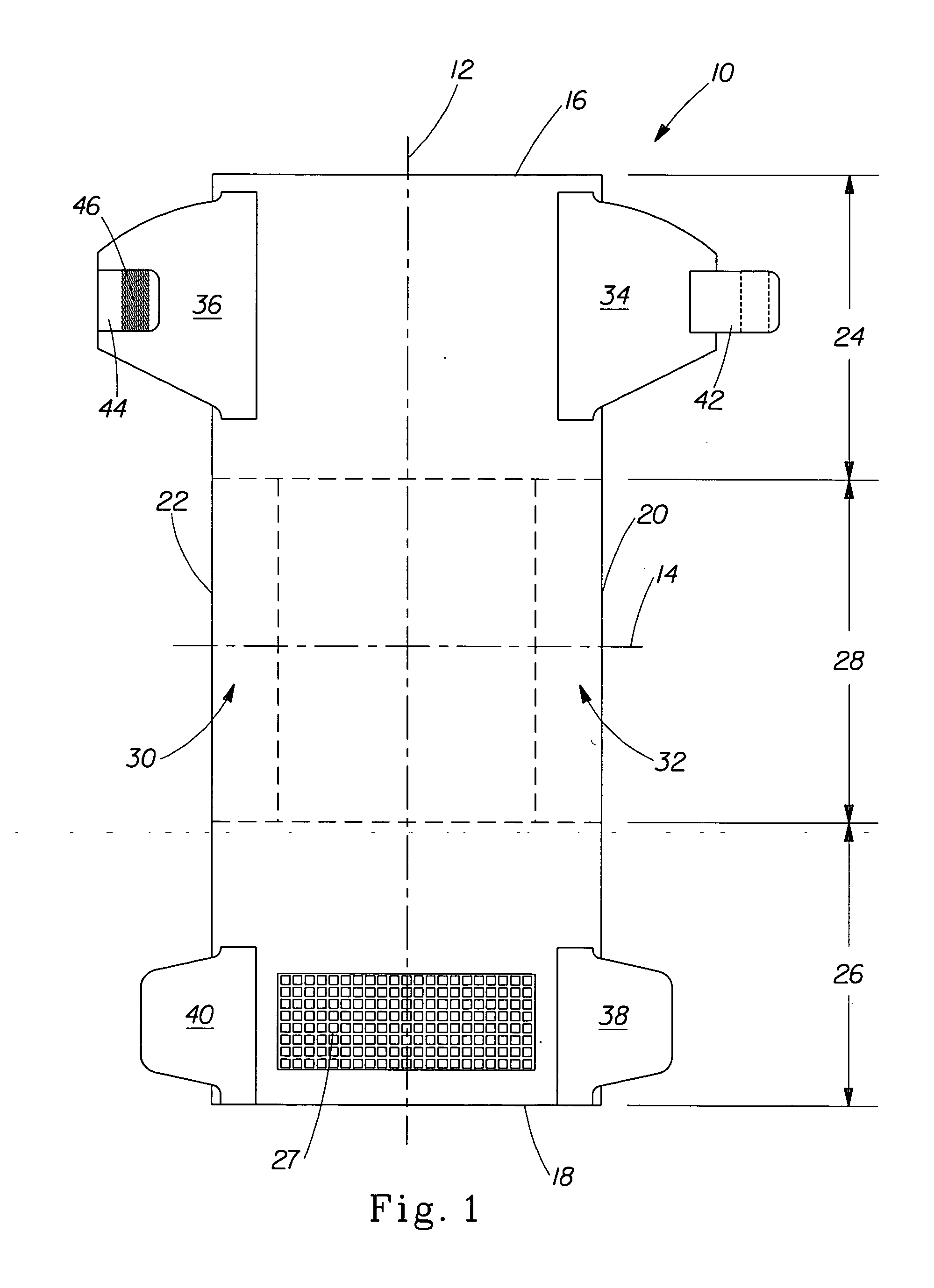
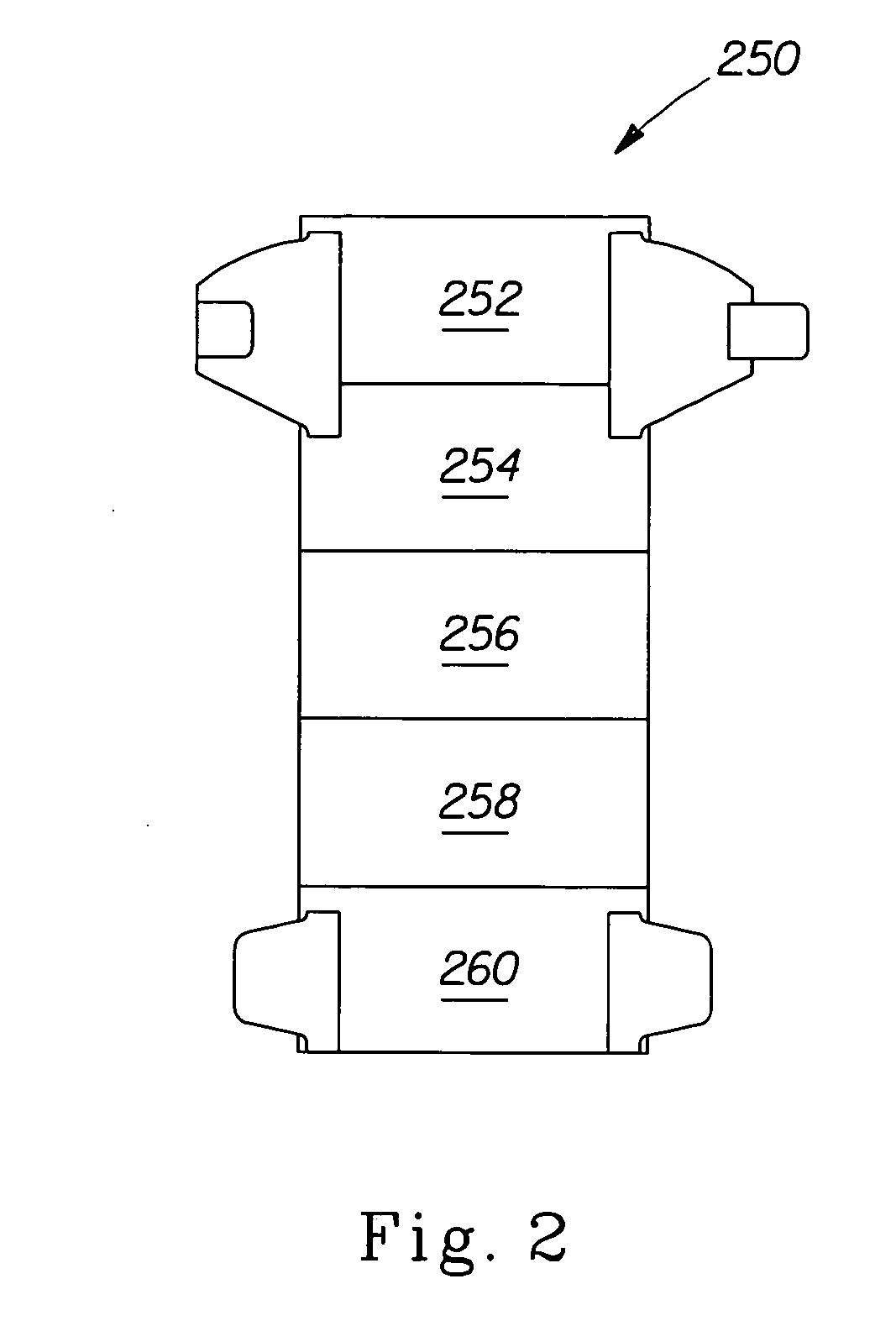
Disposable absorbent articles with zones comprising elastomeric components
a technology of elastomeric components and absorbent articles, which is applied in the direction of bandages, weaving, protective garments, etc., can solve the problems of discomfort of the wearer of the article, material insufficient ability to shape, size or conform to the particularities of the wearer's anatomy upon application, and the absence of features of absorbent articles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Definitions
[0026] The term “disposable” is used herein to describe absorbent articles that generally are not intended to be laundered or otherwise restored or reused as an absorbent article (i.e., they are intended to be discarded after a single use and, preferably, to be recycled, composted or otherwise disposed of in an environmentally compatible manner).
[0027] As used herein, the term “disposed” is used to mean that an element(s) is formed (joined and positioned) in a particular place or position as a unitary structure with other elements or as a separate element joined to another element.
[0028] As used herein, the term “joined” encompasses configurations whereby an element is directly secured to another element by affixing the element directly to the other element, and configurations whereby an element is indirectly secured to another element by affixing the element to intermediate member(s) which in turn are affixed to the other element.
[0029] A “unitary” absorbent article ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com