Aromatics transalkylation to ethylbenzene and xylenes
a technology of ethylbenzene and xylene, which is applied in the direction of hydrocarbons, chemistry apparatus and processes, organic chemistry, etc., to achieve the effects of increasing the selectivity of xylenes, promoting methyl-group species transalkylation, and reducing the overall yield of valuable xylenes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
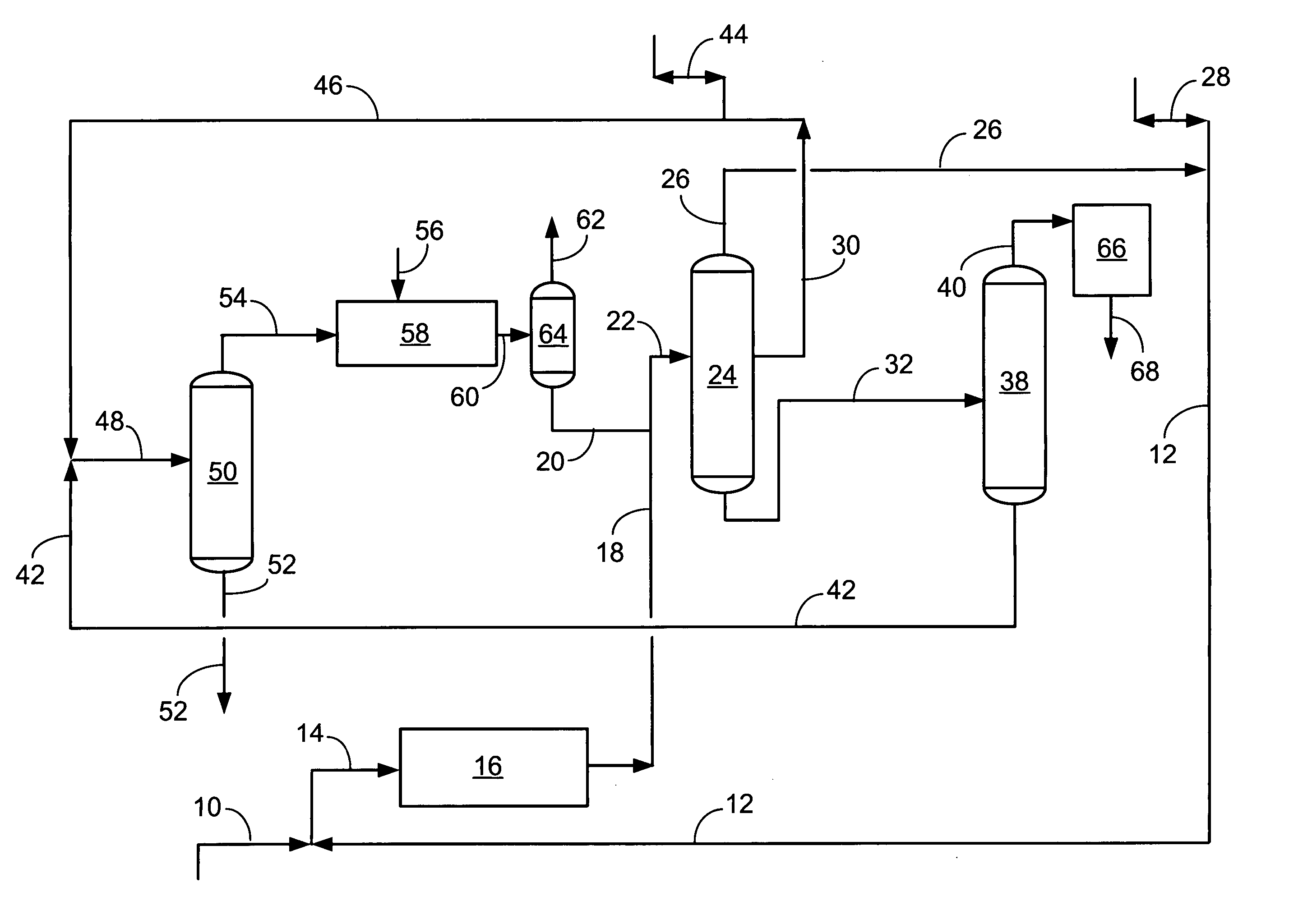
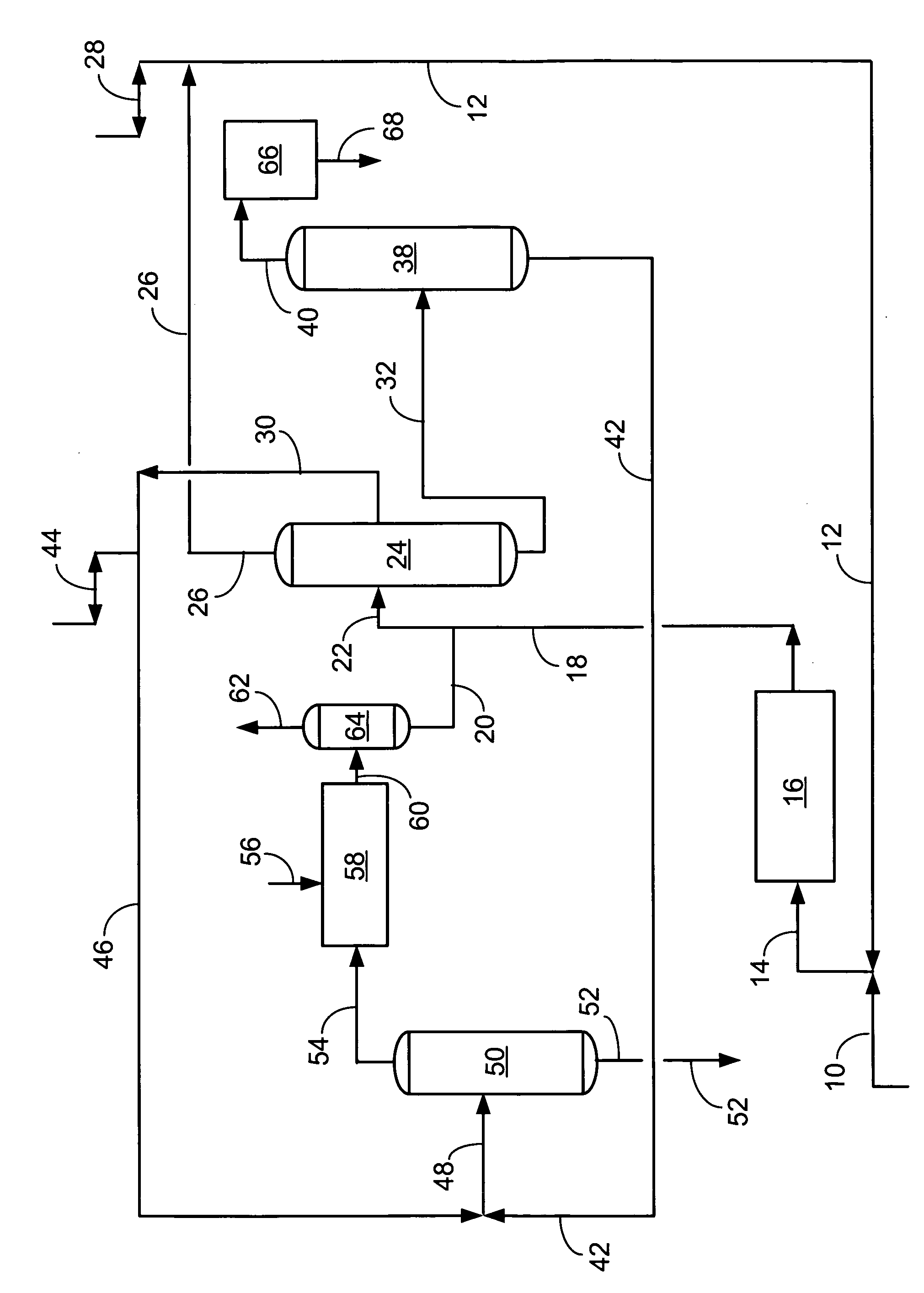
[0032] An increased selectivity to A8s at the expense of light ends has been demonstrated in pilot plant tests and is shown in the following material balance comparison. The prior art, gas-phase transalkylation process, is compared against the present invention, which combines a liquid-phase transalkylation process with a gas-phase process. This comparison shows the benefits of the present invention as increased xylenes and ethylbenzene, and concomitantly decreased benzene and light-end gas (especially ethane). By reducing the production of ethane by de-ethylation in gas-phase reactions within an aromatics complex, the invention provides improved total retention of aromatics relative to prior art transalkylation units used in complexes that produce xylenes.
[0033] With reference to the FIGURE, showing the flow scheme of the present invention, a simulated material balance is shown below. The liquid-phase transalkylation process unit is combined with the gas-phase transalkylation proc...
example ii
[0035] The unexpected transalkylation of methyl groups along with ethyl groups at the expense of light ends has been demonstrated in pilot plant tests with cylindrical down-flow liquid-phase reactors operated at a pressure of about 35 kg / cm2 and is shown in the following results. A stream of A9+ comprising about 75-wt% A9 and about 25 wt-% A10 with an endpoint around 200° C., contacted one of two catalysts comprising a zeolitic aluminosilicate of type Y or type Beta. A pure benzene stream was combined and fed to each catalyst in a different molar ratio with a A9+ stream. These results are summarized in the following table:
CatalystYBetaTemperature (° C.)250250WHSV (hr−1)9.59.5Benzene / Ag+4.31.1(mol / mol)Product Net Wt-%Ethylbenzene4.45.7Toluene5.47.2Xylenes3.34.2Non-Aromatics0.20.3Heavies1.42.5Benzene + A9 + A10 &4.9 (7.8)20.3 (18)(Tri-methylbenzene)conversion
[0036] Thus, the present invention provides a benefit by directly producing more of the desirable xylenes material and indirec...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com