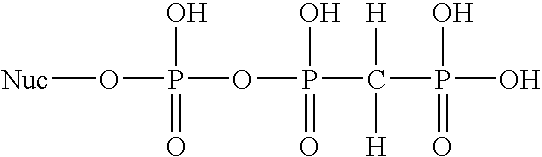
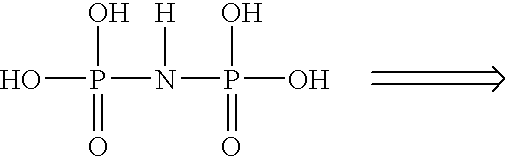
Detection of nucleic acid hybrids
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example
EXAMPLE 1
Comparison of Signal Strengths During Allele Determination Using Probes that Interrogate the Same DNA Strand Versus Probes that Interrogate Different Strands
[0455] Because DNA normally exists in a eukaryotic genome as a double-stranded polymer; in theory, allele discrimination could be performed by:
[0456] A) using probes that are essentially identical in sequence (except for an allele discriminating base) and that hybridize to the same DNA strand; or
[0457] B) using two probes that hybridize to different strands of DNA but match the sequence of only one allele of the gene at a position where the genotype is to be determined.
[0458] In this example, a comparison is made of the signal strengths of these two types of probes in distinguishing a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) target nucleic acid provided as a homozygous target for any known allele or as a heterozygous target containing different alleles.
[0459] Oligonucleotide PH1 (SEQ ID NO:1) is a probe that encodes a...
Example
EXAMPLE 2
Reduction of Probe-Alone Background Values for Probes Designed to Interrogate a Viral Sequence
[0468] In this example, the background light values from probe-alone reactions are reduced by alteration of reaction conditions. More specifically, the values from such background reactions are reduced by lowering the Klenow exo− level in the reactions as shown in Example 43. In addition, the probes are used to assay the relative probe signal strength values for probes that hybridize to the same DNA strand versus probes that hybridize to different strands but that interrogate the same nucleotide polymorphism site.
[0469] Oligonucleotides CV11 (SEQ ID NO:8) and CV12 (SEQ ID NO:9) are a pair of single-stranded DNAs that can hybridize together to produce a segment of the genome of cytomegalovirus (CMV) in a form sensitive to the drug gancyclovir. Oligonucleotides CV13 (SEQ ID NO:10) and CV14 (SEQ ID NO:11) are a pair of single-stranded DNAs that can hybridize together to produce the...
Example
EXAMPLE 3
Multiplex Analysis of Alleles at One Interrogation Site
[0479] For a wide variety of genetic disorders, only a very small percentage of samples will have a particular single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) at any one site. For this reason, it can be much more efficient in these cases to screen for the presence of groups of mutant alleles and to perform secondary, single probe tests only if there is a positive signal for any of the probes designed to detect the mutant sites. Such a form of multiplex analysis will be performed in this example.
[0480] Multiple probes designed to detect a mutant form of a gene in the CMV genome are used in one reaction and the signal from this reaction is compared to that from a probe that is specific for the non-mutated sequence. In this example, the SNP sites are separated by only one base and the alleles are provided as pure nucleic acid target species.
[0481] Oligonucleotides CV19 (SEQ ID NO:16) and CV20 (SEQ ID NO:17) encode a segment of th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electrical conductance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com