Method of stabilizing protein
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Measurement of Binding and Neutralizing Activities of Anti-Human TF Antibody Asn54 Substitution Mutant with TF
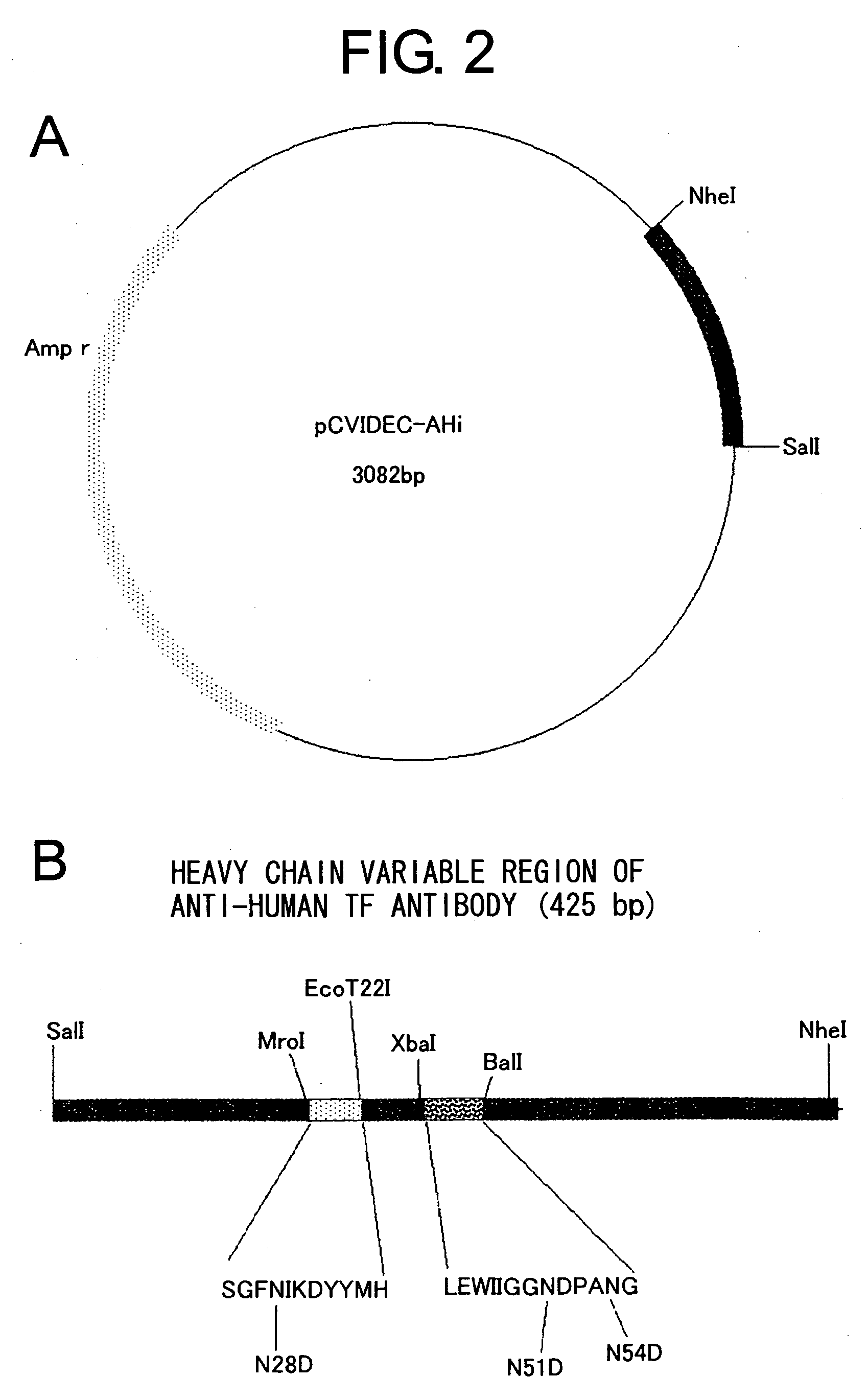
[0098] Humanized antibody against human tissue factor (TF) described in WO 99 / 51743 is expected to suppress thrombus formation without suppressing the extrinsic blood coagulation reaction through the inhibition of the TF mediated Factor X activation in the intrinsic blood coagulation reaction. This anti-human TF antibody contains humanized heavy chain version i (SEQ ID NO: 25, FIG. 1) and humanized light chain version b2 (SEQ ID NO: 26, FIG. 1). The antibody comprises a few asparagine residues that may be deamidated: such as Asn51 and Asn54 in CDR2 of the heavy chain variable region, and Asn28 in FR1 of the heavy chain variable region. Particularly, Asn54 is contained in an Asn-Gly sequence, and thus is considered to be easily deamidated.
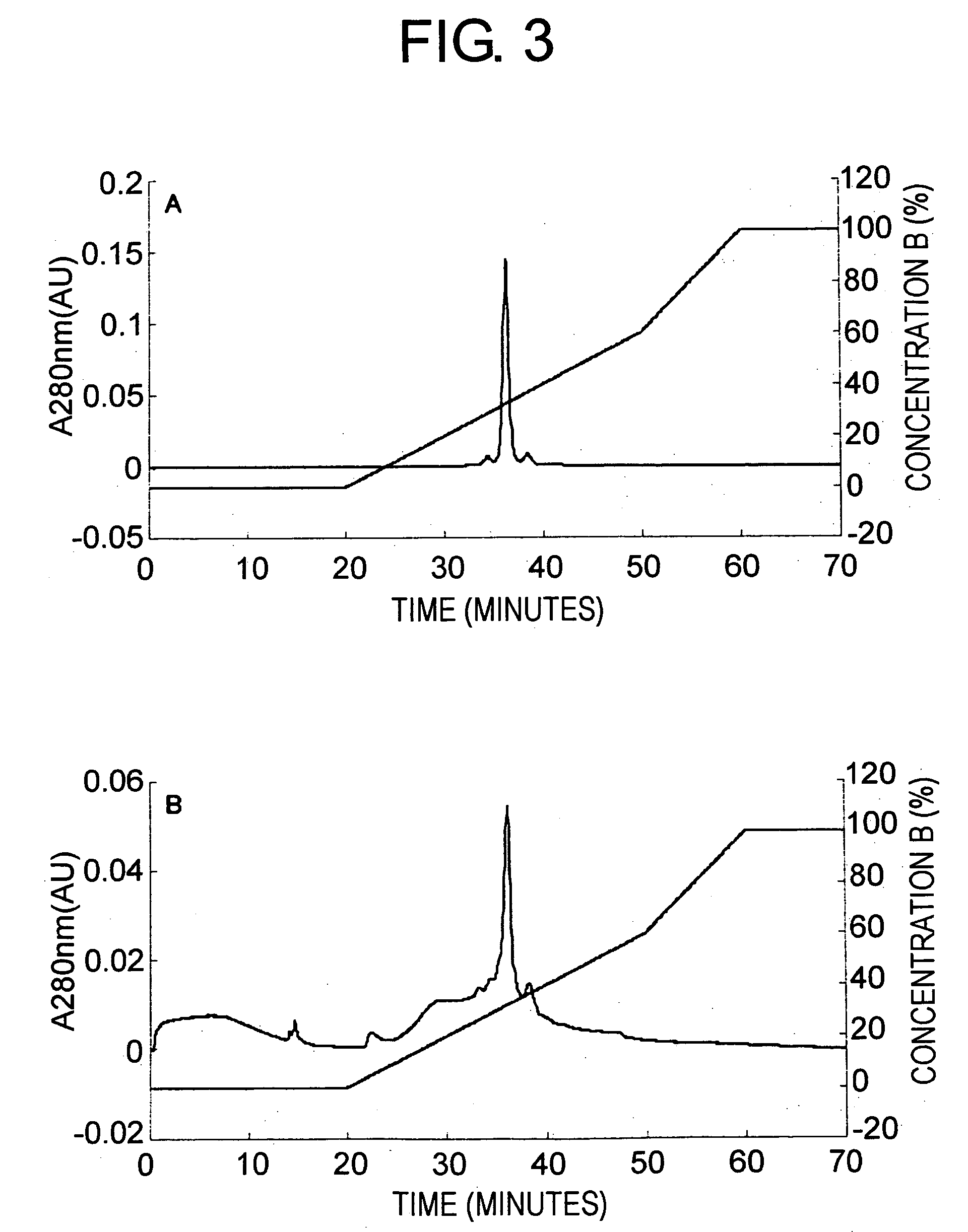
[0099] Pharmaceutical formulation of the antibody has not been established. Under destabilizing conditions of the antibody, the antibody ...
example 2
Measurement of TF Binding and Neutralizing Activities of Gly55 Substitution Mutant of Anti-Human TF Antibody
[0133] The anti-human TF antibody described in WO 99 / 51743 contains the humanized heavy chain version i (SEQ ID NO: 25, FIG. 1) and the humanized light chain version b2 (SEQ ID NO: 26, FIG. 1). Based on its amino acid sequence, mutants were prepared wherein the Gly55 in the heavy chain CDR2 that is considered as an important amino acid in the construction of the loop of CDR2 had been substituted with 19 other amino acids. Then, the binding activity of each mutant with TF was measured. Furthermore, the neutralizing activity and deamidation was observed for the mutants wherein Gly55 had been substituted with Ile, Leu, Phe, Glu and Lys.
[0134] The amino acid sequence of the antibody based on the sequence described by Kabat et al. (Kabat E. A., Wu T. T., Perry H. M., Gottesman K. S. and Foeller C., “Sequences of proteins of immunological interest. 5th ed.”, US Dept. Health and Hu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com