Method for adding chemicals to a nonwoven material
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1a
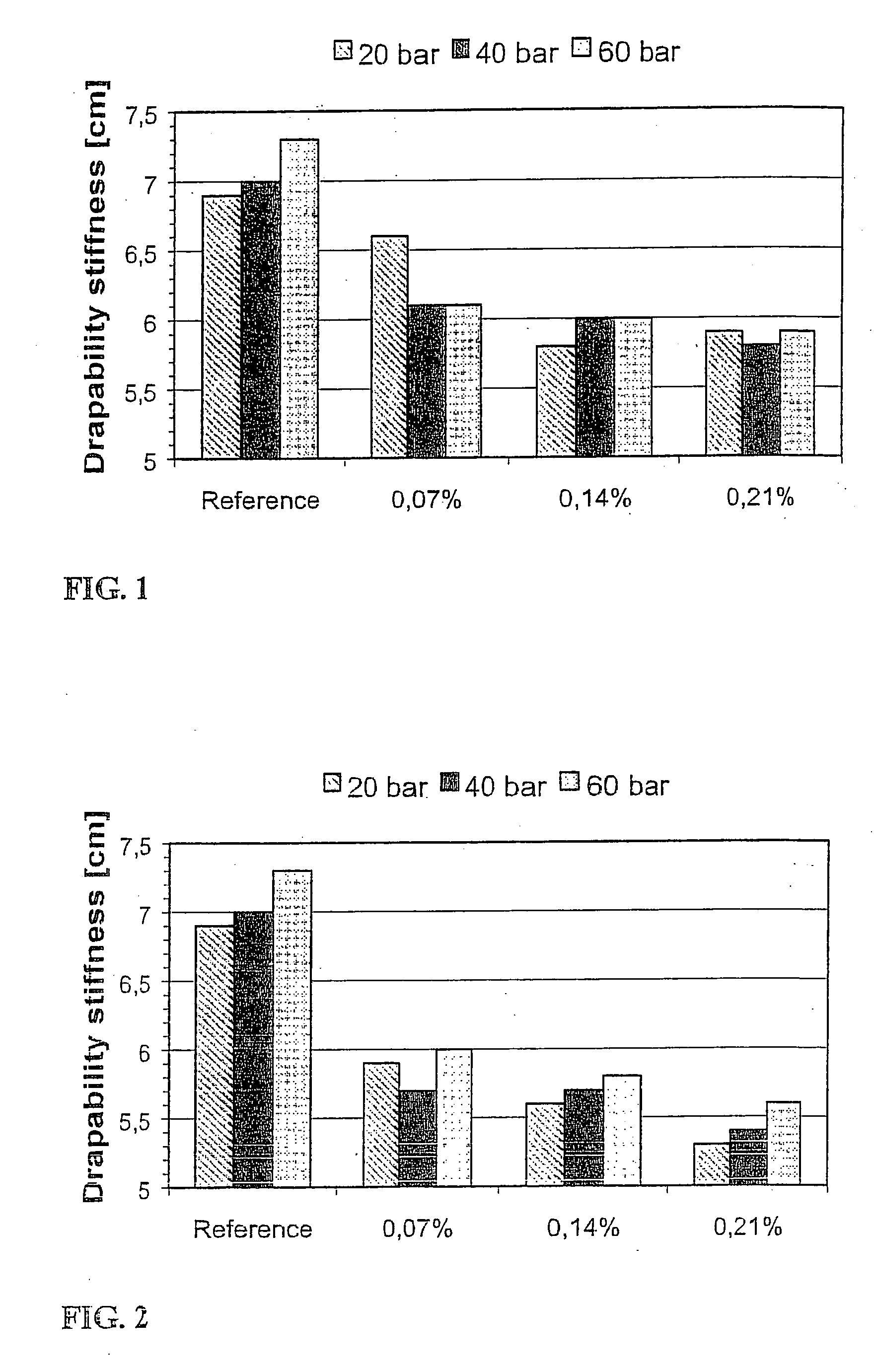
[0050] In Example 1, two different softening agents which enhances bulk softness and surface smoothness were evaluated, Berocell 589 and XP 7026 supplied by Eka Chemicals. The Berocell 589 is an additive in the manufacture of fluff pulp and is a mixture of cationic and nonionic surfactants and comprises alkyl-benzyl-dimethyl ammonium chloride and fatty alcohol ethoxylate. XP 7026 is a softener for tissue and also a mixture of cationic and nonionic surfactants and comprises benxyl-dimethylammonium chloride. The concentration of the softening agents in the hydroentanglement water was 0.07%, 0.14% and 0.21% by volume. This would result in a corresponding concentration of about maximum 0.2%, 0.4% and 0.6% by weight in the fiber material, if a complete exchange to the hydrojet liquid occurs.
[0051] As the spunlace materials were treated with a softening agent, the experience of a much softer material in the hand was obtained. Softness in relation to the drapability stiffness and the tens...
example 1b
[0055] In order to even more show the surprising results and effects of the method in accordance to the invention, it was also compared to results achieved by conventional technique where the chemical additive is added in the wet end.
[0056] The reference used and shown in table 4 has of course the same corresponding nonwoven material, fiber composition and basis weight as used in example 1a as well as in example 2. The reference is thus a nonwoven web with a basis weight of about 87 g / m2 consisting of 60% cellulose pulp fibers and 40% polyester fibers (T-100) supplied by KOSA, 1.7 dtex, 19 mm long. The web was prepared by wet laid technology in a dynamic sheet former and subsequently bonded by hydroentanglement at high pressure of about 100 bar on both sides and about 300 kWh / ton at a speed of about 140 m / min.
[0057] For the first sample no chemical was added to the wet end or to the hydroentanglement water. In the second sample a softening agent was added to the slurry. The soften...
example 2
[0059] In the second example the chemical tested and evaluated was a wet strength resin, Kenores 1445, a polyamidoamine-epichlorohydrin resin (PAE), supplied by EKA chemicals.
[0060] Three different dilute solutions of the wet strength resin in the hydrojet liquid were used corresponding to 0.07%, 0.14% and 0.21% by volume. This would result in a corresponding concentration of about maximum 0.2%, 0.4% and 0.6% by weight in the material, if a complete exchange to the dilute solutions used in the hydrojet treatment occurs. The hydrojet treatment was done at three different hydrojet pressures corresponding to 20, 40 and 60 bars.
[0061] When the spunlace nonwoven materials were treated with the wet strength resin, a significant reduction of linting was observed. The wet linting method used to characterize the linting was the bi-axial shake linting. The results of the bi-axial linting are shown for the wetlaid spunlace material hydrojet treated with Kenores 1445 wet strength resin as a f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com