Segmented cold formed joist
a technology of joists and joints, applied in the field of joists, can solve the problems of increasing the cost of process, increasing the cost of production, and difficulty in achieving the effect of providing sheer bonding capacity between the joist and the concrete in the composite joist,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0066] In the description that follows, like parts are marked throughout the specification and the drawings with the same respective reference numbers. The drawings are not necessary to scale and in some instances proportions may have been exaggerated in order to more clearly depict certain features of the invention.
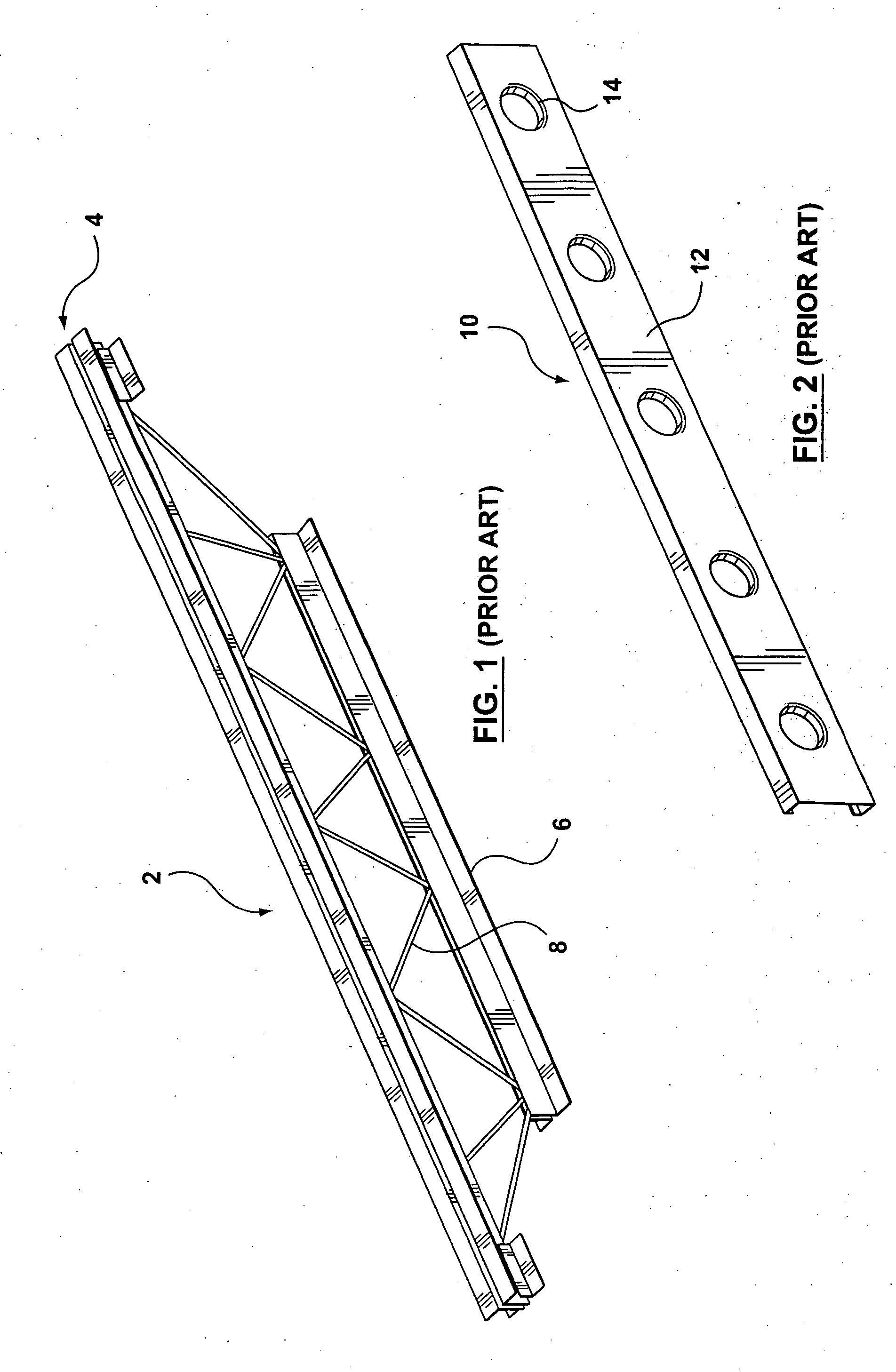
[0067]FIG. 1 illustrates a prior art open web joist construction 2 consisting of an upper chord assembly 4 spaced from a lower chord assembly 6. The chords are joined together by a zig zag web 8 which is generally connected to the upper and lower chord assembly 6 by a number of means including welding or the like.
[0068]FIG. 2 illustrates a prior art cold formed joist construction 10 having a web portion 12 having a plurality of holes 14 disposed there through for receiving utility such as wire or the like.
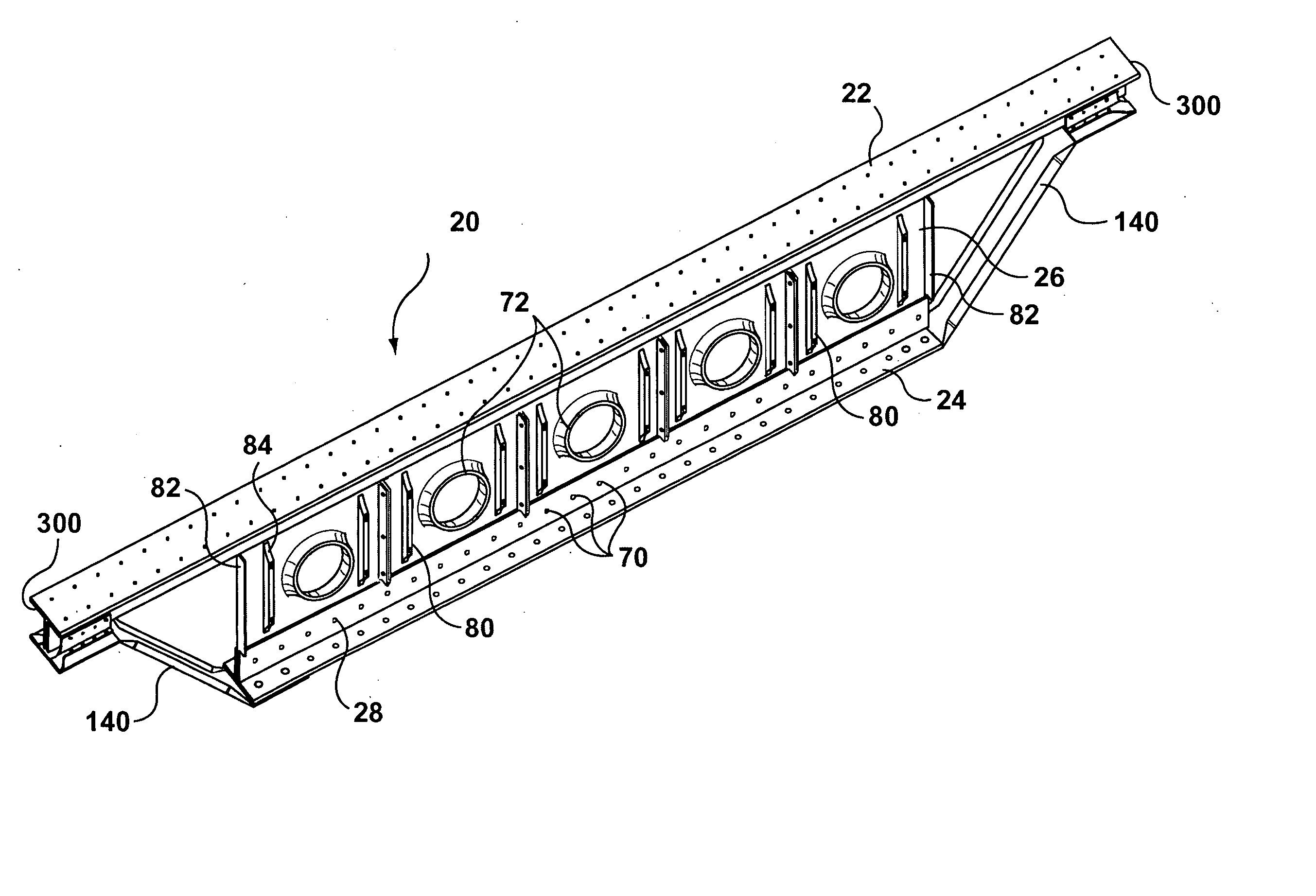
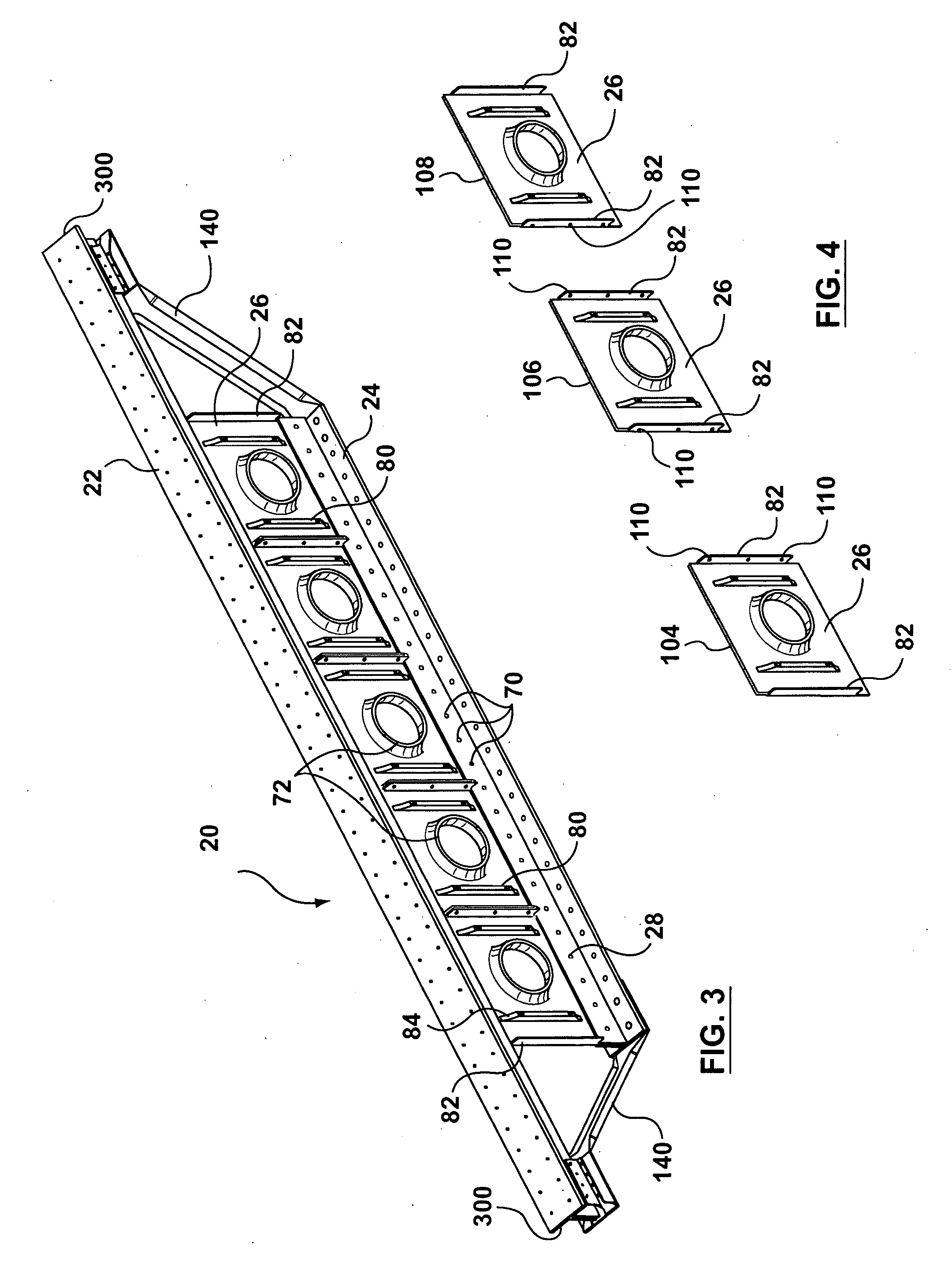
[0069]FIG. 3 illustrates one embodiment of the invention which comprises an assembled joist 20 having a first or upper chord member 22 spaced from a second or lower ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com