Frequency hopping sequence allocation
a frequency hopping sequence and frequency hopping technology, applied in the field of telecommunications, can solve the problems of affecting the signal quality of the radio signal, the likelihood of receiving the signal, and the frequency hopping sequence being so as to minimize the risk of collision between fhss assigned to potentially strong interferers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
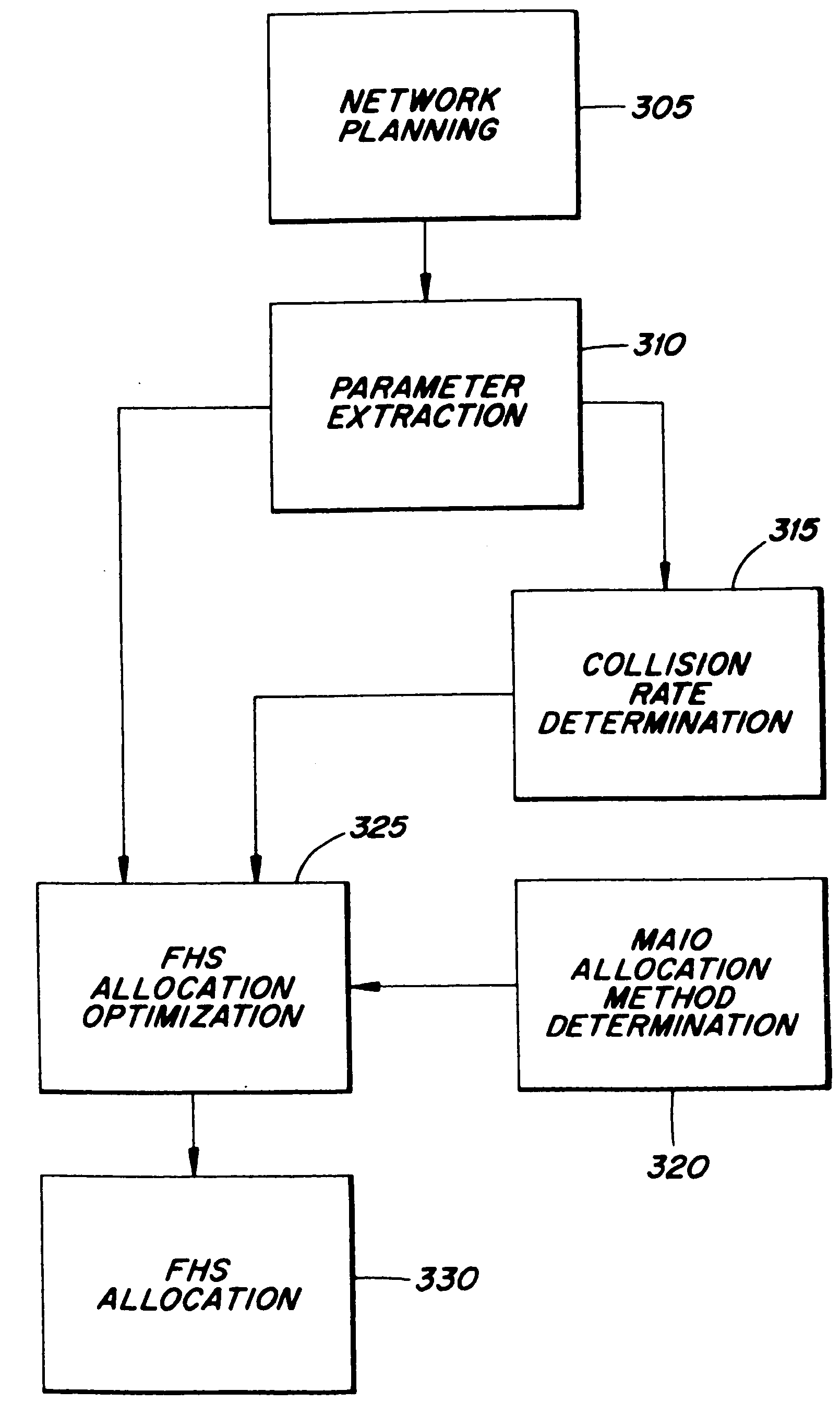
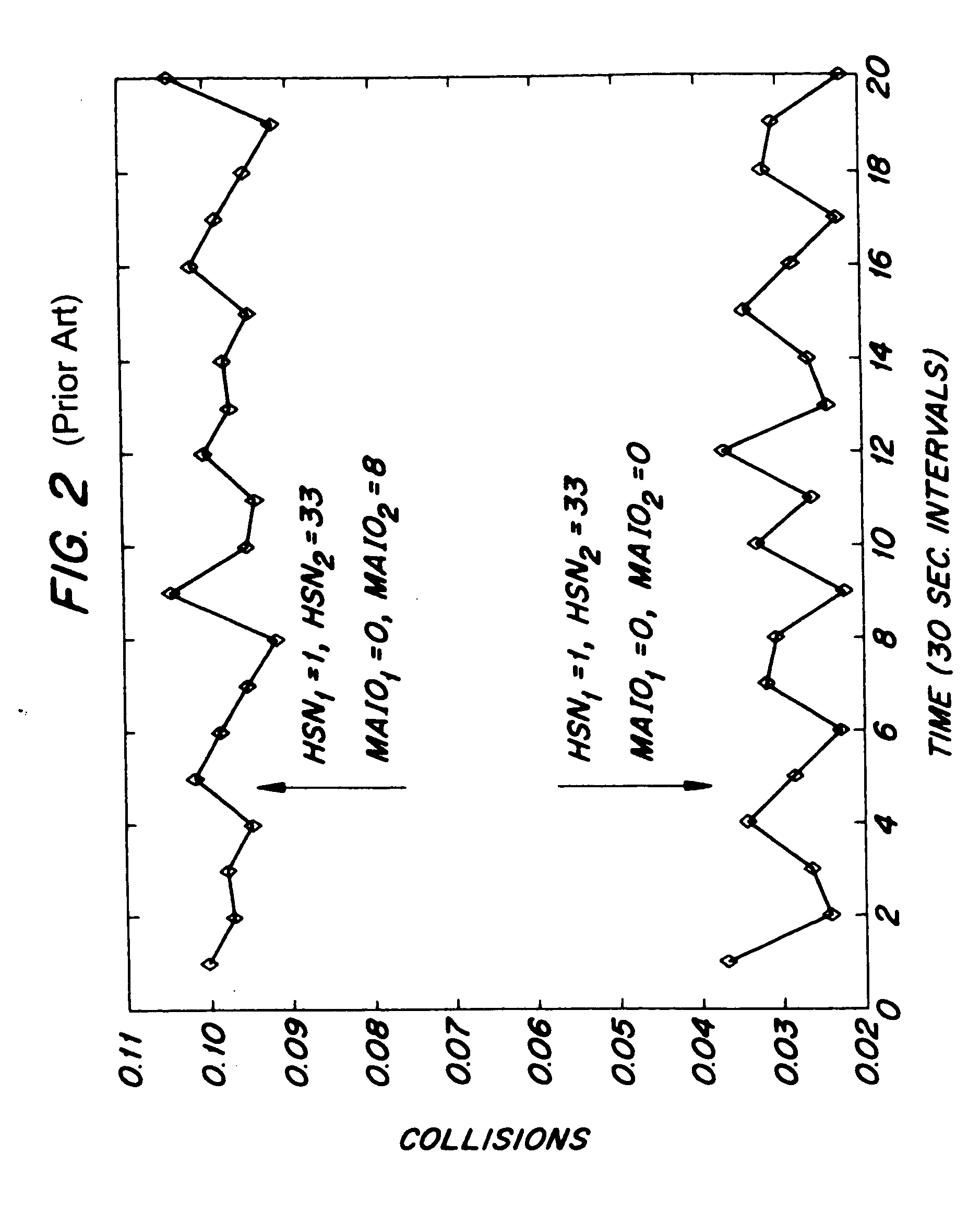
[0026] The present invention involves the allocation of, and ultimately the assignment of, FHSs in a radio telecommunications system, such as the GSM, which employ frequency hopping to enhance signal quality and improve network performance. In accordance with exemplary embodiments of the present invention, the allocation and assignment of FHSs is, in part, based on a level of interaction between FHS pairs, where the level of interaction between a pair of FHSs is measured in terms of a collision rate, or more precisely, a probability of collision between the two FHSs which make up the FHS pair. While the thrust of the present invention is to effectively allocate and assign FHSs based on collision rate information, additional factors may be considered, as explained in greater detail below.
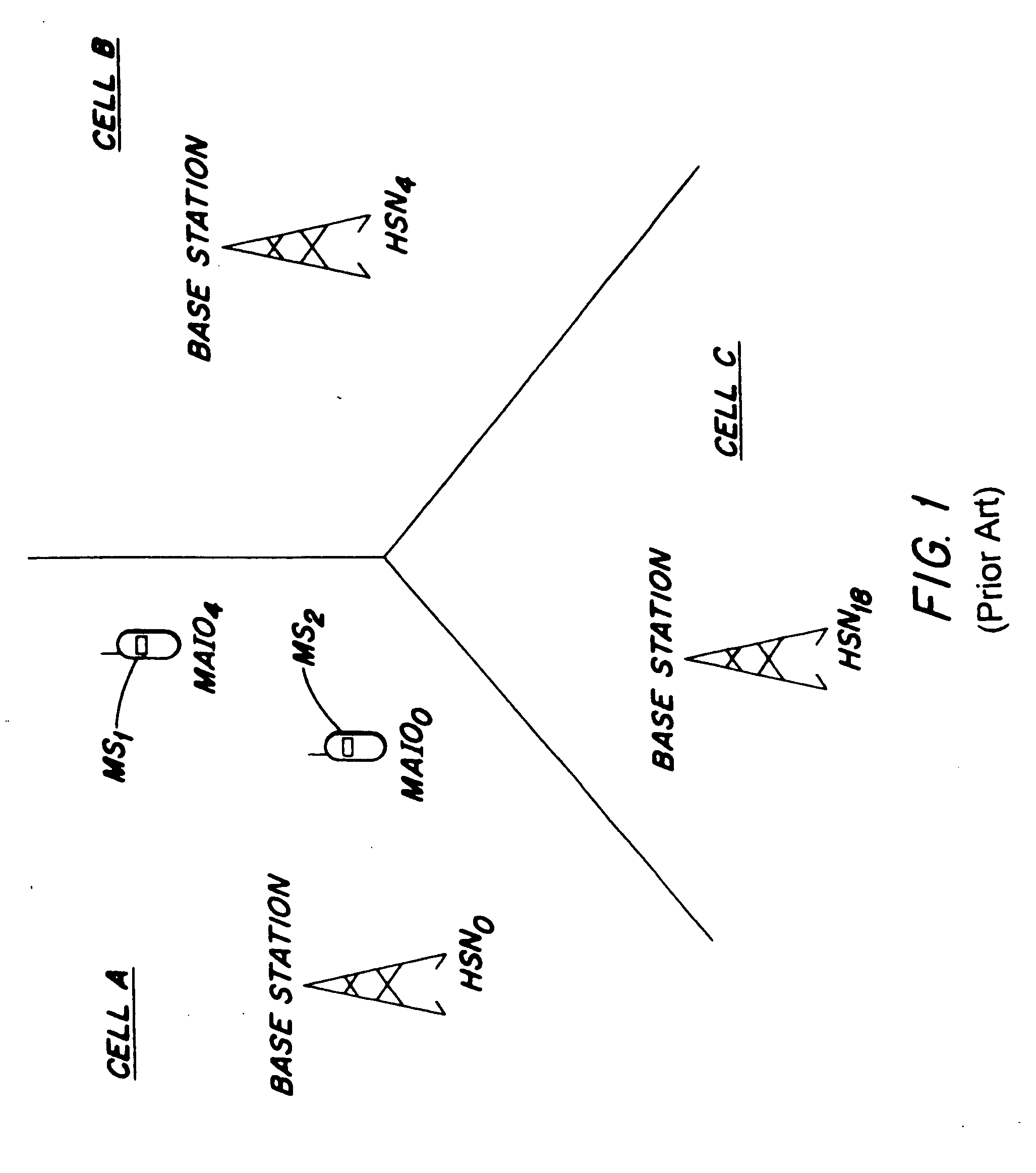
[0027] Each FHS, as explained above, is defined, in whole or in-part, by a HSN and a MAIO. In a cellular system, such as the GSM, each cell is assigned a HSN, whereas each end-user or mobile station...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com