Two-phase, water-absorbent bioadhesive composition for delivery of an active agent to a patient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
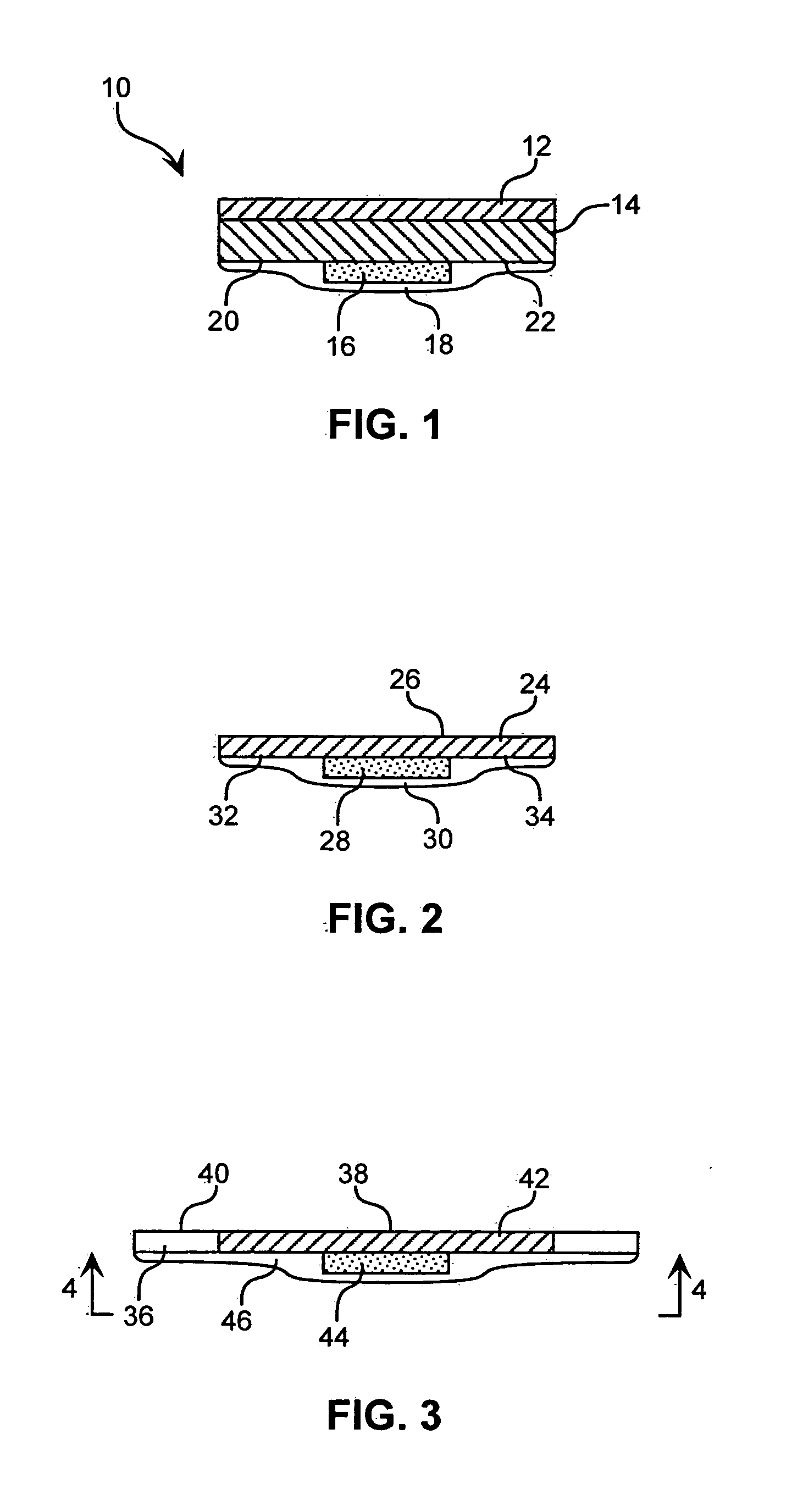
In a first embodiment, an adhesive composition is provided that combines the properties of a hydrophobic PSA with the advantages of a hydrophilic adhesive composition. The composition is comprised of a hydrophobic phase and a hydrophilic phase, wherein the hydrophobic phase includes at least one hydrophobic polymer, and the hydrophilic phase, dispersed or otherwise contained therein, is comprised of a mixture of a hydrophilic polymer and a low molecular weight complementary oligomer capable of hydrogen bonding thereto. The low molecular weight complementary oligomer may also serve to crosslink the hydrophilic polymer via ionic and / or covalent bonding.
A. The Hydrophobic Phase
The hydrophobic phase is comprised of at least one hydrophobic polymer. The hydrophobic polymer is typically a hydrophobic pressure-sensitive adhesive polymer, preferably a thermosetting polymer. Preferred hydrophobic PSA polymers are crosslinked butyl rubbers, wherein a “butyl rubber,” as well known in the ar...
example 1
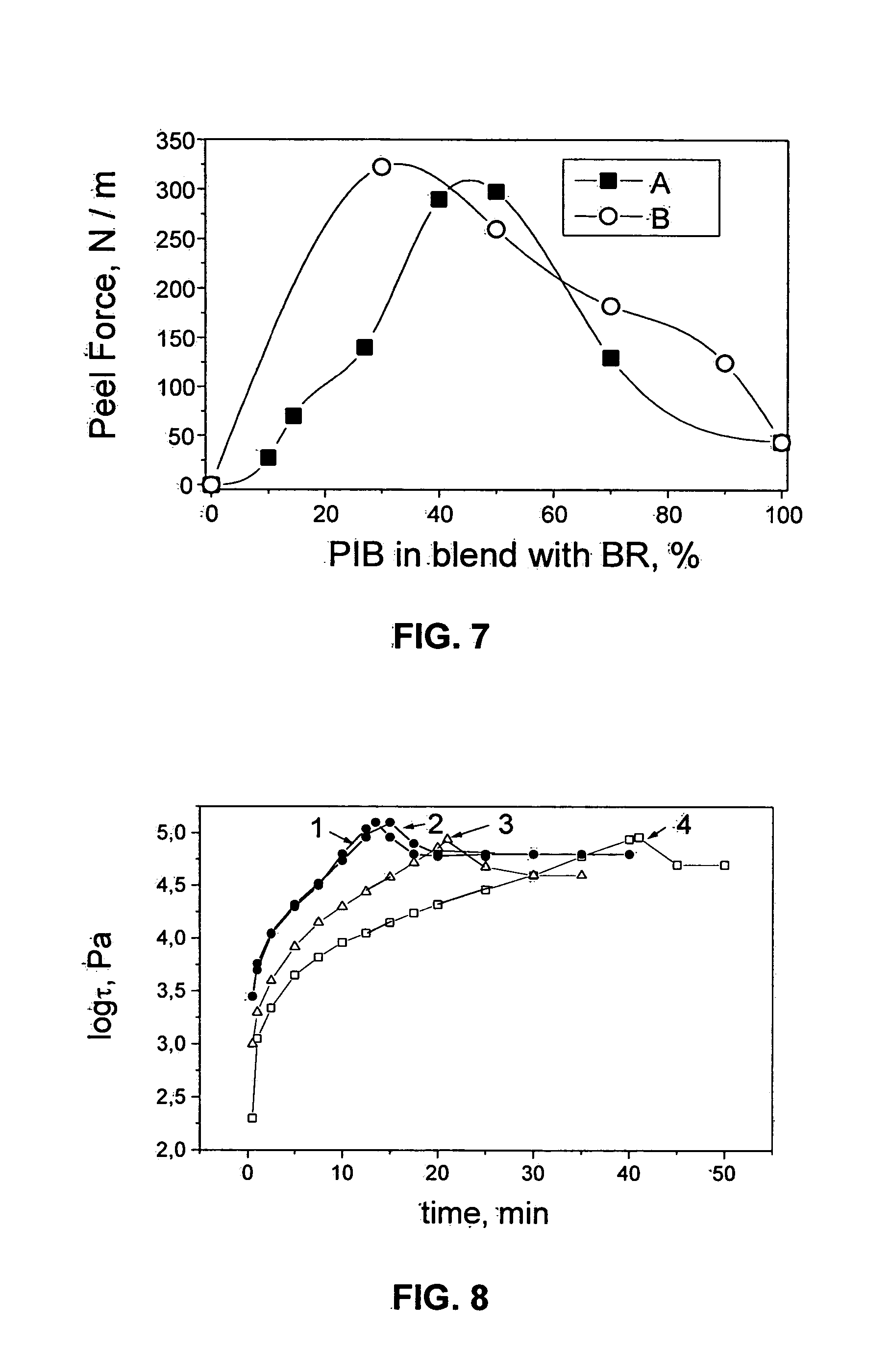
The following example describe formulation of a pressure-sensitive adhesive composition based on a cured blend of polyisobutylene with butyl rubber with PVP-PEG water sorbents, and optionally with cellulose-based water sorbents, to form a two-phase adhesive matrix.
Mixing procedures for the adhesive blend: Two methods of mixing were used: a laboratory mixer of rotor-plunger type (I) and a Haake mixer supplied with a sigma-blade and Banbary rotors (II). With the latter method, a sample is loaded into a working chamber and heated to the desired temperature, at which point a rotating agitator was introduced to a predetermined depth to mix the composition. This procedure was repeated several times to obtain a homogeneous mixture. The temperature-time regime of mixing depended on the components used, particularly on the curing agent used. Usually, mixing may be carried out at a temperature >100° C. However, if Br-APFR was used as the curing agent, the temperature was decreased to 60° C...
example 2
Curing a PVP-PEG hydrogel dispersed within the hydrophobic polymer:
Cured PVP-PEG hydrogels were found to be highly hygroscopic. At relatively low degrees of hydration, these hydrogels provide adhesive and viscoelastic properties that allow them to be used for SCA matrices in cushion patches. If, however, such hydrogels absorb more than about 15% water, they swell so much that they become unsuitable for cushion usage. In order to decrease the PVP-PEG hydrogel hygroscopicity, it was found useful to mix the hydrogel with an appropriate hydrophobic adhesive. The following experimental work was carried out to determine conditions under which such mixtures can be cured so that they become viscoelastic at room temperature and have adhesive properties suitable for use in cushion pads. In these experiments, a PVP-PEG hydrogel was mixed with a PIB-BR-Regalite adhesive. UV-curing to produce PVP-PEG crosslinking, employing dipentaerythritol monohydroxy pentaacrylate SR 399 (Sartomer) as curi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hydrophilicity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com