Semiconductor memory device with magnetoresistance elements and method of writing data into the same
a magnetic resistance element and memory device technology, applied in semiconductor devices, digital storage, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of increasing the chip size of the conventional mram, and achieve the effect of increasing the chip siz
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
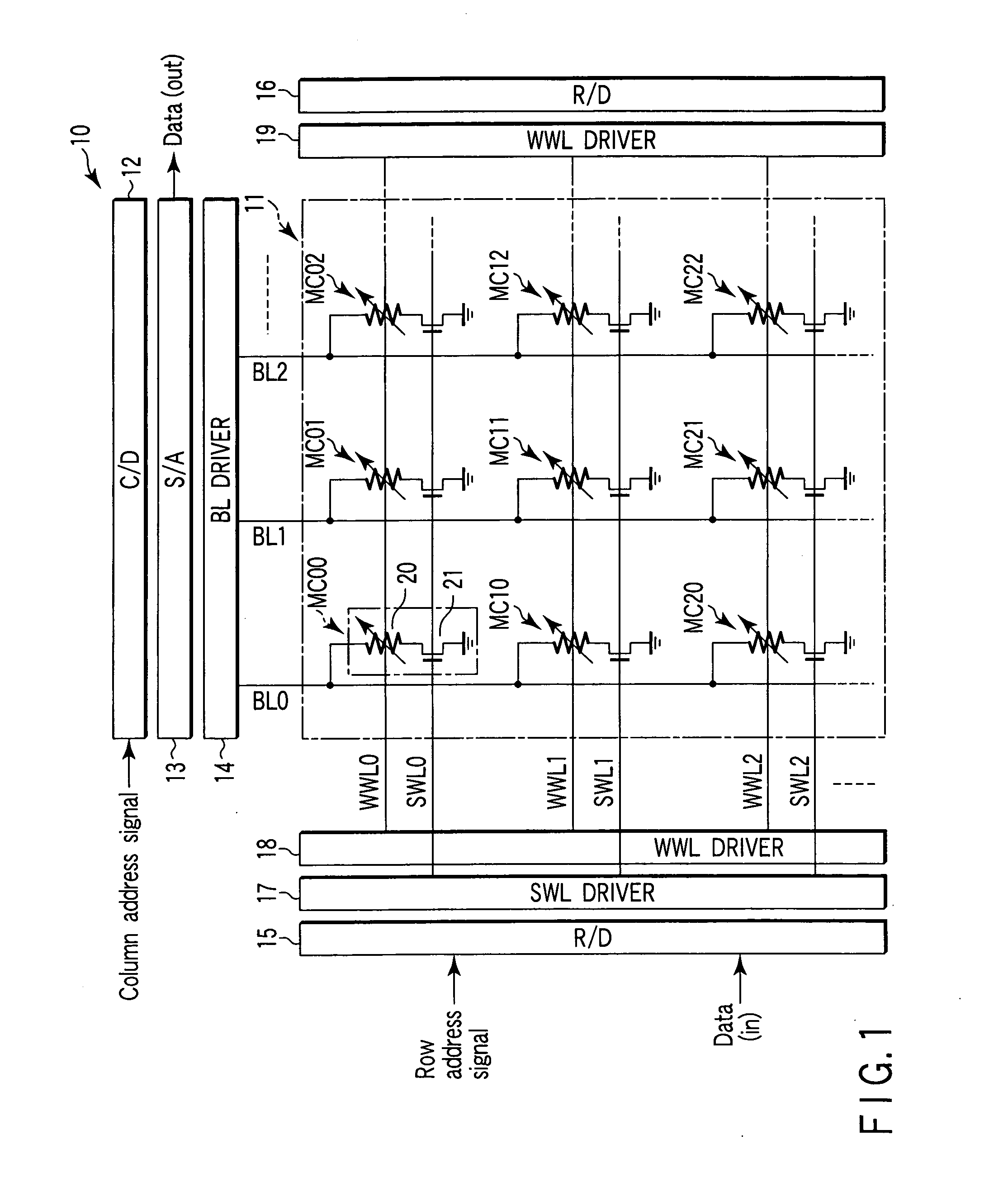
[0099] Next, the operation of the MRAM configured as described above will be explained by reference to FIGS. 1 and 4. A write operation will be explained using a case where data is written into memory cell MC11 provided at the intersection of bit line BL1 and select word line SWL1 (write word line WWL1). FIG. 4 is a flowchart for a write operation in the MRAM of the
[0100] First, the select word line driver 17 selects select word line SWL1 on the basis of a row address decode signal. Then, the select word line driver 17 supplies a voltage to select word line SWL1. This brings the switching transistors 21 of the memory cells MC10, MC11, MC12, . . . , MC1n into the on state (step S1).
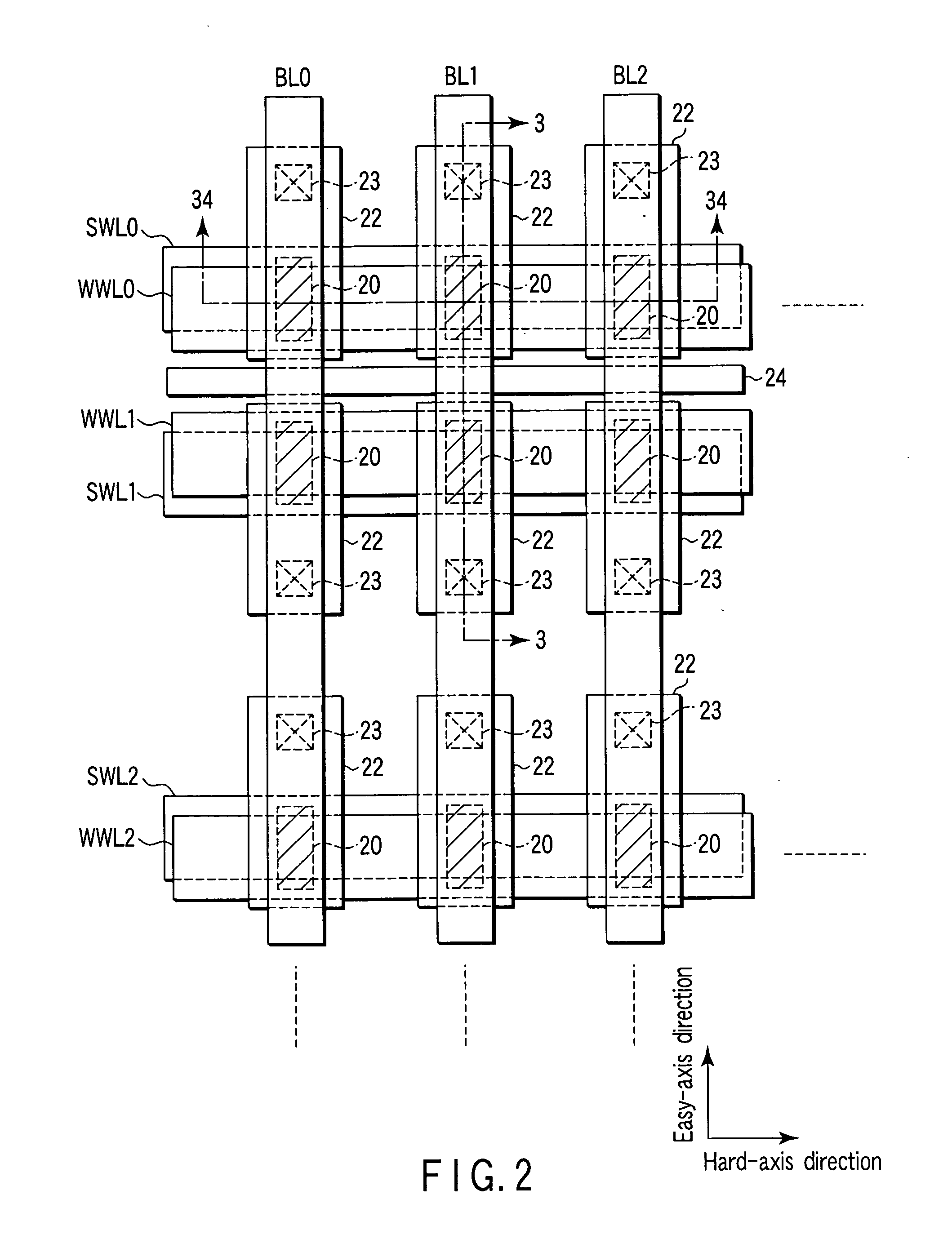
[0101] Next, the bit line driver 14 selects bit line BL1 on the basis of a column address decode signal. Then, the bit line driver 14 supplies a current Iselect of about 10 μA to bit line BL1 (step S2). This is shown in FIG. 5. FIG. 5 is a circuit diagram of a part of the memory cell array 11.
[0102] As s...
second embodiment
[0154] With the data writing method after a write select word line is selected, current is caused to flow in the write word line, with tunnel current flowing in the bit line connected to the memory cell into which “0” data is to be written, thereby writing “0” data. Then, with tunnel current flowing in the bit line connected to the memory cell into which “1” data is to be written, opposite current is caused to flow in the write word line, thereby writing “1” data. By the series of processes, the data has been written into all of the memory cells connected to the same write select word line.
[0155] Moreover, in a read operation, the data held in plurality (all) of the memory cells connected to the same select word line can be read simultaneously by causing current to flow in a plurality of (all) bit lines.
[0156] Accordingly, a plurality of data items can be processed at a time, which enables a high-speed operation. Moreover, when image data or the like is handled, it is desirable th...
third embodiment
[0169] Next, the operation of the MRAM configured as described above will be explained by reference to FIGS. 17 and 20. A write operation will be explained using a case where data is written into memory cell MC11 provided at the intersection of bit line BL1 and select word line SWL1 (write word line WWL1). FIG. 20 is a-flowchart for a write operation in the MRAM of the
[0170] First, in step S31 of FIG. 20, current Iselect is caused to flow from bit line BL1 connected to select memory cell MC11 to select word line SWL1 via the tunnel junction of the magneto-resistive element 20. Specifically, the select word line driver 17 selects select word line SWL1 on the basis of a row address decode signal. At this time, the select word line driver 17 functions as a current sink. Next, the bit line driver 14 selects bit line BL1 on the basis of a column address decode signal. Then, the bit line driver 14 supplies a current Iselect of about 100 μA to bit line BL1. This is shown in FIG. 21. FIG. 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com