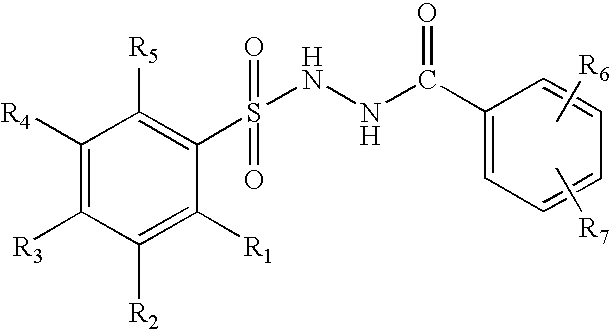
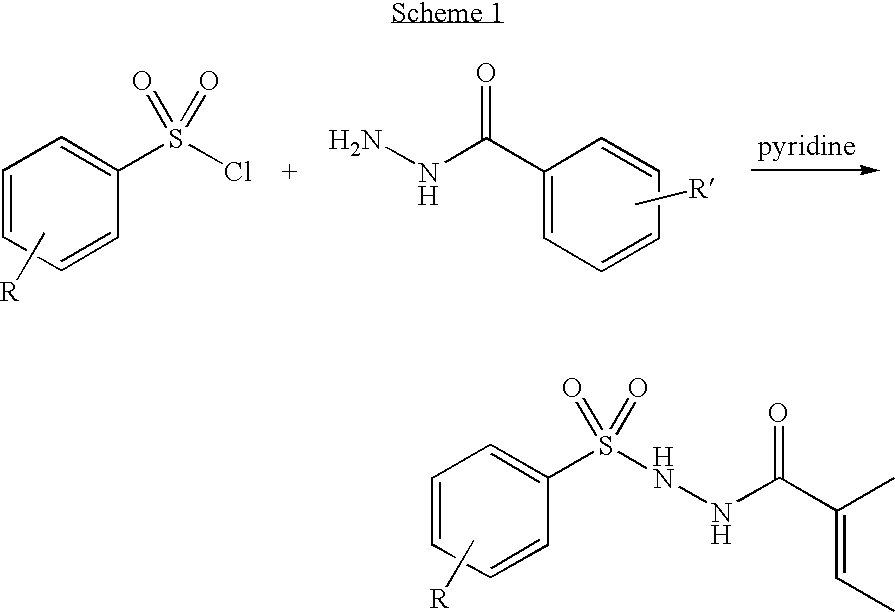
Branched chain amino acid-dependent aminotransferase inhibitors and their use in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
a technology of aminotransferase and branched chain amino acid, which is applied in the direction of biocide, drug composition, metabolic disorder, etc., can solve the problems of neurodegeneration and death, and achieve the effect of preventing neuronal loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
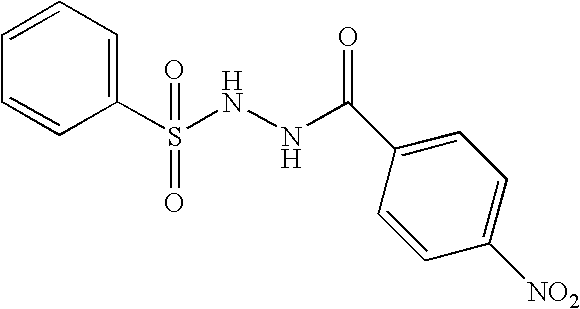
Benzoic acid, 4-nitro-2-(phenylsulfonyl)hydrazide
A solution of 4-nitro benzoic acid (0.2 g, 1.2 mmol in 10 mL of dry THF) was cooled to 0° C., treated with N-methyl-morpholine (1.6 mL, 14.6 mmol) as well as isobutyl-chloroformate (1.7 mL, 1.3 mmol), and stirred for 10 minutes prior to the addition of benzenesulfonyl hydrazide (0.21 g, 1.2 mmol). After the addition of hydrazide, the mixture was stirred for 3 hours at 25° C. Then the reaction was diluted with ethyl acetate (100 mL), washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution as well as brine, and concentrated in vacuum. The crude material was chromatographed on silica gel eluting with hexanes / ethyl acetate=2:1 to give the desired product (65% yield).
MS: 322.0 (M+1 for C13H11N3O5S1); mp 193-195° C.; TLC (SiO2) Rf=0.74 (8% MeOH / CH2Cl2). HPLC (C18 column, 1:1 CH3CN / H2O+0.1% TFA) 94.95%, RT=5.045 min. HRMS (calc for M+1) 321.0419 (found) 321.0421. IR (KBr, cm−1): 3287, 3067, 2822, 1673, 1520, 1340, 1160, 978. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6)...
example 2
Benzoic acid, 4-amino-2-(phenylsulfonyl)hydrazide
Synthesis of Example 2: Benzoic acid, 4-nitro-2-(phenylsulfonyl)hydrazide (0.82 g, Example 1) was dissolved in 50 mL of THF / EtOH (1:1), treated with wet Raney Nickel (0.6 g) and hydrogenated at 50 psi for 15 hours. The reaction was filtered, concentrated in vacuum, and chromatographed on silica gel eluting with 6% MeOH / CH2Cl2 to give 61 mg (84%) of the desired product.
MS: 291.9 (M+1 for C13H13N3O3S1); mp 171-173° C.; TLC (SiO2) Rf=0.45 (8% MeOH / CH2Cl2); HPLC (C18 column, 1:1 CH3CN / H2O+0.1% TFA) 99.14%, RT=2.575 min. HRMS (calc for M+1) 292.0756 (found) 292.0753. IR (KBr, cm−1): 3471, 3367, 3151, 2925, 1661, 1318, 1162. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6) δ 5.69 (s, 2H), 6.44 (d, 2H, J=8.5 Hz), 7.32-7.58 (m, 5H), 7.75-7.80 (m, 2H), 9.68 (br, 1H), 10.12 (br, 1H).
example 3
Benzoic acid, 4-[[(2,4,6-trichlorophenyl)sulfonyl]amino]-, 2-(phenylsulfonyl)hydrazide
Benzoic acid, 4-amino-2-(phenylsulfonyl)hydrazide (0.15 g, 0.52 mmol, Example 2) was dissolved in 7 mL of dry pyridine, then 2,4,6-(trichlorophenyl) sulfonyl chloride (0.15 mL, 0.52 mmol) was added, and the reaction was stirred at 25° C. for overnight. The solvent was removed, and the product was recrystalized from ethyl acetate and hexane to give 0.26 g (96%) of the product as a white solid.
MS: 536.0 (M+1 for C19H14Cl3N3O5S2); mp 195.7-196.2° C.; HPLC (C18 column, 1:1 MeCN / H2O+0.1% TFA) 96.3%, RT=8.0 min. 1H NMR (DMSO-D6) δ 7.10 (d, 1H, J=6.8 Hz), 7.40-7.60 (m, 7H), 7.75 (d, 1H, J=7.5 Hz), 7.79 (S, 1H), 8.63 (S, 1H), 9.92 (S, 1H), 10.49 (S, 1H), 11.35 (S, 1H).
EXAMPLE 4
Benzoic acid, 4-[[[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]sulfonyl]amino]-, 2-(phenylsulfonyl)hydrazide
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com