Sole structure for a shoe
a technology of sole body and lateral direction, which is applied in the direction of uppers, bootlegs, stiffners, etc., can solve the problems of bending of the sole body, and achieve the effect of improving the bendability of the entire sole body in the lateral direction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
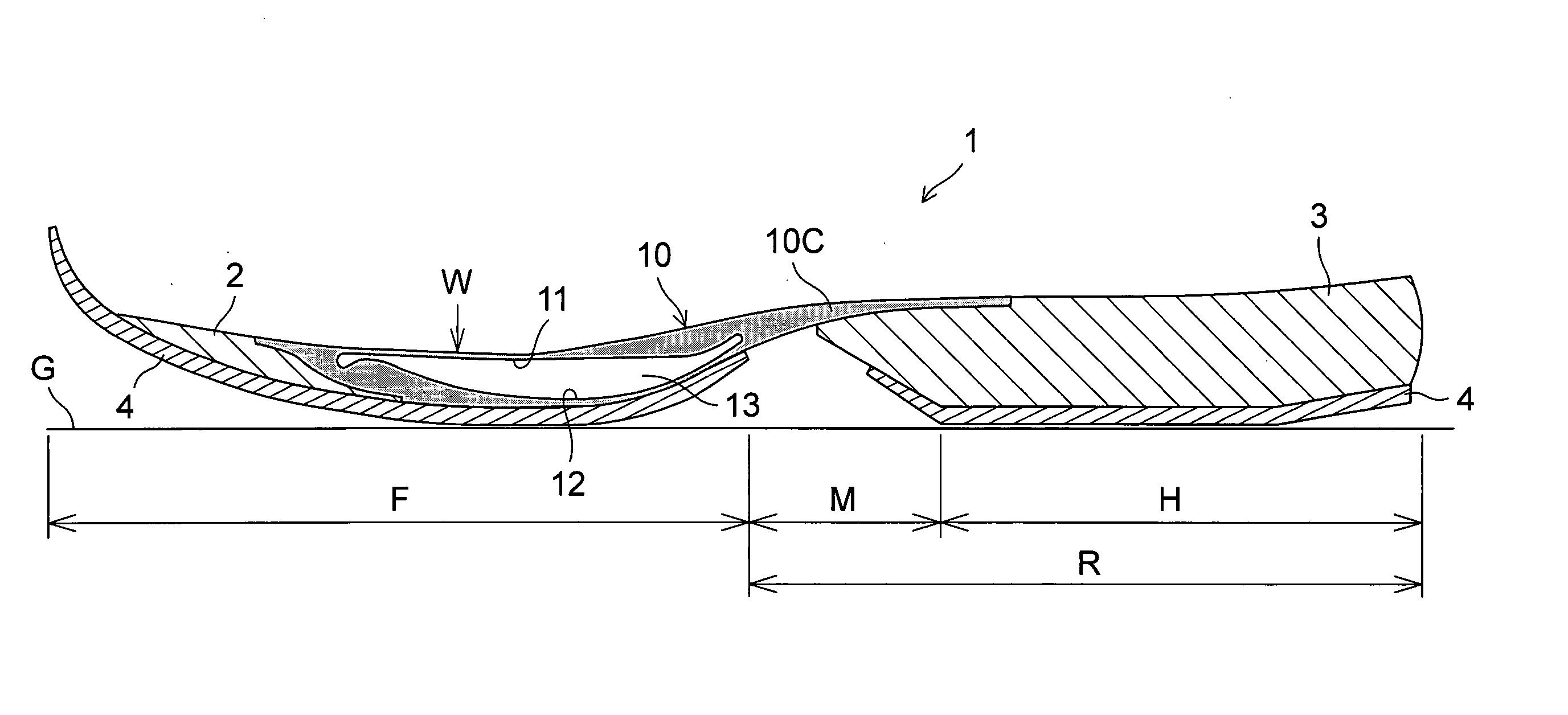
[0061] FIGS. 1 to 5 show a sole assembly of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1, a sole assembly 1 in use for a shoe includes a sole body that is comprised of a sole body forefoot portion 2 disposed mainly at a forefoot region F of the sole assembly 1 and a sole body heel portion 3 disposed at a heel region H to a midfoot or plantar arch region M of the sole assembly 1. An outsole 4 that contacts the ground G is attached to the bottom surface of the sole body. A region including the heel region H and the midfoot region M of the sole assembly 1 is herein referred to as a ‘rearfoot’ region R.
[0062] The sole body may be formed of a soft elastic material. Specifically, thermoplastic synthetic resin foam such as ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA), thermosetting resin foam such as polyurethane (PU), or rubber material foam such as butadiene or chloroprene rubber is used.
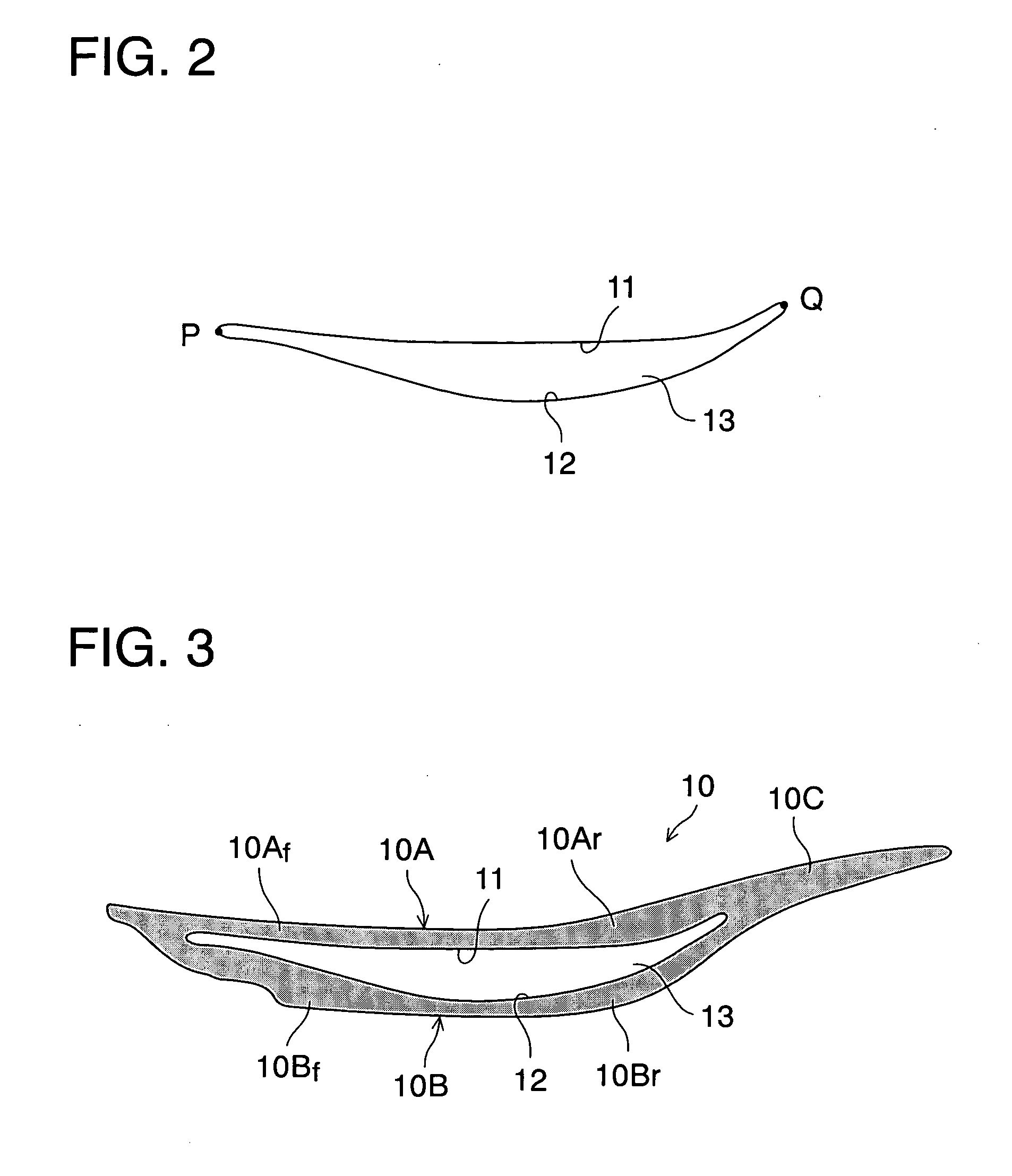
[0063] Mainly at the forefoot region F of the sole assembly 1, there is provided an elastic body 10 having a ...
second embodiment
[0079]FIGS. 6 and 7 show a sole assembly of the present invention. In these drawings, like reference numbers indicate identical or functionally similar elements.
[0080] As shown in FIG. 6, a soft elastic block 20 such as foamed material (e.g. sponge) softer than the sole body 2 is interposed at least at a portion of the cavity 13 of the elastic body 10.
[0081] In this embodiment, the way of deformation of the first and second curved surface 11, 12 such as the amount of elastic deformation or restorative speed after elastic deformation of the first and second curved surface 11, 12 can be adjusted by suitably changing expansion rate of the elastic block 10 inserted into the cavity 13 or the inserted position thereof. In addition, FIG. 7 illustrates the state in which the first and second curved surface 11, 12 is elastically deformed similarly to the state shown in FIG. 4.
third embodiment
[0082] FIGS. 8 shows an elastic structure constituting a sole assembly of the present invention. In the drawing, like reference numbers indicate identical or functionally similar elements.
[0083] In the above-mentioned first and second embodiments, the elastic body 10 was shown that has a cavity 13 formed of the first and second curved surface 11, 12, whereas in this third embodiment, an elastic structure shown in FIG. 8 is used that comprises a band-shaped first and second plate 10A′, 10B′ whose opposite ends are coupled to each other. That is, in this case, a first curved surface 11 is formed of an inner surface of the first plate 10A′ and a second curved surface 12 is formed of an inner surface of the second plate 10B′.
[0084] The elastic structure is preferably formed of a single loop member in which a first plate 10A′ and a second plate 10B′ are integrally formed with each other. This elastic structure is formed of a similar material to the elastic body 10 of the first and secon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com